+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
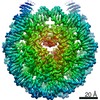
| Title | Human Oct4 bound to nucleosome with human LIN28B sequence | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Oct4 / Nucleosome / LIN28B DNA / iPSC / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells ...cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells / Specification of the neural plate border / Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells / Germ layer formation at gastrulation / miRNA binding / somatic stem cell population maintenance / blastocyst development / anatomical structure morphogenesis / BMP signaling pathway / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / response to wounding / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of gene expression / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sinha KK / Bilokapic S / Du Y / Malik D / Halic M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Histone modifications regulate pioneer transcription factor cooperativity. Authors: Kalyan K Sinha / Silvija Bilokapic / Yongming Du / Deepshikha Malik / Mario Halic /  Abstract: Pioneer transcription factors have the ability to access DNA in compacted chromatin. Multiple transcription factors can bind together to a regulatory element in a cooperative way, and cooperation ...Pioneer transcription factors have the ability to access DNA in compacted chromatin. Multiple transcription factors can bind together to a regulatory element in a cooperative way, and cooperation between the pioneer transcription factors OCT4 (also known as POU5F1) and SOX2 is important for pluripotency and reprogramming. However, the molecular mechanisms by which pioneer transcription factors function and cooperate on chromatin remain unclear. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human OCT4 bound to a nucleosome containing human LIN28B or nMATN1 DNA sequences, both of which bear multiple binding sites for OCT4. Our structural and biochemistry data reveal that binding of OCT4 induces changes to the nucleosome structure, repositions the nucleosomal DNA and facilitates cooperative binding of additional OCT4 and of SOX2 to their internal binding sites. The flexible activation domain of OCT4 contacts the N-terminal tail of histone H4, altering its conformation and thus promoting chromatin decompaction. Moreover, the DNA-binding domain of OCT4 engages with the N-terminal tail of histone H3, and post-translational modifications at H3K27 modulate DNA positioning and affect transcription factor cooperativity. Thus, our findings suggest that the epigenetic landscape could regulate OCT4 activity to ensure proper cell programming. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29846.map.gz emd_29846.map.gz | 40.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29846-v30.xml emd-29846-v30.xml emd-29846.xml emd-29846.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_29846.png emd_29846.png | 30.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29846.cif.gz emd-29846.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29846_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29846_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29846_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29846_half_map_2.map.gz | 40.8 MB 40.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29846 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29846 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29846 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29846 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8g8eMC  8g86C  8g87C  8g88C  8g8bC 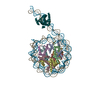 8g8gC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29846.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29846.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
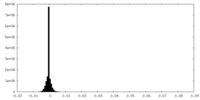
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_29846_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
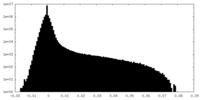
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_29846_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Oct4 bound to a Nucleosome with human LIN28 DNA sequence
| Entire | Name: Human Oct4 bound to a Nucleosome with human LIN28 DNA sequence |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human Oct4 bound to a Nucleosome with human LIN28 DNA sequence
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Oct4 bound to a Nucleosome with human LIN28 DNA sequence type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: LIN28B DNA (32-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: LIN28B DNA (32-MER) / type: dna / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 56.519281 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC) ...String: (DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DG) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DA) (DT) |
-Macromolecule #2: LIN28B DNA (32-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: LIN28B DNA (32-MER) / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.827664 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DT) (DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DG) (DC) |
-Macromolecule #3: POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1
| Macromolecule | Name: POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Details: human Oct4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.299453 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSSHHHHHHS SGLVPRGSHM ASMTGGQQMG RDPNSMAGHL ASDFAFSPPP GGGGDGPGGP EPGWVDPRTW LSFQGPPGGP GIGPGVGPG SEVWGIPPCP PPYEFCGGMA YCGPQVGVGL VPQGGLETSQ PEGEAGVGVE SNSDGASPEP CTVTPGAVKL E KEKLEQNP ...String: GSSHHHHHHS SGLVPRGSHM ASMTGGQQMG RDPNSMAGHL ASDFAFSPPP GGGGDGPGGP EPGWVDPRTW LSFQGPPGGP GIGPGVGPG SEVWGIPPCP PPYEFCGGMA YCGPQVGVGL VPQGGLETSQ PEGEAGVGVE SNSDGASPEP CTVTPGAVKL E KEKLEQNP EESQDIKALQ KELEQFAKLL KQKRITLGYT QADVGLTLGV LFGKVFSQTT ICRFEALQLS FKNMCKLRPL LQ KWVEEAD NNENLQEICK AETLVQARKR KRTSIENRVR GNLENLFLQC PKPTLQQISH IAQQLGLEKD VVRVWFCNRR QKG KRSSSD YAQREDFEAA GSPFSGGPVS FPLAPGPHFG TPGYGSPHFT ALYSSVPFPE GEAFPPVSVT TLGSPMHSN UniProtKB: POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 90.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 65000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





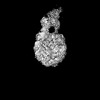
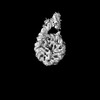
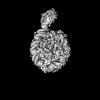
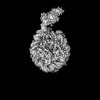


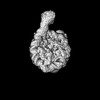



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)