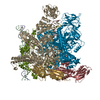
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-28791タイトル EsN-dhsU36duplex composite map Composite of raw full and local maps 複合体 : EsN-dhsU36duplex複合体 : RNA polymerase complex複合体 : DNA / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / Aquifex aeolicus (バクテリア)手法 / / 解像度 : 2.8 Å Mueller AU / Chen J / Darst SA 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH/NIGMS) R35 GM118130
ジャーナル : Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年 : 2023タイトル : A general mechanism for transcription bubble nucleation in bacteria.著者 : Andreas U Mueller / James Chen / Mengyu Wu / Courtney Chiu / B Tracy Nixon / Elizabeth A Campbell / Seth A Darst / 要旨 : Bacterial transcription initiation requires σ factors for nucleation of the transcription bubble. The canonical housekeeping σ factor, σ, nucleates DNA melting via recognition of conserved bases ... Bacterial transcription initiation requires σ factors for nucleation of the transcription bubble. The canonical housekeeping σ factor, σ, nucleates DNA melting via recognition of conserved bases of the promoter -10 motif, which are unstacked and captured in pockets of σ. By contrast, the mechanism of transcription bubble nucleation and formation during the unrelated σ-mediated transcription initiation is poorly understood. Herein, we combine structural and biochemical approaches to establish that σ, like σ, captures a flipped, unstacked base in a pocket formed between its N-terminal region I (RI) and extra-long helix features. Strikingly, RI inserts into the nascent bubble to stabilize the nucleated bubble prior to engagement of the obligate ATPase activator. Our data suggest a general paradigm of transcription initiation that requires σ factors to nucleate an early melted intermediate prior to productive RNA synthesis. 履歴 登録 2022年11月4日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2023年4月5日 - マップ公開 2023年4月5日 - 更新 2024年1月17日 - 現状 2024年1月17日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報

 Aquifex aeolicus (バクテリア)
Aquifex aeolicus (バクテリア) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023
ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_28791.map.gz
emd_28791.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-28791-v30.xml
emd-28791-v30.xml emd-28791.xml
emd-28791.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_28791.png
emd_28791.png emd-28791.cif.gz
emd-28791.cif.gz emd_28791_additional_1.map.gz
emd_28791_additional_1.map.gz emd_28791_additional_2.map.gz
emd_28791_additional_2.map.gz emd_28791_additional_3.map.gz
emd_28791_additional_3.map.gz emd_28791_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_28791_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28791_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_28791_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28791
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28791 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28791
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28791 emd_28791_validation.pdf.gz
emd_28791_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_28791_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_28791_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_28791_validation.xml.gz
emd_28791_validation.xml.gz emd_28791_validation.cif.gz
emd_28791_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28791
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28791 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28791
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28791

 F&H 検索
F&H 検索 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
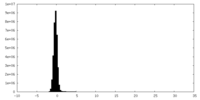
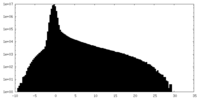
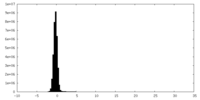
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28791.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 129.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28791.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 129.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素

 Aquifex aeolicus (バクテリア) / Synthetically produced: Yes
Aquifex aeolicus (バクテリア) / Synthetically produced: Yes 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)