[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-33467: Cryo-EM structure of the AKT1-AtKC1 complex from Arabidopsis thaliana -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the AKT1-AtKC1 complex from Arabidopsis thaliana | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complex / Potassium channel / Membrane protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationroot hair elongation / regulation of stomatal closure / response to water deprivation / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to nematode / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / response to salt stress / potassium ion transmembrane transport ...root hair elongation / regulation of stomatal closure / response to water deprivation / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to nematode / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / response to salt stress / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport / endoplasmic reticulum / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang GH / Lu YM / Jia YT / Yang F / Zhang YM / Xu X / Li XM / Lei JL | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for the activity regulation of a potassium channel AKT1 from Arabidopsis. Authors: Yaming Lu / Miao Yu / Yutian Jia / Fan Yang / Yanming Zhang / Xia Xu / Xiaomin Li / Fan Yang / Jianlin Lei / Yi Wang / Guanghui Yang /  Abstract: The voltage-gated potassium channel AKT1 is responsible for primary K uptake in Arabidopsis roots. AKT1 is functionally activated through phosphorylation and negatively regulated by a potassium ...The voltage-gated potassium channel AKT1 is responsible for primary K uptake in Arabidopsis roots. AKT1 is functionally activated through phosphorylation and negatively regulated by a potassium channel α-subunit AtKC1. However, the molecular basis for the modulation mechanism remains unclear. Here we report the structures of AKT1, phosphorylated-AKT1, a constitutively-active variant, and AKT1-AtKC1 complex. AKT1 is assembled in 2-fold symmetry at the cytoplasmic domain. Such organization appears to sterically hinder the reorientation of C-linkers during ion permeation. Phosphorylated-AKT1 adopts an alternate 4-fold symmetric conformation at cytoplasmic domain, which indicates conformational changes associated with symmetry switch during channel activation. To corroborate this finding, we perform structure-guided mutagenesis to disrupt the dimeric interface and identify a constitutively-active variant Asp379Ala mediates K permeation independently of phosphorylation. This variant predominantly adopts a 4-fold symmetric conformation. Furthermore, the AKT1-AtKC1 complex assembles in 2-fold symmetry. Together, our work reveals structural insight into the regulatory mechanism for AKT1. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
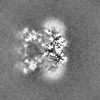
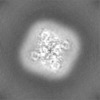
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33467.map.gz emd_33467.map.gz | 78.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33467-v30.xml emd-33467-v30.xml emd-33467.xml emd-33467.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33467.png emd_33467.png | 70.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33467.cif.gz emd-33467.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33467_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33467_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33467_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33467_half_map_2.map.gz | 77.5 MB 77.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33467 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33467 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33467 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33467 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xufMC  7fcvC  7wswC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
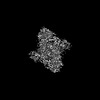
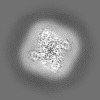
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33467.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33467.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
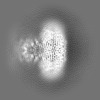
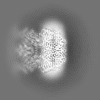
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
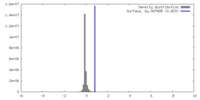
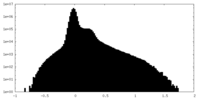
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33467_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
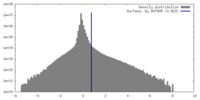
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33467_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Arabidopsis thaliana AKT1-AtKC1 complex
| Entire | Name: Arabidopsis thaliana AKT1-AtKC1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Arabidopsis thaliana AKT1-AtKC1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Arabidopsis thaliana AKT1-AtKC1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium channel KAT3
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium channel KAT3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 75.688023 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSTTTTEARS PLPLLLRRGR SSTALSASTA EARSPLSILQ FRRRSSKDVR NITSVSSSLL PAFGTFIEDD NPSSKPFIVL HFDRRYRLW ELFLVILVGY SAWASLFELA FEKAAEGALL TIDLVVDFFF AVDIILTFFV SYLDNTTYLN VTDHKLIAKR Y LKSVAFVM ...String: MSTTTTEARS PLPLLLRRGR SSTALSASTA EARSPLSILQ FRRRSSKDVR NITSVSSSLL PAFGTFIEDD NPSSKPFIVL HFDRRYRLW ELFLVILVGY SAWASLFELA FEKAAEGALL TIDLVVDFFF AVDIILTFFV SYLDNTTYLN VTDHKLIAKR Y LKSVAFVM DVASTLPIQF IYKTITGDVG RGQAFGFLNL LRLWRLRRVA ELFKRLEKDA HFNYFVIRVI KLLCVTIFWI HL AGCILYW IAYHYPRPTD TWIGSQVEDF KERSVWLGYT YSMYWSIVTL TTVGYGDLHA VNSREKTFNM FYMLFNIGLT SYI IGIMTN LVVHGALRTF AMRSAINDIL RYTSKNRLPD TMREQMLAHM QLKFKTAELR QEEVLQDLPK AIRSSINQHL FRSI IEEAY LFKGFPEGLL VQLVSQIQAE YFPPKMEIIL QNEIPTDFYV IVSGGVDIIA SKGVSEQVLA KLGPGSMAGE IGVVF NIPQ PFTVRTRRLS QVIRIGHHKF KEMVQSDNDV DAKMIIANFM TYLKGLNDEL KKEIPFLRDL LDDADAQVQE TVQSEE TPQ SNDEEIVTVS RHENGQIEER RREGVPKRVI IHGQAPPNQD NKNNGDSNGR LIILPDSIQL LFDLAEKKLG KRGSTIA MA DGAHVEQIDA LRENDHLYIF UniProtKB: Potassium channel KAT3 |
-Macromolecule #2: Potassium channel AKT1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium channel AKT1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 97.109625 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MRGGALLCGQ VQDEIEQLSR ESSHFSLSTG ILPSLGARSN RRVKLRRFVV SPYDHKYRIW EAFLVVLVVY TAWVSPFEFG FLRKPRPPL SITDNIVNAF FAIDIIMTFF VGYLDKSTYL IVDDRKQIAF KYLRSWFLLD LVSTIPSEAA MRISSQSYGL F NMLRLWRL ...String: MRGGALLCGQ VQDEIEQLSR ESSHFSLSTG ILPSLGARSN RRVKLRRFVV SPYDHKYRIW EAFLVVLVVY TAWVSPFEFG FLRKPRPPL SITDNIVNAF FAIDIIMTFF VGYLDKSTYL IVDDRKQIAF KYLRSWFLLD LVSTIPSEAA MRISSQSYGL F NMLRLWRL RRVGALFARL EKDRNFNYFW VRCAKLVCVT LFAVHCAACF YYLIAARNSN PAKTWIGANV ANFLEESLWM RY VTSMYWS ITTLTTVGYG DLHPVNTKEM IFDIFYMLFN LGLTAYLIGN MTNLVVHGTS RTRNFRDTIQ AASNFAHRNH LPP RLQDQM LAHLCLKYRT DSEGLQQQET LDALPKAIRS SISHFLFYSL MDKVYLFRGV SNDLLFQLVS EMKAEYFPPK EDVI LQNEA PTDFYILVNG TADLVDVDTG TESIVREVKA GDIIGEIGVL CYRPQLFTVR TKRLCQLLRM NRTTFLNIIQ ANVGD GTII MNNLLQHLKE MNDPVMTNVL LEIENMLARG KMDLPLNLCF AAIREDDLLL HQLLKRGLDP NESDNNGRTP LHIAAS KGT LNCVLLLLEY HADPNCRDAE GSVPLWEAMV EGHEKVVKVL LEHGSTIDAG DVGHFACTAA EQGNLKLLKE IVLHGGD VT RPRATGTSAL HTAVCEENIE MVKYLLEQGA DVNKQDMHGW TPRDLAEQQG HEDIKALFRE KLHERRVHIE TSSSVPIL K TGIRFLGRFT SEPNIRPASR EVSFRIRETR ARRKTNNFDN SLFGILANQS VPKNGLATVD EGRTGNPVRV TISCAEKDD IAGKLVLLPG SFKELLELGS NKFGIVATKV MNKDNNAEID DVDVIRDGDH LIFATDS UniProtKB: Potassium channel AKT1 |
-Macromolecule #3: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.5959 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)