+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
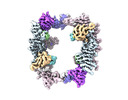
| タイトル | EM map of the human UBR5 HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligase in a tetrameric form | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | The final composite map | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | HECT / E3 ligase / LIGASE | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報heterochromatin boundary formation / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / protein branched polyubiquitination / HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / cytoplasm protein quality control / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling ...heterochromatin boundary formation / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / protein branched polyubiquitination / HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / cytoplasm protein quality control / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin binding / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / protein polyubiquitination / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / DNA repair / DNA damage response / positive regulation of gene expression / chromatin / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein-containing complex / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
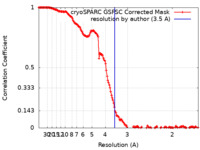
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Wang F / He Q / Lin G / Li H | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Structure / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: Structure / 年: 2023タイトル: Structure of the human UBR5 E3 ubiquitin ligase. 著者: Feng Wang / Qing He / Wenhu Zhan / Ziqi Yu / Efrat Finkin-Groner / Xiaojing Ma / Gang Lin / Huilin Li /  要旨: The human UBR5 is a single polypeptide chain homology to E6AP C terminus (HECT)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase essential for embryonic development in mammals. Dysregulated UBR5 functions like an ...The human UBR5 is a single polypeptide chain homology to E6AP C terminus (HECT)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase essential for embryonic development in mammals. Dysregulated UBR5 functions like an oncoprotein to promote cancer growth and metastasis. Here, we report that UBR5 assembles into a dimer and a tetramer. Our cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures reveal that two crescent-shaped UBR5 monomers assemble head to tail to form the dimer, and two dimers bind face to face to form the cage-like tetramer with all four catalytic HECT domains facing the central cavity. Importantly, the N-terminal region of one subunit and the HECT of the other form an "intermolecular jaw" in the dimer. We show the jaw-lining residues are important for function, suggesting that the intermolecular jaw functions to recruit ubiquitin-loaded E2 to UBR5. Further work is needed to understand how oligomerization regulates UBR5 ligase activity. This work provides a framework for structure-based anticancer drug development and contributes to a growing appreciation of E3 ligase diversity. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_28646.map.gz emd_28646.map.gz | 277 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-28646-v30.xml emd-28646-v30.xml emd-28646.xml emd-28646.xml | 26 KB 26 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_28646_fsc.xml emd_28646_fsc.xml | 14.6 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_28646.png emd_28646.png | 88.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28646.cif.gz emd-28646.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_28646_additional_1.map.gz emd_28646_additional_1.map.gz emd_28646_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28646_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28646_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28646_half_map_2.map.gz | 159.9 MB 302 MB 302 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28646 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28646 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28646 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28646 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_28646_validation.pdf.gz emd_28646_validation.pdf.gz | 797.3 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_28646_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_28646_full_validation.pdf.gz | 796.9 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_28646_validation.xml.gz emd_28646_validation.xml.gz | 23.6 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_28646_validation.cif.gz emd_28646_validation.cif.gz | 30.8 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28646 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28646 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28646 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28646 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28646.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 325 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28646.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 325 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
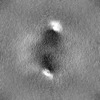
| 注釈 | The final composite map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-追加マップ: Focused on refine map A
| ファイル | emd_28646_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
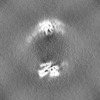
| 注釈 | Focused_on_refine_map_A | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
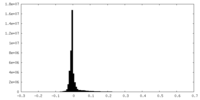
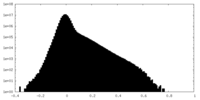
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half map a
| ファイル | emd_28646_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
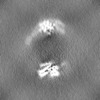
| 注釈 | Half_map_a | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half map B
| ファイル | emd_28646_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Half_map_B | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Homodimer of human E3 ligase UBR5
| 全体 | 名称: Homodimer of human E3 ligase UBR5 |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Homodimer of human E3 ligase UBR5
| 超分子 | 名称: Homodimer of human E3 ligase UBR5 / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1 / 詳細: UBR5 expressed in insect cell |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 610 KDa |
-分子 #1: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5
| 分子 | 名称: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 4 / 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 309.72275 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (その他) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MTSIHFVVHP LPGTEDQLND RLREVSEKLN KYNLNSHPPL NVLEQATIKQ CVVGPNHAAF LLEDGRVCRI GFSVQPDRLE LGKPDNNDG SKLNSNSGAG RTSRPGRTSD SPWFLSGSET LGRLAGNTLG SRWSSGVGGS GGGSSGRSSA GARDSRRQTR V IRTGRDRG ...文字列: MTSIHFVVHP LPGTEDQLND RLREVSEKLN KYNLNSHPPL NVLEQATIKQ CVVGPNHAAF LLEDGRVCRI GFSVQPDRLE LGKPDNNDG SKLNSNSGAG RTSRPGRTSD SPWFLSGSET LGRLAGNTLG SRWSSGVGGS GGGSSGRSSA GARDSRRQTR V IRTGRDRG SGLLGSQPQP VIPASVIPEE LISQAQVVLQ GKSRSVIIRE LQRTNLDVNL AVNNLLSRDD EDGDDGDDTA SE SYLPGED LMSLLDADIH SAHPSVIIDA DAMFSEDISY FGYPSFRRSS LSRLGSSRVL LLPLERDSEL LRERESVLRL RER RWLDGA SFDNERGSTS KEGEPNLDKK NTPVQSPVSL GEDLQWWPDK DGTKFICIGA LYSELLAVSS KGELYQWKWS ESEP YRNAQ NPSLHHPRAT FLGLTNEKIV LLSANSIRAT VATENNKVAT WVDETLSSVA SKLEHTAQTY SELQGERIVS LHCCA LYTC AQLENSLYWW GVVPFSQRKK MLEKARAKNK KPKSSAGISS MPNITVGTQV CLRNNPLYHA GAVAFSISAG IPKVGV LME SVWNMNDSCR FQLRSPESLK NMEKASKTTE AKPESKQEPV KTEMGPPPSP ASTCSDASSI ASSASMPYKR RRSTPAP KE EEKVNEEQWS LREVVFVEDV KNVPVGKVLK VDGAYVAVKF PGTSSNTNCQ NSSGPDADPS SLLQDCRLLR IDELQVVK T GGTPKVPDCF QRTPKKLCIP EKTEILAVNV DSKGVHAVLK TGNWVRYCIF DLATGKAEQE NNFPTSSIAF LGQNERNVA IFTAGQESPI ILRDGNGTIY PMAKDCMGGI RDPDWLDLPP ISSLGMGVHS LINLPANSTI KKKAAVIIMA VEKQTLMQHI LRCDYEACR QYLMNLEQAV VLEQNLQMLQ TFISHRCDGN RNILHACVSV CFPTSNKETK EEEEAERSER NTFAERLSAV E AIANAISV VSSNGPGNRA GSSSSRSLRL REMMRRSLRA AGLGRHEAGA SSSDHQDPVS PPIAPPSWVP DPPAMDPDGD ID FILAPAV GSLTTAATGT GQGPSTSTIP GPSTEPSVVE SKDRKANAHF ILKLLCDSVV LQPYLRELLS AKDARGMTPF MSA VSGRAY PAAITILETA QKIAKAEISS SEKEEDVFMG MVCPSGTNPD DSPLYVLCCN DTCSFTWTGA EHINQDIFEC RTCG LLESL CCCTECARVC HKGHDCKLKR TSPTAYCDCW EKCKCKTLIA GQKSARLDLL YRLLTATNLV TLPNSRGEHL LLFLV QTVA RQTVEHCQYR PPRIREDRNR KTASPEDSDM PDHDLEPPRF AQLALERVLQ DWNALKSMIM FGSQENKDPL SASSRI GHL LPEEQVYLNQ QSGTIRLDCF THCLIVKCTA DILLLDTLLG TLVKELQNKY TPGRREEAIA VTMRFLRSVA RVFVILS VE MASSKKKNNF IPQPIGKCKR VFQALLPYAV EELCNVAESL IVPVRMGIAR PTAPFTLAST SIDAMQGSEE LFSVEPLP P RPSSDQSSSS SQSQSSYIIR NPQQRRISQS QPVRGRDEEQ DDIVSADVEE VEVVEGVAGE EDHHDEQEEH GEENAEAEG QHDEHDEDGS DMELDLLAAA ETESDSESNH SNQDNASGRR SVVTAATAGS EAGASSVPAF FSEDDSQSND SSDSDSSSSQ SDDIEQETF MLDEPLERTT NSSHANGAAQ APRSMQWAVR NTQHQRAAST APSSTSTPAA SSAGLIYIDP SNLRRSGTIS T SAAAAAAA LEASNASSYL TSASSLARAY SIVIRQISDL MGLIPKYNHL VYSQIPAAVK LTYQDAVNLQ NYVEEKLIPT WN WMVSIMD STEAQLRYGS ALASAGDPGH PNHPLHASQN SARRERMTAR EEASLRTLEG RRRATLLSAR QGMMSARGDF LNY ALSLMR SHNDEHSDVL PVLDVCSLKH VAYVFQALIY WIKAMNQQTT LDTPQLERKR TRELLELGID NEDSEHENDD DTNQ SATLN DKDDDSLPAE TGQNHPFFRR SDSMTFLGCI PPNPFEVPLA EAIPLADQPH LLQPNARKED LFGRPSQGLY SSSAS SGKC LMEVTVDRNC LEVLPTKMSY AANLKNVMNM QNRQKKEGEE QPVLPEETES SKPGPSAHDL AAQLKSSLLA EIGLTE SEG PPLTSFRPQC SFMGMVISHD MLLGRWRLSL ELFGRVFMED VGAEPGSILT ELGGFEVKES KFRREMEKLR NQQSRDL SL EVDRDRDLLI QQTMRQLNNH FGRRCATTPM AVHRVKVTFK DEPGEGSGVA RSFYTAIAQA FLSNEKLPNL ECIQNANK G THTSLMQRLR NRGERDRERE REREMRRSSG LRAGSRRDRD RDFRRQLSID TRPFRPASEG NPSDDPEPLP AHRQALGER LYPRVQAMQP AFASKITGML LELSPAQLLL LLASEDSLRA RVDEAMELII AHGRENGADS ILDLGLVDSS EKVQQENRKR HGSSRSVVD MDLDDTDDGD DNAPLFYQPG KRGFYTPRPG KNTEARLNCF RNIGRILGLC LLQNELCPIT LNRHVIKVLL G RKVNWHDF AFFDPVMYES LRQLILASQS SDADAVFSAM DLAFAIDLCK EEGGGQVELI PNGVNIPVTP QNVYEYVRKY AE HRMLVVA EQPLHAMRKG LLDVLPKNSL EDLTAEDFRL LVNGCGEVNV QMLISFTSFN DESGENAEKL LQFKRWFWSI VEK MSMTER QDLVYFWTSS PSLPASEEGF QPMPSITIRP PDDQHLPTAN TCISRLYVPL YSSKQILKQK LLLAIKTKNF GFV UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 |
-分子 #2: ZINC ION
| 分子 | 名称: ZINC ION / タイプ: ligand / ID: 2 / コピー数: 12 / 式: ZN |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 65.409 Da |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.7 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 構成要素:
| ||||||||||||
| グリッド | モデル: Quantifoil R2/1 / 支持フィルム - 材質: GOLD / 支持フィルム - トポロジー: CONTINUOUS | ||||||||||||
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 279 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / 詳細: blot 2S, blot forth 2. | ||||||||||||
| 詳細 | freshly purified UBR5 |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 温度 | 最低: 193.0 K / 最高: 193.0 K |
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / 平均電子線量: 65.0 e/Å2 詳細: Images were collected in movie-mode at 75 frames per second |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | C2レンズ絞り径: 70.0 µm / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.0 µm / 倍率(公称値): 105000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: RIGID BODY FIT / 温度因子: 119 / 当てはまり具合の基準: Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-8ewi: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)