[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
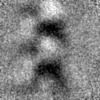
Yorodumi- EMDB-29808: Subtomogram average of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Subtomogram average of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Subtomogram average of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Parasite / Inner membrane complex / apicomplexa / CELL INVASION | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cryptosporidium parvum Iowa (eukaryote) Cryptosporidium parvum Iowa (eukaryote) | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 38.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Martinez M / Mageswaran SK / Chang Y-W | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Origin and arrangement of actin filaments for gliding motility in apicomplexan parasites revealed by cryo-electron tomography. Authors: Matthew Martinez / Shrawan Kumar Mageswaran / Amandine Guérin / William David Chen / Cameron Parker Thompson / Sabine Chavin / Dominique Soldati-Favre / Boris Striepen / Yi-Wei Chang /   Abstract: The phylum Apicomplexa comprises important eukaryotic parasites that invade host tissues and cells using a unique mechanism of gliding motility. Gliding is powered by actomyosin motors that ...The phylum Apicomplexa comprises important eukaryotic parasites that invade host tissues and cells using a unique mechanism of gliding motility. Gliding is powered by actomyosin motors that translocate host-attached surface adhesins along the parasite cell body. Actin filaments (F-actin) generated by Formin1 play a central role in this critical parasitic activity. However, their subcellular origin, path and ultrastructural arrangement are poorly understood. Here we used cryo-electron tomography to image motile Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites and reveal the cellular architecture of F-actin at nanometer-scale resolution. We demonstrate that F-actin nucleates at the apically positioned preconoidal rings and is channeled into the pellicular space between the parasite plasma membrane and the inner membrane complex in a conoid extrusion-dependent manner. Within the pellicular space, filaments on the inner membrane complex surface appear to guide the apico-basal flux of F-actin. F-actin concordantly accumulates at the basal end of the parasite. Finally, analyzing a Formin1-depleted Toxoplasma gondii mutant pinpoints the upper preconoidal ring as the conserved nucleation hub for F-actin in Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma. Together, we provide an ultrastructural model for the life cycle of F-actin for apicomplexan gliding motility. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29808.map.gz emd_29808.map.gz | 14.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29808-v30.xml emd-29808-v30.xml emd-29808.xml emd-29808.xml | 15.2 KB 15.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29808_fsc.xml emd_29808_fsc.xml | 5.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_29808.png emd_29808.png | 98.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_29808_msk_1.map emd_29808_msk_1.map | 15.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_29808_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29808_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29808_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29808_half_map_2.map.gz | 14.5 MB 14.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29808 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29808 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_29808_validation.pdf.gz emd_29808_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_29808_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_29808_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_29808_validation.xml.gz emd_29808_validation.xml.gz | 11.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_29808_validation.cif.gz emd_29808_validation.cif.gz | 15.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-29808 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-29808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-29808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-29808 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29808.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29808.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Subtomogram average of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.65 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_29808_msk_1.map emd_29808_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_29808_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_29808_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : IMC surface filaments, top view
| Entire | Name: IMC surface filaments, top view |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: IMC surface filaments, top view
| Supramolecule | Name: IMC surface filaments, top view / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 Details: In situ structure of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptosporidium parvum Iowa (eukaryote) Cryptosporidium parvum Iowa (eukaryote) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 99 % / Chamber temperature: 310 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP Details: Isolated sporozoites were resuspended in media, and 4 uL was applied to the carbon side of the grid and front blotted for 4s. |
| Details | Sample was averaged from within frozen-hydrated Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE / Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 0.4 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 33000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)