[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-33477: the cryo-EM structure of human mini-SNAPc in complex with hU6-1 PSE -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | the cryo-EM structure of human mini-SNAPc in complex with hU6-1 PSE | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | snRNA / Transcription factor / Complex / PSE. / TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsnRNA-activating protein complex / snRNA transcription / snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / bent DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / RNA polymerase III general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Abortive And Retractive Initiation / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity ...snRNA-activating protein complex / snRNA transcription / snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / bent DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / RNA polymerase III general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Abortive And Retractive Initiation / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity / transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / sequence-specific DNA binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / nuclear body / nucleolus / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang W / Sun JF | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 3 items China, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis of human SNAPc recognizing proximal sequence element of snRNA promoter. Authors: Jianfeng Sun / Xue Li / Xuben Hou / Sujian Cao / Wenjin Cao / Ye Zhang / Jinyang Song / Manfu Wang / Hao Wang / Xiaodong Yan / Zengpeng Li / Robert G Roeder / Wei Wang /   Abstract: In eukaryotes, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) function in many fundamental cellular events such as precursor messenger RNA splicing, gene expression regulation, and ribosomal RNA processing. The snRNA ...In eukaryotes, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) function in many fundamental cellular events such as precursor messenger RNA splicing, gene expression regulation, and ribosomal RNA processing. The snRNA activating protein complex (SNAPc) exclusively recognizes the proximal sequence element (PSE) at snRNA promoters and recruits RNA polymerase II or III to initiate transcription. In view that homozygous gene-knockout of SNAPc core subunits causes mouse embryonic lethality, functions of SNAPc are almost housekeeping. But so far, the structural insight into how SNAPc assembles and regulates snRNA transcription initiation remains unclear. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the essential part of human SNAPc in complex with human U6-1 PSE at an overall resolution of 3.49 Å. This structure reveals the three-dimensional features of three conserved subunits (N-terminal domain of SNAP190, SNAP50, and SNAP43) and explains how they are assembled into a stable mini-SNAPc in PSE-binding state with a "wrap-around" mode. We identify three important motifs of SNAP50 that are involved in both major groove and minor groove recognition of PSE, in coordination with the Myb domain of SNAP190. Our findings further elaborate human PSE sequence conservation and compatibility for SNAPc recognition, providing a clear framework of snRNA transcription initiation, especially the U6 system. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33477.map.gz emd_33477.map.gz | 97.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33477-v30.xml emd-33477-v30.xml emd-33477.xml emd-33477.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33477.png emd_33477.png | 52.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33477.cif.gz emd-33477.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33477_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33477_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33477_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33477_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.4 MB 95.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33477 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33477 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33477 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33477 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xurMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33477.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33477.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
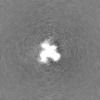
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.076 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33477_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
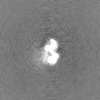
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
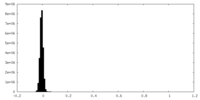
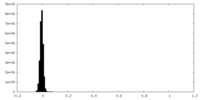
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33477_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
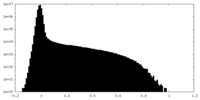
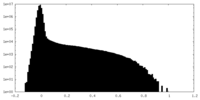
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : the complex of human mini-SNAPc with hU6-1 PSE
| Entire | Name: the complex of human mini-SNAPc with hU6-1 PSE |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: the complex of human mini-SNAPc with hU6-1 PSE
| Supramolecule | Name: the complex of human mini-SNAPc with hU6-1 PSE / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: human mini-SNAPc
| Supramolecule | Name: human mini-SNAPc / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4-#5 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 4
| Macromolecule | Name: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.780254 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DYKDDDDKSL EVLFQGPMDV DAEREKITQE IKELERILDP GSSGSHVEIS ESSLESDSEA DSLPSEDLDP ADPPISEEER WGEASNDED DPKDKTLPED PETCLQLNMV YQEVIQEKLA EANLLLAQNR EQQEELMRDL AGSKGTKVKD GKSLPPSTYM G HFMKPYFK ...String: DYKDDDDKSL EVLFQGPMDV DAEREKITQE IKELERILDP GSSGSHVEIS ESSLESDSEA DSLPSEDLDP ADPPISEEER WGEASNDED DPKDKTLPED PETCLQLNMV YQEVIQEKLA EANLLLAQNR EQQEELMRDL AGSKGTKVKD GKSLPPSTYM G HFMKPYFK DKVTGVGPPA NEDTREKAAQ GIKAFEELLV TKWKNWEKAL LRKSVVSDRL QRLLQPKLLK LEYLHQKQSK VS SELERQA LEKQGREAEK EIQDINQLPE EALLGNRLDS HDWEKISNIN FEGSRSAEEI RKFWQNSEHP SINKQEWSRE EEE RLQAIA AAHGHLEWQK IAEELGTSRS AFQCLQKFQQ HNKALKRKEW TEEEDRMLTQ LVQEMRVGSH IPYRRIVYYM EGRD SMQLI YRWTKSLDPG LKKGYWAPEE DAKLLQAVAK YGEQDWFKIR EEVPGRSDAQ CRDRYLRRLH FSLKKGRWNL KEEEQ LIEL IEKYGVGHWA KIASELPHRS GSQCLSKWKI MMGKKQGL UniProtKB: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 4 |
-Macromolecule #2: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 3
| Macromolecule | Name: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.812605 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAEGSRGGPT CSGVGGRQDP VSGSGGCNFP EYELPELNTR AFHVGAFGEL WRGRLRGAGD LSLREPPASA LPGSQAADSD REDAAVARD LDCSLEAAAE LRAVCGLDKL KCLEDGEDPE VIPENTDLVT LGVRKRFLEH REETITIDRA CRQETFVYEM E SHAIGKKP ...String: MAEGSRGGPT CSGVGGRQDP VSGSGGCNFP EYELPELNTR AFHVGAFGEL WRGRLRGAGD LSLREPPASA LPGSQAADSD REDAAVARD LDCSLEAAAE LRAVCGLDKL KCLEDGEDPE VIPENTDLVT LGVRKRFLEH REETITIDRA CRQETFVYEM E SHAIGKKP ENSADMIEEG ELILSVNILY PVIFHKHKEH KPYQTMLVLG SQKLTQLRDS IRCVSDLQIG GEFSNTPDQA PE HISKDLY KSAFFYFEGT FYNDKRYPEC RDLSRTIIEW SESHDRGYGK FQTARMEDFT FNDLCIKLGF PYLYCHQGDC EHV IVITDI RLVHHDDCLD RTLYPLLIKK HWLWTRKCFV CKMYTARWVT NNDSFAPEDP CFFCDVCFRM LHYDSEGNKL GEFL AYPYV DPGTFN UniProtKB: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 3 |
-Macromolecule #3: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 1
| Macromolecule | Name: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.559516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: HHHHHHSENL YFQGMGTPPG LQTDCEALLS RFQETDSVRF EDFTELWRNM KFGTIFCGRM RNLEKNMFTK EALALAWRYF LPPYTFQIR VGALYLLYGL YNTQLCQPKQ KIRVALKDWD EVLKFQQDLV NAQHFDAAYI FRKLRLDRAF HFTAMPKLLS Y RMKKKIHR ...String: HHHHHHSENL YFQGMGTPPG LQTDCEALLS RFQETDSVRF EDFTELWRNM KFGTIFCGRM RNLEKNMFTK EALALAWRYF LPPYTFQIR VGALYLLYGL YNTQLCQPKQ KIRVALKDWD EVLKFQQDLV NAQHFDAAYI FRKLRLDRAF HFTAMPKLLS Y RMKKKIHR AEVTEEFKDP SDRVMKLITS DVLEEMLNVH DHYQNMKHVI SVDKSKPDKA LSLIKDDFFD NIKNIVLEHQ QW HKDRKNP SLKSKTNDGE EKMEGNSQET ERCERAESLA KIKSK UniProtKB: snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA (35-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (35-MER) / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.72693 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (35-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (35-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.803009 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #6: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)