[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25920: Cryo-EM structure of the human Nax channel in complex with beta3 ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human Nax channel in complex with beta3 solved in GDN | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Sodium Channel / NaV / Ion Channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / SA node cell action potential / osmolarity-sensing monoatomic cation channel activity / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / sodium ion homeostasis / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport ...regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / SA node cell action potential / osmolarity-sensing monoatomic cation channel activity / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / sodium ion homeostasis / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / osmosensory signaling pathway / cellular homeostasis / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / sodium channel inhibitor activity / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium ion transport / sodium channel activity / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / sodium channel regulator activity / membrane depolarization / glial cell projection / positive regulation of heart rate / cardiac muscle contraction / sodium ion transmembrane transport / protein localization to plasma membrane / response to bacterium / Z disc / nervous system development / transmembrane transporter binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Noland CL / Kschonsak M | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structure-guided unlocking of Na reveals a non-selective tetrodotoxin-sensitive cation channel. Authors: Cameron L Noland / Han Chow Chua / Marc Kschonsak / Stephanie Andrea Heusser / Nina Braun / Timothy Chang / Christine Tam / Jia Tang / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio Ciferri / Stephan ...Authors: Cameron L Noland / Han Chow Chua / Marc Kschonsak / Stephanie Andrea Heusser / Nina Braun / Timothy Chang / Christine Tam / Jia Tang / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio Ciferri / Stephan Alexander Pless / Jian Payandeh /    Abstract: Unlike classical voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels, Na has been characterized as a voltage-insensitive, tetrodotoxin-resistant, sodium (Na)-activated channel involved in regulating Na homeostasis. ...Unlike classical voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels, Na has been characterized as a voltage-insensitive, tetrodotoxin-resistant, sodium (Na)-activated channel involved in regulating Na homeostasis. However, Na remains refractory to functional characterization in traditional heterologous systems. Here, to gain insight into its atypical physiology, we determine structures of the human Na channel in complex with the auxiliary β3-subunit. Na reveals structural alterations within the selectivity filter, voltage sensor-like domains, and pore module. We do not identify an extracellular Na-sensor or any evidence for a Na-based activation mechanism in Na. Instead, the S6-gate remains closed, membrane lipids fill the central cavity, and the domain III-IV linker restricts S6-dilation. We use protein engineering to identify three pore-wetting mutations targeting the hydrophobic S6-gate that unlock a robust voltage-insensitive leak conductance. This constitutively active Na-QTT channel construct is non-selective among monovalent cations, inhibited by extracellular calcium, and sensitive to classical Na channel blockers, including tetrodotoxin. Our findings highlight a functional diversity across the Na channel scaffold, reshape our understanding of Na physiology, and provide a template to demystify recalcitrant ion channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25920.map.gz emd_25920.map.gz | 58.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25920-v30.xml emd-25920-v30.xml emd-25920.xml emd-25920.xml | 16.8 KB 16.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25920.png emd_25920.png | 88.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25920.cif.gz emd-25920.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25920 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25920 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25920 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25920 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 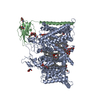 7tj9MC 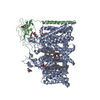 7tj8C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25920.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25920.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1648 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex between human Nax and the Beta3 auxiliary subunit
| Entire | Name: Complex between human Nax and the Beta3 auxiliary subunit |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex between human Nax and the Beta3 auxiliary subunit
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex between human Nax and the Beta3 auxiliary subunit type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sodium channel protein type 7 subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel protein type 7 subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 199.684469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKF FSFFDYKDDD DKGGSGGDYK DDDDKMLASP EPKGLVPFTK ESFELIKQHI AKTHNEDHE EEDLKPTPDL EVGKKLPFIY GNLSQGMVSE PLEDVDPYYY KKKNTFIVLN KNRTIFRFNA ASILCTLSPF N CIRRTTIK ...String: MWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKF FSFFDYKDDD DKGGSGGDYK DDDDKMLASP EPKGLVPFTK ESFELIKQHI AKTHNEDHE EEDLKPTPDL EVGKKLPFIY GNLSQGMVSE PLEDVDPYYY KKKNTFIVLN KNRTIFRFNA ASILCTLSPF N CIRRTTIK VLVHPFFQLF ILISVLIDCV FMSLTNLPKW RPVLENTLLG IYTFEILVKL FARGVWAGSF SFLGDPWNWL DF SVTVFEV IIRYSPLDFI PTLQTARTLR ILKIIPLNQG LKSLVGVLIH CLKQLIGVII LTLFFLSIFS LIGMGLFMGN LKH KCFRWP QENENETLHN RTGNPYYIRE TENFYYLEGE RYALLCGNRT DAGQCPEGYV CVKAGINPDQ GFTNFDSFGW ALFA LFRLM AQDYPEVLYH QILYASGKVY MIFFVVVSFL FSFYMASLFL GILAMAYEEE KQRVGEISKK IEPKFQQTGK ELQEG NETD EAKTIQIEMK KRSPISTDTS LDVLEDATLR HKEELEKSKK ICPLYWYKFA KTFLIWNCSP CWLKLKEFVH RIIMAP FTD LFLIICIILN VCFLTLEHYP MSKQTNTLLN IGNLVFIGIF TAEMIFKIIA MHPYGYFQVG WNIFDSMIVF HGLIELC LA NVAGMALLRL FRMLRIFKLG KYWPTFQILM WSLSNSWVAL KDLVLLLFTF IFFSAAFGMK LFGKNYEEFV CHIDKDCQ L PRWHMHDFFH SFLNVFRILC GEWVETLWDC MEVAGQSWCI PFYLMVILIG NLLVLYLFLA LVSSFSSCKD VTAEENNEA KNLQLAVARI KKGINYVLLK ILCKTQNVPK DTMDHVNEVY VKEDISDHTL SELSNTQDFL KDKEKSSGTE KNATENESQS LIPSPSVSE TVPIASGESD IENLDNKEIQ SKSGDGGSKE KIKQSSSSEC STVDIAISEE EEMFYGGERS KHLKNGCRRG S SLGQISGA SKKGKIWQNI RKTCCKIVEN NWFKCFIGLV TLLSTGTLAF EDIYMDQRKT IKILLEYADM IFTYIFILEM LL KWMAYGF KAYFSNGWYR LDFVVVIVFC LSLIGKTREE LKPLISMKFL RPLRVLSQFE RMKVVVRALI KTTLPTLNVF LVC LMIWLI FSIMGVDLFA GRFYECIDPT SGERFPSSEV MNKSRCESLL FNESMLWENA KMNFDNVGNG FLSLLQVATF NGWI TIMNS AIDSVAVNIQ PHFEVNIYMY CYFINFIIFG VFLPLSMLIT VIIDNFNKHK IKLGGSNIFI TVKQRKQYRR LKKLM YEDS QRPVPRPLNK LQGFIFDVVT SQAFNVIVMV LICFQAIAMM IDTDVQSLQM SIALYWINSI FVMLYTMECI LKLIAF RCF YFTIAWNIFD FMVVIFSITG LCLPMTVGSY LVPPSLVQLI LLSRIIHMLR LGKGPKVFHN LMLPLMLSLP ALLNIIL LI FLVMFIYAVF GMYNFAYVKK EAGINDVSNF ETFGNSMLCL FQVAIFAGWD GMLDAIFNSK WSDCDPDKIN PGTQVRGD C GNPSVGIFYF VSYILISWLI IVNMYIVVVM EFLNIASKKK NKTLSEDDFR KFFQVWKRFD PDRTQYIDSS KLSDFAAAL DPPLFMAKPN KGQLIALDLP MAVGDRIHCL DILLAFTKRV MGQDVRMEKV VSEIESGFLL ANPFKITCEP ITTTLKRKQE AVSATIIQR AYKNYRLRRN DKNTSDIHMI DGDRDVHATK EGAYFDKAKE KSPIQSQI UniProtKB: Sodium channel protein type 7 subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Sodium channel subunit beta-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel subunit beta-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.723209 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPAFNRLFPL ASLVLIYWVS VCFPVCVEVP SETEAVQGNP MKLRCISCMK REEVEATTVV EWFYRPEGGK DFLIYEYRNG HQEVESPFQ GRLQWNGSKD LQDVSITVLN VTLNDSGLYT CNVSREFEFE AHRPFVKTTR LIPLRVTEEA GEDFTSVVSE I MMYILLVF ...String: MPAFNRLFPL ASLVLIYWVS VCFPVCVEVP SETEAVQGNP MKLRCISCMK REEVEATTVV EWFYRPEGGK DFLIYEYRNG HQEVESPFQ GRLQWNGSKD LQDVSITVLN VTLNDSGLYT CNVSREFEFE AHRPFVKTTR LIPLRVTEEA GEDFTSVVSE I MMYILLVF LTLWLLIEMI YCYRKVSKAE EAAQENASDY LAIPSENKEN SAVPVEE UniProtKB: Sodium channel regulatory subunit beta-3 |
-Macromolecule #4: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]ETHYL STEARATE type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: PEV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 720.012 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PEV: |
-Macromolecule #5: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #6: PALMITIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PLM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.424 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PLM: |
-Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #8: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #9: 2-{[(4-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]methyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-{[(4-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]methyl}-4-{[(3beta,9beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-spirost-5-en-3-yl]oxy}butyl 4-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: Q7G |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.165315 KDa |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Q7G: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.067 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)