+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of Arabidopsis thaliana CLCa | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nitrate / antiporter / transport protein / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnitrate transmembrane transporter activity / nitrate transmembrane transport / response to nitrate / voltage-gated chloride channel activity / chloride transport / chloride channel complex Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.84 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ji S / Jin H / Kaiming Z / Mingxing W / Shanshan L / Long C | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM structure of the plant nitrate transporter AtCLCa reveals characteristics of the anion-binding site and the ATP-binding pocket. Authors: Jin He / Mingxing Wang / Shanshan Li / Long Chen / Kaiming Zhang / Ji She /  Abstract: Nitrate is one of the major nitrogen sources for most plants. Chloride channel (CLC) proteins mediate the transport and vacuole storage of nitrate in plants, but the structural basis of nitrate ...Nitrate is one of the major nitrogen sources for most plants. Chloride channel (CLC) proteins mediate the transport and vacuole storage of nitrate in plants, but the structural basis of nitrate transport by plant CLC proteins remains unknown. Here, we solved the cryo-EM structure of ATP-bound Arabidopsis thaliana CLCa (AtCLCa) at 2.8 Å resolution. Structural comparison between nitrate-selective AtCLCa and chloride-selective CLC-7 reveals key differences in the central anion-binding site. We observed that the central nitrate is shifted by ∼1.4 Å from chloride, which is likely caused by a weaker interaction between the anion and Pro160; the side chains of aromatic residues around the central binding site are rearranged to accommodate the larger nitrate. Additionally, we identified the ATP-binding pocket of AtCLCa to be located between the cytosolic cystathionine β-synthase domains and the N-terminus. The N-terminus may mediate the ATP inhibition of AtCLCa by interacting with both ATP and the pore-forming transmembrane helix. Together, our studies provide insights into the nitrate selectivity and ATP regulation of plant CLCs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33088.map.gz emd_33088.map.gz | 483.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33088-v30.xml emd-33088-v30.xml emd-33088.xml emd-33088.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33088.png emd_33088.png | 64.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33088.cif.gz emd-33088.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33088_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33088_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33088_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33088_half_map_2.map.gz | 474.9 MB 474.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33088 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33088 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33088 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33088 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_33088_validation.pdf.gz emd_33088_validation.pdf.gz | 868.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_33088_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_33088_full_validation.pdf.gz | 868.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_33088_validation.xml.gz emd_33088_validation.xml.gz | 18.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_33088_validation.cif.gz emd_33088_validation.cif.gz | 22.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33088 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33088 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33088 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33088 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xa9MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33088.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33088.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
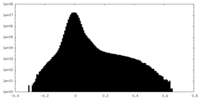
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33088_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
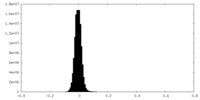
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33088_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : AtCLCa
| Entire | Name: AtCLCa |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: AtCLCa
| Supramolecule | Name: AtCLCa / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Chloride channel protein CLC-a
| Macromolecule | Name: Chloride channel protein CLC-a / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 88.17682 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDEDGNLQIS NSNYNGEEEG EDPENNTLNQ PLLKRHRTLS STPLALVGAK VSHIESLDYE INENDLFKHD WRSRSKAQVF QYIFLKWTL ACLVGLFTGL IATLINLAVE NIAGYKLLAV GYYIAQDRFW TGLMVFTGAN LGLTLVATVL VVYFAPTAAG P GIPEIKAY ...String: MDEDGNLQIS NSNYNGEEEG EDPENNTLNQ PLLKRHRTLS STPLALVGAK VSHIESLDYE INENDLFKHD WRSRSKAQVF QYIFLKWTL ACLVGLFTGL IATLINLAVE NIAGYKLLAV GYYIAQDRFW TGLMVFTGAN LGLTLVATVL VVYFAPTAAG P GIPEIKAY LNGIDTPNMF GFTTMMVKIV GSIGAVAAGL DLGKEGPLVH IGSCIASLLG QGGPDNHRIK WRWLRYFNND RD RRDLITC GSASGVCAAF RSPVGGVLFA LEEVATWWRS ALLWRTFFST AVVVVVLRAF IEICNSGKCG LFGSGGLIMF DVS HVEVRY HAADIIPVTL IGVFGGILGS LYNHLLHKVL RLYNLINQKG KIHKVLLSLG VSLFTSVCLF GLPFLAECKP CDPS IDEIC PTNGRSGNFK QFNCPNGYYN DLSTLLLTTN DDAVRNIFSS NTPNEFGMVS LWIFFGLYCI LGLITFGIAT PSGLF LPII LMGSAYGRML GTAMGSYTNI DQGLYAVLGA ASLMAGSMRM TVSLCVIFLE LTNNLLLLPI TMFVLLIAKT VGDSFN LSI YEIILHLKGL PFLEANPEPW MRNLTVGELN DAKPPVVTLN GVEKVANIVD VLRNTTHNAF PVLDGADQNT GTELHGL IL RAHLVKVLKK RWFLNEKRRT EEWEVREKFT PVELAEREDN FDDVAITSSE MQLYVDLHPL TNTTPYTVVQ SMSVAKAL V LFRSVGLRHL LVVPKIQASG MSPVIGILTR QDLRAYNILQ AFPHLDKHKS GKARASGGSL EVLFQGPGGS GGSWSHPQF EK UniProtKB: Chloride channel protein CLC-a |
-Macromolecule #2: NITRATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: NITRATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.005 Da |
| Chemical component information | 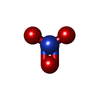 ChemComp-NO3: |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)