[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2451: Cryo-EM structure of the CSFV IRES in complex with eIF3, small ri... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2451 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
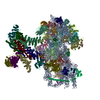
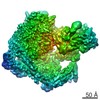
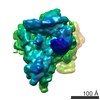
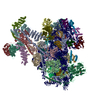
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the CSFV IRES in complex with eIF3, small ribosomal 40S subunit and DHX29 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound to eukaryotic initiation factor 3, the Rabbit 40S subunit and DHX29. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Internal Ribosomal Entry Site / 5'-end independent initiation / HCV-like IRES / eIF3/HCV-like IRES interaction | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mRNA binding / viral translational termination-reinitiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3e / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3m / IRES-dependent viral translational initiation / translation reinitiation / formation of cytoplasmic translation initiation complex / multi-eIF complex / cytoplasmic translational initiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex ...positive regulation of mRNA binding / viral translational termination-reinitiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3e / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3m / IRES-dependent viral translational initiation / translation reinitiation / formation of cytoplasmic translation initiation complex / multi-eIF complex / cytoplasmic translational initiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex / eukaryotic 43S preinitiation complex / eukaryotic 48S preinitiation complex / regulation of translational initiation / metal-dependent deubiquitinase activity / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Translation initiation complex formation / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / translation initiation factor binding / negative regulation of translational initiation / translation initiation factor activity / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of translation / translational initiation / PML body / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / fibrillar center / metallopeptidase activity / ribosome binding / microtubule / ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1 / cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity / postsynaptic density / cadherin binding / mRNA binding / synapse / chromatin / nucleolus / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Classical swine fever virus / Classical swine fever virus /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hashem Y / des-Georges A / Dhote V / Langlois R / Liao HY / Grassucci RA / Pestova TV / Hellen CUT / Frank J | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2013 Journal: Nature / Year: 2013Title: Hepatitis-C-virus-like internal ribosome entry sites displace eIF3 to gain access to the 40S subunit. Authors: Yaser Hashem / Amedee des Georges / Vidya Dhote / Robert Langlois / Hstau Y Liao / Robert A Grassucci / Tatyana V Pestova / Christopher U T Hellen / Joachim Frank /  Abstract: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and classical swine fever virus (CSFV) messenger RNAs contain related (HCV-like) internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) that promote 5'-end independent initiation of ...Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and classical swine fever virus (CSFV) messenger RNAs contain related (HCV-like) internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) that promote 5'-end independent initiation of translation, requiring only a subset of the eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) needed for canonical initiation on cellular mRNAs. Initiation on HCV-like IRESs relies on their specific interaction with the 40S subunit, which places the initiation codon into the P site, where it directly base-pairs with eIF2-bound initiator methionyl transfer RNA to form a 48S initiation complex. However, all HCV-like IRESs also specifically interact with eIF3 (refs 2, 5-7, 9-12), but the role of this interaction in IRES-mediated initiation has remained unknown. During canonical initiation, eIF3 binds to the 40S subunit as a component of the 43S pre-initiation complex, and comparison of the ribosomal positions of eIF3 and the HCV IRES revealed that they overlap, so that their rearrangement would be required for formation of ribosomal complexes containing both components. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a 40S ribosomal complex containing eIF3 and the CSFV IRES. Remarkably, although the position and interactions of the CSFV IRES with the 40S subunit in this complex are similar to those of the HCV IRES in the 40S-IRES binary complex, eIF3 is completely displaced from its ribosomal position in the 43S complex, and instead interacts through its ribosome-binding surface exclusively with the apical region of domain III of the IRES. Our results suggest a role for the specific interaction of HCV-like IRESs with eIF3 in preventing ribosomal association of eIF3, which could serve two purposes: relieving the competition between the IRES and eIF3 for a common binding site on the 40S subunit, and reducing formation of 43S complexes, thereby favouring translation of viral mRNAs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2451.map.gz emd_2451.map.gz | 37.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2451-v30.xml emd-2451-v30.xml emd-2451.xml emd-2451.xml | 12.1 KB 12.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2451-40S-IRES-DHX29-eIF3-500X500.jpg EMD-2451-40S-IRES-DHX29-eIF3-500X500.jpg | 108.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2451 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2451 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2451 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2451 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j8bM  2450C  4c4qC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2451.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 39.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2451.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 39.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound to eukaryotic initiation factor 3, the Rabbit 40S subunit and DHX29. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.245 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound...
| Entire | Name: Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound to eukaryotic initiation factor 3, the Rabbit 40S subunit and DHX29. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound...
| Supramolecule | Name: Reconstruction of a mutant Classical Swine Fever Virus IRES bound to eukaryotic initiation factor 3, the Rabbit 40S subunit and DHX29. type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: one 40S, one CSFV IRES, one eIF3 and one DHX29 Number unique components: 4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.6 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: eukaryotic small ribosmal subunit
| Supramolecule | Name: eukaryotic small ribosmal subunit / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: 40S subunit / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: SSU 40S, SSU RNA 18S |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Internal Ribosomal Entry Site
| Macromolecule | Name: Internal Ribosomal Entry Site / type: rna / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: IRES / Classification: OTHER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Classical swine fever virus / synonym: CSFV Classical swine fever virus / synonym: CSFV |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 100 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GACUAGCCGU AGUGGCGAGC UCCCUGGGUG GUCUAAGUCC UGAGUACAGG ACAGUCGUCA GUAGUUCGAC GUGAGCACUA GCCCACCUCG AGAUGCUACG UGGACGAGGG CAUGCCCAAG ACACACCUUA ACCCUGGCGG GGGUCGCUAG GGUGAAAUCA CAUUAUGUGA ...String: GACUAGCCGU AGUGGCGAGC UCCCUGGGUG GUCUAAGUCC UGAGUACAGG ACAGUCGUCA GUAGUUCGAC GUGAGCACUA GCCCACCUCG AGAUGCUACG UGGACGAGGG CAUGCCCAAG ACACACCUUA ACCCUGGCGG GGGUCGCUAG GGUGAAAUCA CAUUAUGUGA UGGGGGUACG ACCUGAUAGG GUGCUGCAGA GGCCCACUAG CAGGCUAGUA UAAAAAUCUC UGC |
-Macromolecule #2: DHX29
| Macromolecule | Name: DHX29 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 150 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #3: eukaryotic initiation factor 3
| Macromolecule | Name: eukaryotic initiation factor 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: eIF3 / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 850 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.105 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM Tris , 75 mM KCl, 5 mM Mg, 2 mM DTT and 0.25 mM spermidine |
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh copper/molybdenum holey carbon-coated Quantifoil 2/4 grid (Quantifoil Micro Tools GmbH) containing an additional continuous thin layer of carbon |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 120 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II Method: 30 seconds waiting after sample deposition on the grid, blotting for seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 110 K |
| Date | Feb 1, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 12000 / Average electron dose: 12 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 32 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 51570 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.26 mm / Nominal defocus max: -4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Gatan CT3500 side-entry cryo-holder / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The particles constituting this reconstruction were sorted using RELION. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.3 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Spider, Relion / Number images used: 26000 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















