[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2486: Electron microscopy of negatively-stained p9 tail protein from ba... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2486 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Electron microscopy of negatively-stained p9 tail protein from bacillus phi29 bacteriophage | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of bacteriophage phi29 tail protein | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Bacteriophage / Tail protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology | : / Bacillus phage phi29, Tail knob protein gp9, C-terminal domain / Distal tube protein, N-terminal / Caudoviral major tail protein N-terminus / virus tail, tube / symbiont genome ejection through host cell envelope, short tail mechanism / virus tail / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / Tail knob protein gp9 Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  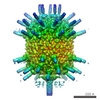 Bacillus phage phi29 (virus) Bacillus phage phi29 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 20.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cuervo A / Chagoyen M / Pulido-Cid M / Camacho A / Carrascosa JL | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Structural characterization of T7 tail machinery reveals a conserved tubular structure among other members of the Podoviridae family suggesting a common mechanism for DNA delivery Authors: Cuervo A / Chagoyen M / Pulido-Cid M / Camacho A / Carrascosa JL | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2486.map.gz emd_2486.map.gz | 769.5 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2486-v30.xml emd-2486-v30.xml emd-2486.xml emd-2486.xml | 8.2 KB 8.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2486.png EMD-2486.png | 99.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2486 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2486 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2486 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2486 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2486.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 825.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2486.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 825.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of bacteriophage phi29 tail protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.14 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
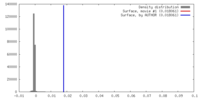
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : p9 protein from phi29 bacteriophage
| Entire | Name: p9 protein from phi29 bacteriophage |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: p9 protein from phi29 bacteriophage
| Supramolecule | Name: p9 protein from phi29 bacteriophage / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: hexamer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 402 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: p9
| Macromolecule | Name: p9 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: The protein was cloned with an His-tag / Number of copies: 6 / Oligomeric state: hexamer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bacillus phage phi29 (virus) Bacillus phage phi29 (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 67 KDa / Theoretical: 67 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Tail knob protein gp9 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 / Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100mM NaCl and 10 mM MgCl2 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: GraFix-fixated proteins stained on 2% w/v uranyl acetate for 1 min. |
| Grid | Details: 400 mesh cupper grid coated with a carbon layer, glow discharged |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Date | Jan 25, 2012 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 100 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.26 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 108696 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: PHILIPS ROTATION HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each micrograph |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C6 (6 fold cyclic) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 20.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: EMAN, Xmipp / Number images used: 4362 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)