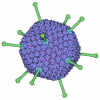
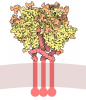
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-27408タイトル Ectodomain of full-length wild-type KIT-SCF dimers Ectodomain local refinement of full-length KIT-SCF dimers 複合体 : Full-length wild-type KIT-SCF dimers reconstituted in amphipolタンパク質・ペプチド : Isoform 2 of Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kitタンパク質・ペプチド : Soluble KIT ligandリガンド : 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
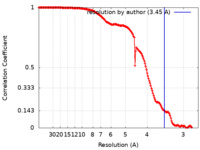
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.45 Å Krimmer SG / Bertoletti N / Mi W / Schlessinger J 資金援助 1件 Organization Grant number 国 Not funded
ジャーナル : Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年 : 2023タイトル : Cryo-EM analyses of KIT and oncogenic mutants reveal structural oncogenic plasticity and a target for therapeutic intervention.著者 : Stefan G Krimmer / Nicole Bertoletti / Yoshihisa Suzuki / Luka Katic / Jyotidarsini Mohanty / Sheng Shu / Sangwon Lee / Irit Lax / Wei Mi / Joseph Schlessinger / 要旨 : The receptor tyrosine kinase KIT and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) are required for the development of hematopoietic stem cells, germ cells, and other cells. A variety of human cancers, such as ... The receptor tyrosine kinase KIT and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) are required for the development of hematopoietic stem cells, germ cells, and other cells. A variety of human cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, and mast cell leukemia, are driven by somatic gain-of-function KIT mutations. Here, we report cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural analyses of full-length wild-type and two oncogenic KIT mutants, which show that the overall symmetric arrangement of the extracellular domain of ligand-occupied KIT dimers contains asymmetric D5 homotypic contacts juxtaposing the plasma membrane. Mutational analysis of KIT reveals in D5 region an "Achilles heel" for therapeutic intervention. A ligand-sensitized oncogenic KIT mutant exhibits a more comprehensive and stable D5 asymmetric conformation. A constitutively active ligand-independent oncogenic KIT mutant adopts a V-shaped conformation solely held by D5-mediated contacts. Binding of SCF to this mutant fully restores the conformation of wild-type KIT dimers, including the formation of salt bridges responsible for D4 homotypic contacts and other hallmarks of SCF-induced KIT dimerization. These experiments reveal an unexpected structural plasticity of oncogenic KIT mutants and a therapeutic target in D5. 履歴 登録 2022年6月22日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2023年3月29日 - マップ公開 2023年3月29日 - 更新 2023年4月5日 - 現状 2023年4月5日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 引用
引用 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023
ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_27408.map.gz
emd_27408.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-27408-v30.xml
emd-27408-v30.xml emd-27408.xml
emd-27408.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_27408_fsc.xml
emd_27408_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_27408.png
emd_27408.png emd_27408_msk_1.map
emd_27408_msk_1.map マスクマップ
マスクマップ emd_27408_additional_1.map.gz
emd_27408_additional_1.map.gz emd_27408_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_27408_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27408_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_27408_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27408
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27408
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27408 emd_27408_validation.pdf.gz
emd_27408_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_27408_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_27408_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_27408_validation.xml.gz
emd_27408_validation.xml.gz emd_27408_validation.cif.gz
emd_27408_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27408
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27408
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27408


 F&H 検索
F&H 検索 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27408.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 347.6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27408.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 347.6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) emd_27408_msk_1.map
emd_27408_msk_1.map 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)

 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー




















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X