+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of Xenopus KCNQ1-CaM | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of gastric acid secretion / membrane repolarization / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / intestinal absorption / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels ...regulation of gastric acid secretion / membrane repolarization / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / intestinal absorption / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / renal absorption / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / inner ear development / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / monoatomic ion channel complex / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / presynaptic cytosol / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Protein methylation / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / spindle pole / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / RAS processing / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / calcium-dependent protein binding / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / long-term synaptic potentiation Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
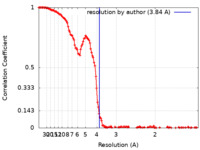
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.84 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Willegems K / Kyriakis E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural and electrophysiological basis for the modulation of KCNQ1 channel currents by ML277. Authors: Katrien Willegems / Jodene Eldstrom / Efthimios Kyriakis / Fariba Ataei / Harutyun Sahakyan / Ying Dou / Sophia Russo / Filip Van Petegem / David Fedida /   Abstract: The KCNQ1 ion channel plays critical physiological roles in electrical excitability and K recycling in organs including the heart, brain, and gut. Loss of function is relatively common and can cause ...The KCNQ1 ion channel plays critical physiological roles in electrical excitability and K recycling in organs including the heart, brain, and gut. Loss of function is relatively common and can cause sudden arrhythmic death, sudden infant death, epilepsy and deafness. Here, we report cryogenic electron microscopic (cryo-EM) structures of Xenopus KCNQ1 bound to Ca/Calmodulin, with and without the KCNQ1 channel activator, ML277. A single binding site for ML277 was identified, localized to a pocket lined by the S4-S5 linker, S5 and S6 helices of two separate subunits. Several pocket residues are not conserved in other KCNQ isoforms, explaining specificity. MD simulations and point mutations support this binding location for ML277 in open and closed channels and reveal that prevention of inactivation is an important component of the activator effect. Our work provides direction for therapeutic intervention targeting KCNQ1 loss of function pathologies including long QT interval syndrome and seizures. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25816.map.gz emd_25816.map.gz | 162.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25816-v30.xml emd-25816-v30.xml emd-25816.xml emd-25816.xml | 17.3 KB 17.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_25816_fsc.xml emd_25816_fsc.xml | 17.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
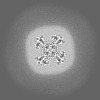
| Images |  emd_25816.png emd_25816.png | 82.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25816.cif.gz emd-25816.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25816 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25816 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7tcpMC  7tciC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 209.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 209.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.73 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 in complex...
| Entire | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 in complex with calmodulin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 in complex...
| Supramolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 in complex with calmodulin type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 317.56 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.663398 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATDPPRPTI NLDPRVSIYS GRRPLLSRTN IQGRVYNFLE RPTGWKCFVY HFTVFLIVLI CLIFSVLSTI QQYNNLATET LFWMEIVLV VFFGAEYVVR LWSAGCRSKY VGVWGRLRFA RKPISVIDLI VVVASVIVLC VGSNGQVFAT SAIRGIRFLQ I LRMLHVDR ...String: MATDPPRPTI NLDPRVSIYS GRRPLLSRTN IQGRVYNFLE RPTGWKCFVY HFTVFLIVLI CLIFSVLSTI QQYNNLATET LFWMEIVLV VFFGAEYVVR LWSAGCRSKY VGVWGRLRFA RKPISVIDLI VVVASVIVLC VGSNGQVFAT SAIRGIRFLQ I LRMLHVDR QGGTWRLLGS VVFIHRQELI TTLYIGFLGL IFSSYFVYLA EKDAIDSSGE YQFGSYADAL WWGVVTVTTI GY GDKVPQT WIGKTIASCF SVFAISFFAL PAGILGSGFA LKVQQKQRQK HFNRQIPAAA SLIQTAWRCY AAENPDSATW KIY IRKQSR NHHLMSPSPK PKKSAMVKKK KIRTERDEGS TDKMLNIPHI TYDHVADDRK NDGYSVESYE NTVRKPFGFL DPST GPFIR TSSFTDDLDM EGDTLLTPIT HISELKEHHR AAIKVIRRMQ YFVAKKKFQQ ARKPYDVRDV IEQYSQGHLN LMVRI KELQ RRLDQSLGKP SLFLSVSDKV KDKGINTIGS RLNRVEDKVT QMDHKLNLIT DMLHHLLTNQ QSNS UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 25 sec. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 98 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 19997 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.36 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)