[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-35069: Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cryo-EM / N15MsDps2 / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationoxidoreductase activity, acting on metal ions / ferric iron binding / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | |||||||||
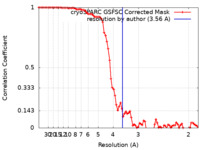
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Garg P / Dutta S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 2 items India, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM Reveals the Mechanism of DNA Compaction by Mycobacterium smegmatis Dps2. Authors: Priyanka Garg / Thejas Satheesh / Mahipal Ganji / Somnath Dutta /  Abstract: DNA binding protein from starved cells (Dps) is a miniature ferritin complex, which plays a vital role in protecting bacterial DNA during starvation to maintain the integrity of bacteria under ...DNA binding protein from starved cells (Dps) is a miniature ferritin complex, which plays a vital role in protecting bacterial DNA during starvation to maintain the integrity of bacteria under hostile conditions. Several approaches, including cryo-electron tomography, have been previously implemented by other research groups to decipher the structure of the Dps protein bound to DNA. However, none of the structures of the Dps-DNA complex was resolved to high resolution to identify the DNA binding residues. Like other bacteria, Mycobacterium smegmatis also expresses Dps2 (called MsDps2), which binds DNA to protect it under oxidative stress conditions. In this study, we implemented various biochemical and biophysical studies to characterize the DNA protein interactions of Dps2 protein from Mycobacterium smegmatis. We employed single-particle cryo-EM-based structural analysis of MsDps2-DNA complexes and identified that the region close to the N-terminus confers the DNA binding property. Based on cryo-EM data, we also pinpointed several arginine residues, proximal to the DNA binding region, responsible for DNA binding. We also performed mutations of these residues, which dramatically reduced the MsDps2-DNA interaction. In addition, we proposed a model that elucidates the mechanism of DNA compaction, which adapts a lattice-like structure. We performed single-molecule imaging of MsDps2-DNA interactions that corroborate well with our structural studies. Taken together, our results delineate the specific MsDps2 residues that play an important role in DNA binding and compaction, providing new insights into Mycobacterial DNA compaction mechanisms under stress conditions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35069.map.gz emd_35069.map.gz | 49.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35069-v30.xml emd-35069-v30.xml emd-35069.xml emd-35069.xml | 16.9 KB 16.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_35069_fsc.xml emd_35069_fsc.xml | 7.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_35069.png emd_35069.png | 89.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35069.cif.gz emd-35069.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35069_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35069_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35069_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35069_half_map_2.map.gz | 48.9 MB 48.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35069 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35069 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35069 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35069 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8hwzMC  8hx0C  8hx1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35069.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35069.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.92 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
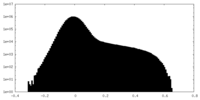
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35069_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
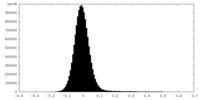
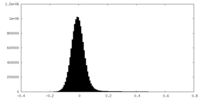
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35069_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
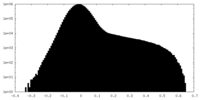
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of delta N15 MsDps2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Starvation-inducible DNA-binding protein or fine tangled pili maj...
| Macromolecule | Name: Starvation-inducible DNA-binding protein or fine tangled pili major subunit type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.163995 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: TPEFGGNLQK VLVDLIELSL QGKQAHWNVV GSNFRDLHLQ LDELVDFARE GSDTIAERMR ALDAVPDGRS DTVAATTTLP EFPAFERST ADVVDLITTR INATVDTIRR VHDAVDAEDP STADLLHGLI DGLEKQAWLI RSENRKV UniProtKB: Starvation-inducible DNA-binding protein or fine tangled pili major subunit |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.25 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.75 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8hwz: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




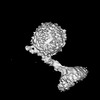




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)