+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CopC-CaM-caspase-3 with NAD+ | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | type III secretion system / Chromobacterium violaceum / caspase-3 / new PTM / programmed cell deathA / DP-ribosylation / ADPR-deacylization / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationLyases; Carbon-nitrogen lyases; Other carbon-nitrogen lyases / ADP-riboxanase activity / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host programmed cell death / caspase-3 / phospholipase A2 activator activity / Stimulation of the cell death response by PAK-2p34 / anterior neural tube closure / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to osmotic stress / leukocyte apoptotic process / positive regulation of pyroptotic inflammatory response ...Lyases; Carbon-nitrogen lyases; Other carbon-nitrogen lyases / ADP-riboxanase activity / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host programmed cell death / caspase-3 / phospholipase A2 activator activity / Stimulation of the cell death response by PAK-2p34 / anterior neural tube closure / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to osmotic stress / leukocyte apoptotic process / positive regulation of pyroptotic inflammatory response / glial cell apoptotic process / NADE modulates death signalling / luteolysis / response to cobalt ion / cellular response to staurosporine / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / death-inducing signaling complex / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / Apoptotic cleavage of cell adhesion proteins / Caspase activation via Dependence Receptors in the absence of ligand / SMAC, XIAP-regulated apoptotic response / Activation of caspases through apoptosome-mediated cleavage / Signaling by Hippo / SMAC (DIABLO) binds to IAPs / SMAC(DIABLO)-mediated dissociation of IAP:caspase complexes / axonal fasciculation / regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle / death receptor binding / fibroblast apoptotic process / CaM pathway / epithelial cell apoptotic process / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / platelet formation / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Other interleukin signaling / response to anesthetic / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / execution phase of apoptosis / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of cytokine production / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / Apoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins / negative regulation of B cell proliferation / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / pyroptotic inflammatory response / presynaptic endocytosis / neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / response to tumor necrosis factor / negative regulation of cell cycle / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / T cell homeostasis / B cell homeostasis / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / protein phosphatase activator activity / Long-term potentiation / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / catalytic complex / Smooth Muscle Contraction / cell fate commitment / detection of calcium ion / Pyroptosis / regulation of macroautophagy / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / response to X-ray / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / response to amino acid / response to glucose / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / response to UV / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Chromobacterium violaceum (bacteria) Chromobacterium violaceum (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.35 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang K / Peng T / Tao XY / Tian M / Li YX / Wang Z / Ma SF / Hu SF / Pan X / Xue J ...Zhang K / Peng T / Tao XY / Tian M / Li YX / Wang Z / Ma SF / Hu SF / Pan X / Xue J / Luo JW / Wu QL / Fu Y / Li S | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into caspase ADPR deacylization catalyzed by a bacterial effector and host calmodulin. Authors: Kuo Zhang / Ting Peng / Xinyuan Tao / Miao Tian / Yanxin Li / Zhao Wang / Shuaifei Ma / Shufan Hu / Xing Pan / Juan Xue / Jiwei Luo / Qiulan Wu / Yang Fu / Shan Li /  Abstract: Programmed cell death and caspase proteins play a pivotal role in host innate immune response combating pathogen infections. Blocking cell death is employed by many bacterial pathogens as a universal ...Programmed cell death and caspase proteins play a pivotal role in host innate immune response combating pathogen infections. Blocking cell death is employed by many bacterial pathogens as a universal virulence strategy. CopC family type III effectors, including CopC from an environmental pathogen Chromobacterium violaceum, utilize calmodulin (CaM) as a co-factor to inactivate caspases by arginine ADPR deacylization. However, the molecular basis of the catalytic and substrate/co-factor binding mechanism is unknown. Here, we determine successive cryo-EM structures of CaM-CopC-caspase-3 ternary complex in pre-reaction, transition, and post-reaction states, which elucidate a multistep enzymatic mechanism of CopC-catalyzed ADPR deacylization. Moreover, we capture a snapshot of the detachment of modified caspase-3 from CopC. These structural insights are validated by mutagenesis analyses of CopC-mediated ADPR deacylization in vitro and animal infection in vivo. Our study offers a structural framework for understanding the molecular basis of arginine ADPR deacylization catalyzed by the CopC family. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33310.map.gz emd_33310.map.gz | 167.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33310-v30.xml emd-33310-v30.xml emd-33310.xml emd-33310.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33310.png emd_33310.png | 173.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33310.cif.gz emd-33310.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33310_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33310_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33310_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33310_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33310 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33310 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33310 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33310 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_33310_validation.pdf.gz emd_33310_validation.pdf.gz | 918 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_33310_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_33310_full_validation.pdf.gz | 917.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_33310_validation.xml.gz emd_33310_validation.xml.gz | 15.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_33310_validation.cif.gz emd_33310_validation.cif.gz | 18.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33310 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33310 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33310 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33310 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 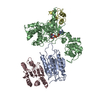 7xn4MC  7xn5C  7xn6C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33310.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33310.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.842 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33310_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
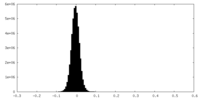
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33310_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of CopC-CaM-caspase-3 with NAD+
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CopC-CaM-caspase-3 with NAD+ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of CopC-CaM-caspase-3 with NAD+
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CopC-CaM-caspase-3 with NAD+ / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Caspase-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Caspase-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: caspase-3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 31.651938 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) |
| Sequence | String: MENTENSVDS KSIKNLEPKI IHGSESMDSG ISLDNSYKMD YPEMGLCIII NNKNFHKSTG MTSRSGTDVD AANLRETFRN LKYEVRNKN DLTREEIVEL MRDVSKEDHS KRSSFVCVLL SHGEEGIIFG TNGPVDLKKI TNFFRGDRCR SLTGKPKLFI I QACRGTEL ...String: MENTENSVDS KSIKNLEPKI IHGSESMDSG ISLDNSYKMD YPEMGLCIII NNKNFHKSTG MTSRSGTDVD AANLRETFRN LKYEVRNKN DLTREEIVEL MRDVSKEDHS KRSSFVCVLL SHGEEGIIFG TNGPVDLKKI TNFFRGDRCR SLTGKPKLFI I QACRGTEL DCGIETDSGV DDDMACHKIP VEADFLYAYS TAPGYYSWRN SKDGSWFIQS LCAMLKQYAD KLEFMHILTR VN RKVATEF ESFSFDATFH AKKQIPCIVS MLTKELYFYH UniProtKB: Caspase-3 |
-Macromolecule #2: Arginine ADP-riboxanase CopC
| Macromolecule | Name: Arginine ADP-riboxanase CopC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Lyases; Carbon-nitrogen lyases; Other carbon-nitrogen lyases |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chromobacterium violaceum (bacteria) Chromobacterium violaceum (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 12472 / DSM 30191 / JCM 1249 / NBRC 12614 / NCIMB 9131 / NCTC 9757 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.985516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) |
| Sequence | String: MRVENHSPSL SKLNPPEAGS GDPTAIGRRL SGIRRAPLPH VSAGSDGEAA AAGKIGAFLR KAVAAQSYGL MFANGKLFEA TGDALEKRG QYGFSALQRL DGLSRRNLAA VEARLGALDS AERGLKERIM TGAWHFRHQS NAALDDGKTA AIASNHLLAR E SRSSGGNT ...String: MRVENHSPSL SKLNPPEAGS GDPTAIGRRL SGIRRAPLPH VSAGSDGEAA AAGKIGAFLR KAVAAQSYGL MFANGKLFEA TGDALEKRG QYGFSALQRL DGLSRRNLAA VEARLGALDS AERGLKERIM TGAWHFRHQS NAALDDGKTA AIASNHLLAR E SRSSGGNT FAGDKALLSN HDFVFFGVEF SGRGKQDKPL NHKHSTMDFG ANAYVVPDTL PACRHGYLTL TDHFFNRVPG GR EAEHQDF VGSFPQMGAE TGRWIHEGKY RQNAPIFNYR DMKAAVALHL IEFLRDSKDA AFKAYVFDQA MQSGQALDRV LNS VFQAEF HIPRLMATTD YAKHPLRPML LKEAVDSVNL PALSGLVSSK GDAVTAMWHA IDKGKDAVAA HLLGNWRFEA GDFA SAPPG FYHELNYALS EHGASVYILD QFLSRGWAAV NAPFEHVNSG ETMLDNAVKY GNREMAAALI KHGADRNLLS EWNGG KLDA LLA UniProtKB: Arginine ADP-riboxanase CopC |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) Bacteria Latreille et al. 1825 (Bacteria stick insect) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAD |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 663.425 Da |
| Chemical component information | 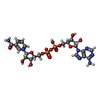 ChemComp-NAD: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 102210 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








































 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)