+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21004 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
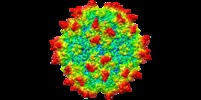
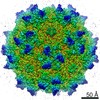
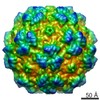
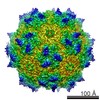
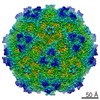
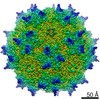
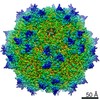
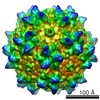
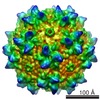
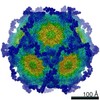
| Title | genome-containing AAV8 particles | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample | Adeno-associated virus != Adeno-associated virus - 8 Adeno-associated virus
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AAV8 / capsid / genome / nucleotide binding pocket / VIRUS | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationT=1 icosahedral viral capsid / nucleotide binding / structural molecule activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Adeno-associated virus - 8 / synthetic construct (others) Adeno-associated virus - 8 / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.77 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mietzsch M / Agbandje-McKenna M | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2020 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2020Title: Comparative Analysis of the Capsid Structures of AAVrh.10, AAVrh.39, and AAV8. Authors: Mario Mietzsch / Candace Barnes / Joshua A Hull / Paul Chipman / Jun Xie / Nilakshee Bhattacharya / Duncan Sousa / Robert McKenna / Guangping Gao / Mavis Agbandje-McKenna /  Abstract: Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) from clade E are often used as vectors in gene delivery applications. This clade includes rhesus isolate 10 (AAVrh.10) and 39 (AAVrh.39) which, unlike representative ...Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) from clade E are often used as vectors in gene delivery applications. This clade includes rhesus isolate 10 (AAVrh.10) and 39 (AAVrh.39) which, unlike representative AAV8, are capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB), thereby enabling the delivery of therapeutic genes to the central nervous system. Here, the capsid structures of AAV8, AAVrh.10 and AAVrh.39 have been determined by cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction to 3.08-, 2.75-, and 3.39-Å resolution, respectively, to enable a direct structural comparison. AAVrh.10 and AAVrh.39 are 98% identical in amino acid sequence but only ∼93.5% identical to AAV8. However, the capsid structures of all three viruses are similar, with only minor differences observed in the previously described surface variable regions, suggesting that specific residues S269 and N472, absent in AAV8, may confer the ability to cross the BBB in AAVrh.10 and AAVrh.39. Head-to-head comparison of empty and genome-containing particles showed DNA ordered in the previously described nucleotide-binding pocket, supporting the suggested role of this pocket in DNA packaging for the The structural characterization of these viruses provides a platform for future vector engineering efforts toward improved gene delivery success with respect to specific tissue targeting, transduction efficiency, antigenicity, or receptor retargeting. Recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors (rAAVs), based on AAV8 and AAVrh.10, have been utilized in multiple clinical trials to treat different monogenetic diseases. The closely related AAVrh.39 has also shown promise As recently attained for other AAV biologics, e.g., Luxturna and Zolgensma, based on AAV2 and AAV9, respectively, the vectors in this study will likely gain U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval for commercialization in the near future. This study characterized the capsid structures of these clinical vectors at atomic resolution using cryo-electron microscopy and image reconstruction for comparative analysis. The analysis suggested two key residues, S269 and N472, as determinants of BBB crossing for AAVrh.10 and AAVrh.39, a feature utilized for central nervous system delivery of therapeutic genes. The structure information thus provides a platform for engineering to improve receptor retargeting or tissue specificity. These are important challenges in the field that need attention. Capsid structure information also provides knowledge potentially applicable for regulatory product approval. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21004.map.gz emd_21004.map.gz | 91.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21004-v30.xml emd-21004-v30.xml emd-21004.xml emd-21004.xml | 16.3 KB 16.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21004.png emd_21004.png | 288.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21004.cif.gz emd-21004.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21004 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21004 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21004 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21004 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6v10MC  0663C  6o9rC  6v12C  6v1gC  6v1tC  6v1zC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21004.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 242.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21004.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 242.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.97 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Adeno-associated virus
| Entire | Name:   Adeno-associated virus Adeno-associated virus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Adeno-associated virus - 8
| Supramolecule | Name: Adeno-associated virus - 8 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 / NCBI-ID: 202813 / Sci species name: Adeno-associated virus - 8 / Sci species strain: AAV8 / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SEROTYPE / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Adeno-associated virus - 8 Adeno-associated virus - 8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 58.656512 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GADGVGSSSG NWHCDSTWLG DRVITTSTRT WALPTYNNHL YKQISNGTSG GATNDNTYFG YSTPWGYFDF NRFHCHFSPR DWQRLINNN WGFRPKRLSF KLFNIQVKEV TQNEGTKTIA NNLTSTIQVF TDSEYQLPYV LGSAHQGCLP PFPADVFMIP Q YGYLTLNN ...String: GADGVGSSSG NWHCDSTWLG DRVITTSTRT WALPTYNNHL YKQISNGTSG GATNDNTYFG YSTPWGYFDF NRFHCHFSPR DWQRLINNN WGFRPKRLSF KLFNIQVKEV TQNEGTKTIA NNLTSTIQVF TDSEYQLPYV LGSAHQGCLP PFPADVFMIP Q YGYLTLNN GSQAVGRSSF YCLEYFPSQM LRTGNNFQFT YTFEDVPFHS SYAHSQSLDR LMNPLIDQYL YYLSRTQTTG GT ANTQTLG FSQGGPNTMA NQAKNWLPGP CYRQQRVSTT TGQNNNSNFA WTAGTKYHLN GRNSLANPGI AMATHKDDEE RFF PSNGIL IFGKQNAARD NADYSDVMLT SEEEIKTTNP VATEEYGIVA DNLQQQNTAP QIGTVNSQGA LPGMVWQNRD VYLQ GPIWA KIPHTDGNFH PSPLMGGFGL KHPPPQILIK NTPVPADPPT TFNQSKLNSF ITQYSTGQVS VEIEWELQKE NSKRW NPEI QYTSNYYKST SVDFAVNTEG VYSEPRPIGT RYLTRNL UniProtKB: Capsid protein |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (5'-D(*CP*A)-3')
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(*CP*A)-3') / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 60 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 557.431 Da |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DA) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-20 (5k x 3k) / Average electron dose: 67.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



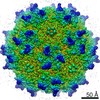
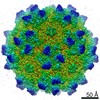
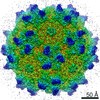




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)