[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21405: Structure of the human clamp loader (Replication Factor C, RFC) b... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21405 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
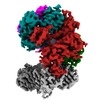
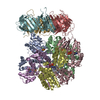
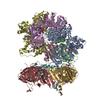
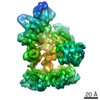
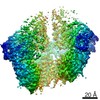
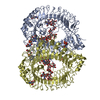
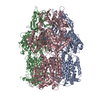
| Title | Structure of the human clamp loader (Replication Factor C, RFC) bound to the sliding clamp (Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen, PCNA) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of the human clamp loader RFC bound to the sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sliding clamp / DNA replication / AAA+ / ATPase / clamp loader / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / REPLICATION | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA clamp unloader activity / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / DNA clamp loader activity ...DNA clamp unloader activity / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / DNA clamp loader activity / nuclear lamina / Polymerase switching / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / MutLalpha complex binding / PCNA complex / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / replisome / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / response to L-glutamate / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / response to dexamethasone / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / histone acetyltransferase binding / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / leading strand elongation / G1/S-Specific Transcription / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / response to cadmium ion / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / estrous cycle / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / telomere maintenance via telomerase / mismatch repair / translesion synthesis / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / base-excision repair, gap-filling / DNA polymerase binding / epithelial cell differentiation / liver regeneration / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of DNA replication / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / replication fork / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / positive regulation of DNA repair / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / male germ cell nucleus / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / enzyme activator activity / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / DNA-templated DNA replication / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / response to estradiol / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / double-stranded DNA binding / sequence-specific DNA binding / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / damaged DNA binding / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / nuclear body / protein domain specific binding / DNA repair / chromatin binding / centrosome / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gaubitz C / Liu X | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Switzerland, 3 items Switzerland, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the human clamp loader reveals an autoinhibited conformation of a substrate-bound AAA+ switch. Authors: Christl Gaubitz / Xingchen Liu / Joseph Magrino / Nicholas P Stone / Jacob Landeck / Mark Hedglin / Brian A Kelch /  Abstract: DNA replication requires the sliding clamp, a ring-shaped protein complex that encircles DNA, where it acts as an essential cofactor for DNA polymerases and other proteins. The sliding clamp needs to ...DNA replication requires the sliding clamp, a ring-shaped protein complex that encircles DNA, where it acts as an essential cofactor for DNA polymerases and other proteins. The sliding clamp needs to be opened and installed onto DNA by a clamp loader ATPase of the AAA+ family. The human clamp loader replication factor C (RFC) and sliding clamp proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) are both essential and play critical roles in several diseases. Despite decades of study, no structure of human RFC has been resolved. Here, we report the structure of human RFC bound to PCNA by cryogenic electron microscopy to an overall resolution of ∼3.4 Å. The active sites of RFC are fully bound to adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) analogs, which is expected to induce opening of the sliding clamp. However, we observe the complex in a conformation before PCNA opening, with the clamp loader ATPase modules forming an overtwisted spiral that is incapable of binding DNA or hydrolyzing ATP. The autoinhibited conformation observed here has many similarities to a previous yeast RFC:PCNA crystal structure, suggesting that eukaryotic clamp loaders adopt a similar autoinhibited state early on in clamp loading. Our results point to a "limited change/induced fit" mechanism in which the clamp first opens, followed by DNA binding, inducing opening of the loader to release autoinhibition. The proposed change from an overtwisted to an active conformation reveals an additional regulatory mechanism for AAA+ ATPases. Finally, our structural analysis of disease mutations leads to a mechanistic explanation for the role of RFC in human health. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21405.map.gz emd_21405.map.gz | 3.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21405-v30.xml emd-21405-v30.xml emd-21405.xml emd-21405.xml | 21.3 KB 21.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21405.png emd_21405.png | 118 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21405.cif.gz emd-21405.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21405 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21405 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6vvoMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21405.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21405.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of the human clamp loader RFC bound to the sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Human Replication factor C (RFC) complex bound to the sliding cla...
+Supramolecule #1: Human Replication factor C (RFC) complex bound to the sliding cla...
+Macromolecule #1: Replication factor C subunit 1
+Macromolecule #2: Replication factor C subunit 2
+Macromolecule #3: Replication factor C subunit 5
+Macromolecule #4: Replication factor C subunit 4
+Macromolecule #5: Replication factor C subunit 3
+Macromolecule #6: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
+Macromolecule #7: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #8: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
+Macromolecule #9: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: GOLD / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K |
- Electron microscopy #1
Electron microscopy #1
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 1 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 3695 / Average electron dose: 40.3 e/Å2 / Details: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #1~
Electron microscopy #1~
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 7840 / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 / Details: Quantifoil R0.6/1 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Initial local fitting was peformed using UCSF Chimera, followed by manual model adjustment, then refinement in PHENIX. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
| Output model |  PDB-6vvo: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)
























