+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
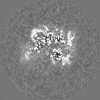
| Title | Structure of nucleosome-DI complex (-55I, Apo state) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nucleosome / AAG / Cryo-EM / DNA repair / Base excision repair / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstructural constituent of chromatin / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species | ||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zheng L / Tsai B / Gao N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2023Title: Structural and mechanistic insights into the DNA glycosylase AAG-mediated base excision in nucleosome. Authors: Lvqin Zheng / Bin Tsai / Ning Gao /  Abstract: The engagement of a DNA glycosylase with a damaged DNA base marks the initiation of base excision repair. Nucleosome-based packaging of eukaryotic genome obstructs DNA accessibility, and how DNA ...The engagement of a DNA glycosylase with a damaged DNA base marks the initiation of base excision repair. Nucleosome-based packaging of eukaryotic genome obstructs DNA accessibility, and how DNA glycosylases locate the substrate site on nucleosomes is currently unclear. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of nucleosomes bearing a deoxyinosine (DI) in various geometric positions and structures of them in complex with the DNA glycosylase AAG. The apo nucleosome structures show that the presence of a DI alone perturbs nucleosomal DNA globally, leading to a general weakening of the interface between DNA and the histone core and greater flexibility for the exit/entry of the nucleosomal DNA. AAG makes use of this nucleosomal plasticity and imposes further local deformation of the DNA through formation of the stable enzyme-substrate complex. Mechanistically, local distortion augmentation, translation/rotational register shift and partial opening of the nucleosome are employed by AAG to cope with substrate sites in fully exposed, occluded and completely buried positions, respectively. Our findings reveal the molecular basis for the DI-induced modification on the structural dynamics of the nucleosome and elucidate how the DNA glycosylase AAG accesses damaged sites on the nucleosome with different solution accessibility. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33177.map.gz emd_33177.map.gz | 3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33177-v30.xml emd-33177-v30.xml emd-33177.xml emd-33177.xml | 21.3 KB 21.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33177.png emd_33177.png | 98.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33177.cif.gz emd-33177.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33177_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33177_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33177_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33177_half_map_2.map.gz | 23.4 MB 23.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33177 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33177 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33177 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33177 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xfnMC  7xfcC  7xfhC 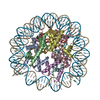 7xfiC  7xfjC 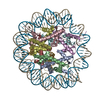 7xflC  7xfmC 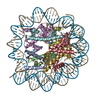 7xnpC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33177.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33177.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.052 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33177_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33177_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : complex
| Entire | Name: complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: complex
| Supramolecule | Name: complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.2
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.421101 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK STGGKAPRKQ LATKAARKSA PATGGVKKPH RYRPGTVALR EIRRYQKSTE LLIRKLPFQR LVREIAQDFK TDLRFQSSA VMALQEASEA YLVGLFEDTN LCAIHAKRVT IMPKDIQLAR RIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.394426 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.093436 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK TRAKAKTRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY AERVGAGAPV YLAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAVR NDEELNKLLG RVTIAQGGVL PNIQSVLLPK KTESAKSAKS K UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B 1.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B 1.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.965265 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAVT KTQKKDGKKR RKSRKESYAI YVYKVLKQVH PDTGISSKAM SIMNSFVNDV FERIAGEASR LAHYNKRST ITSREIQTAV RLLLPGELAK HAVSEGTKAV TKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B 1.1 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (152-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (152-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.170023 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DI)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DI)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (152-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (152-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.655711 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) ...String: (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DT) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Acetate |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 64.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)