+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human FPR1-Gi complex with fMLFII | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | FPR1_fmlfii | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / membrane protein / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationN-formyl peptide receptor activity / complement receptor activity / scavenger receptor binding / RAGE receptor binding / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / G-protein activation / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste ...N-formyl peptide receptor activity / complement receptor activity / scavenger receptor binding / RAGE receptor binding / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / G-protein activation / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / Ca2+ pathway / G alpha (z) signalling events / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / G alpha (q) signalling events / G alpha (i) signalling events / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Ca2+ pathway / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / G alpha (z) signalling events / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / azurophil granule membrane / G alpha (s) signalling events / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / G alpha (q) signalling events / spectrin binding / G alpha (i) signalling events / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase activity / Interleukin-10 signaling / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / photoreceptor outer segment / adenylate cyclase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / T cell migration / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / response to prostaglandin E / D2 dopamine receptor binding / photoreceptor inner segment / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to forskolin / secretory granule membrane / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / negative regulation of insulin secretion / G protein-coupled receptor binding / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / response to peptide hormone / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / centriolar satellite / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / chemotaxis / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / GDP binding / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / sensory perception of taste / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / cell body Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo (humans) / Homo (humans) /  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhuang YW | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Molecular recognition of formylpeptides and diverse agonists by the formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2. Authors: Youwen Zhuang / Lei Wang / Jia Guo / Dapeng Sun / Yue Wang / Weiyi Liu / H Eric Xu / Cheng Zhang /   Abstract: The formylpeptide receptors (FPRs) mediate pattern recognition of formylated peptides derived from invading pathogens or mitochondria from dead host cells. They can also sense other structurally ...The formylpeptide receptors (FPRs) mediate pattern recognition of formylated peptides derived from invading pathogens or mitochondria from dead host cells. They can also sense other structurally distinct native peptides and even lipid mediators to either promote or resolve inflammation. Pharmacological targeting of FPRs represents a novel therapeutic approach in treating inflammatory diseases. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying FPR ligand recognition are elusive. We report cryo-EM structures of G-coupled FPR1 and FPR2 bound to a formylpeptide and G-coupled FPR2 bound to two synthetic peptide and small-molecule agonists. Together with mutagenesis data, our structures reveal the molecular mechanism of formylpeptide recognition by FPRs and structural variations of FPR1 and FPR2 leading to their different ligand preferences. Structural analysis also suggests that diverse FPR agonists sample a conserved activation chamber at the bottom of ligand-binding pockets to activate FPRs. Our results provide a basis for rational drug design on FPRs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25727.map.gz emd_25727.map.gz | 28.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25727-v30.xml emd-25727-v30.xml emd-25727.xml emd-25727.xml | 14.2 KB 14.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25727.png emd_25727.png | 60.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25727.cif.gz emd-25727.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25727 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25727 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25727 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25727 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7t6tMC  7t6sC  7t6uC  7t6vC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25727.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25727.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | FPR1_fmlfii | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.045 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : formylpeptide receptors FPR1
| Entire | Name: formylpeptide receptors FPR1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: formylpeptide receptors FPR1
| Supramolecule | Name: formylpeptide receptors FPR1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo (humans) Homo (humans) |
-Macromolecule #1: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.313863 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: GCTLSAEDKA AVERSKMIDR NLREDGEKAA REVKLLLLGA GESGKSTIVK QMKIIHEAGY SEEECKQYKA VVYSNTIQSI IAIIRAMGR LKIDFGDSAR ADDARQLFVL AGAAEEGFMT AELAGVIKRL WKDSGVQACF NRSREYQLND SAAYYLNDLD R IAQPNYIP ...String: GCTLSAEDKA AVERSKMIDR NLREDGEKAA REVKLLLLGA GESGKSTIVK QMKIIHEAGY SEEECKQYKA VVYSNTIQSI IAIIRAMGR LKIDFGDSAR ADDARQLFVL AGAAEEGFMT AELAGVIKRL WKDSGVQACF NRSREYQLND SAAYYLNDLD R IAQPNYIP TQQDVLRTRV KTTGIVETHF TFKDLHFKMF DVGAQRSERK KWIHCFEGVT AIIFCVALSD YDLVLAEDEE MN RMHESMK LFDSICNNKW FTDTSIILFL NKKDLFEEKI KKSPLTICYP EYAGSNTYEE AAAYIQCQFE DLNKRKDTKE IYT HFTCST DTKNVQFVFD AVTDVIIKNN LKDCGLF UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.021648 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: HHHHHHHHMG SLLQSELDEL RQEAEQLKNQ IRDARKACAD ATLSQITNNI DPVGRIQMRT RRTLRGHLAK IYAMHWGTDS RLLVSASQD GKLIIWDSYT TNKVHAIPLR SSWVMTCAYA PSGNYVACGG LDNICSIYNL KTREGNVRVS RELAGHTGYL S CCRFLDDN ...String: HHHHHHHHMG SLLQSELDEL RQEAEQLKNQ IRDARKACAD ATLSQITNNI DPVGRIQMRT RRTLRGHLAK IYAMHWGTDS RLLVSASQD GKLIIWDSYT TNKVHAIPLR SSWVMTCAYA PSGNYVACGG LDNICSIYNL KTREGNVRVS RELAGHTGYL S CCRFLDDN QIVTSSGDTT CALWDIETGQ QTTTFTGHTG DVMSLSLAPD TRLFVSGACD ASAKLWDVRE GMCRQTFTGH ES DINAICF FPNGNAFATG SDDATCRLFD LRADQELMTY SHDNIICGIT SVSFSKSGRL LLAGYDDFNC NVWDALKADR AGV LAGHDN RVSCLGVTDD GMAVATGSWD SFLKIWN UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.432554 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: ASNNTASIAQ ARKLVEQLKM EANIDRIKVS KAAADLMAYC EAHAKEDPLL TPVPASENPF REKKFFC UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 |
-Macromolecule #4: Synthetic peptide
| Macromolecule | Name: Synthetic peptide / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo (humans) Homo (humans) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 663.868 Da |
| Sequence | String: (FME)LFII |
-Macromolecule #5: fMet-Leu-Phe receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: fMet-Leu-Phe receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.041699 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: DYKDDDDVDG SAENLYFQGA SMETNSSLPT NISGGTPAVS AGYLFLDIIT YLVFAVTFVL GVLGNGLVIW VAGFRMTHTV TTISYLNLA VADFCFTSTL PFFMVRKAMG GHWPFGWFLC KFVFTIVDIN LFGSVFLIAL IALDRCVCVL HPVWTQNHRT V SLAKKVII ...String: DYKDDDDVDG SAENLYFQGA SMETNSSLPT NISGGTPAVS AGYLFLDIIT YLVFAVTFVL GVLGNGLVIW VAGFRMTHTV TTISYLNLA VADFCFTSTL PFFMVRKAMG GHWPFGWFLC KFVFTIVDIN LFGSVFLIAL IALDRCVCVL HPVWTQNHRT V SLAKKVII GPWVMALLLT LPVIIRVTTV PGKTGTVACT FNFSPWTNDP KERINVAVAM LTVRGIIRFI IGFSAPMSIV AV SYGLIAT KIHKQGLIKS SRPLRVLSFV AAAFFLCWSP YQVVALIATV RIRELLQGMY KEIGIAVDVT SALAFFNSCL NPM LYVFMG QDFRERLIHA LPASLERALT EDSTQTSD UniProtKB: fMet-Leu-Phe receptor |
-Macromolecule #6: PALMITIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PLM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.424 Da |
| Chemical component information | 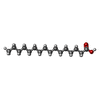 ChemComp-PLM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 258740 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















