+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Transport protein in inhibited state 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion transport inhibited state / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpolyamine transmembrane transport / spermine transmembrane transport / : / polyamine transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type polyamine transporter activity / regulation of autophagosome size / extracellular exosome biogenesis / negative regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / P-type ion transporter activity ...polyamine transmembrane transport / spermine transmembrane transport / : / polyamine transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type polyamine transporter activity / regulation of autophagosome size / extracellular exosome biogenesis / negative regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / P-type ion transporter activity / regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion / regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process / intracellular monoatomic cation homeostasis / autophagosome-lysosome fusion / autophagosome organization / protein localization to lysosome / positive regulation of exosomal secretion / phosphatidic acid binding / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / multivesicular body membrane / intracellular zinc ion homeostasis / cupric ion binding / regulation of protein localization to nucleus / regulation of mitochondrion organization / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of other compounds; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate / lysosomal transport / regulation of intracellular protein transport / cellular response to zinc ion / lipid homeostasis / autophagosome membrane / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / regulation of macroautophagy / transport vesicle / cellular response to manganese ion / multivesicular body / lysosomal lumen / autophagosome / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / positive regulation of protein secretion / autophagy / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / late endosome / late endosome membrane / manganese ion binding / cellular response to oxidative stress / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / vesicle / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / lysosome / neuron projection / lysosomal membrane / neuronal cell body / positive regulation of gene expression / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee KPK | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural mechanisms for gating and ion selectivity of the human polyamine transporter ATP13A2. Authors: Jordan Tillinghast / Sydney Drury / Darren Bowser / Alana Benn / Kenneth Pak Kin Lee /  Abstract: Mutations in ATP13A2, also known as PARK9, cause a rare monogenic form of juvenile-onset Parkinson's disease named Kufor-Rakeb syndrome and other neurodegenerative diseases. ATP13A2 encodes a ...Mutations in ATP13A2, also known as PARK9, cause a rare monogenic form of juvenile-onset Parkinson's disease named Kufor-Rakeb syndrome and other neurodegenerative diseases. ATP13A2 encodes a neuroprotective P5B P-type ATPase highly enriched in the brain that mediates selective import of spermine ions from lysosomes into the cytosol via an unknown mechanism. Here we present three structures of human ATP13A2 bound to an ATP analog or to spermine in the presence of phosphomimetics determined by cryoelectron microscopy. ATP13A2 autophosphorylation opens a lysosome luminal gate to reveal a narrow lumen access channel that holds a spermine ion in its entrance. ATP13A2's architecture suggests physical principles underlying selective polyamine transport and anticipates a "pump-channel" intermediate that could function as a counter-cation conduit to facilitate lysosome acidification. Our findings establish a firm foundation to understand ATP13A2 mutations associated with disease and bring us closer to realizing ATP13A2's potential in neuroprotective therapy. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23684.map.gz emd_23684.map.gz | 108.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23684-v30.xml emd-23684-v30.xml emd-23684.xml emd-23684.xml | 14.1 KB 14.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23684.png emd_23684.png | 58.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23684.cif.gz emd-23684.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23684 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23684 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7m5xMC 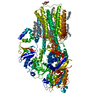 7m5vC  7m5yC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23684.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23684.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Transport protein in inhibited state 1
+Supramolecule #1: Transport protein in inhibited state 1
+Macromolecule #1: Polyamine-transporting ATPase 13A2
+Macromolecule #2: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #3: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
+Macromolecule #4: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #5: DODECYL-BETA-D-MALTOSIDE
+Macromolecule #6: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #7: DECANE
+Macromolecule #8: TETRADECANE
+Macromolecule #9: DODECANE
+Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #11: SPERMINE (FULLY PROTONATED FORM)
+Macromolecule #12: (2R)-3-{[(S)-hydroxy{[(1S,2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2,4,6-trihydroxy-3,5-bi...
+Macromolecule #13: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 76.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 648247 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)