[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-19364: Structure of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel in complex with synthet... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
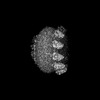
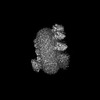
| Title | Structure of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel in complex with synthetic nanobodies SbC2 and SbC4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / large pore channels / sybody / CALHM / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of microglial cell activation / ATP export / calcium ion import / monoatomic cation channel activity / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of apoptotic process / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
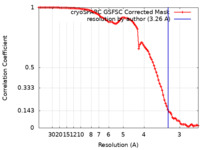
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.26 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Drozdzyk K / Dutzler R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 1 items Switzerland, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: Structural features of heteromeric channels composed of CALHM2 and CALHM4 paralogs. Authors: Katarzyna Drożdżyk / Martina Peter / Raimund Dutzler /  Abstract: The CALHM proteins constitute a family of large pore channels that contains six closely related paralogs in humans. Two family members, CALHM1 and 3, have been associated with the release of ATP ...The CALHM proteins constitute a family of large pore channels that contains six closely related paralogs in humans. Two family members, CALHM1 and 3, have been associated with the release of ATP during taste sensation. Both proteins form heteromeric channels that activate at positive potential and decreased extracellular Ca concentration. Although the structures of several family members displayed large oligomeric organizations of different size, their function has in most cases remained elusive. Our previous study has identified the paralogs CALHM2, 4 and, 6 to be highly expressed in the placenta and defined their structural properties as membrane proteins exhibiting features of large pore channels with unknown activation properties (Drożdżyk et al., 2020). Here, we investigated whether these placental paralogs would form heteromers and characterized heteromeric complexes consisting of CALHM2 and CALHM4 subunits using specific binders as fiducial markers. Both proteins assemble with different stoichiometries with the largest population containing CALHM2 as the predominant component. In these oligomers, the subunits segregate and reside in their preferred conformation found in homomeric channels. Our study has thus revealed the properties that govern the formation of CALHM heteromers in a process of potential relevance in a cellular context. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
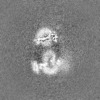
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19364.map.gz emd_19364.map.gz | 79.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19364-v30.xml emd-19364-v30.xml emd-19364.xml emd-19364.xml | 20.1 KB 20.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19364_fsc.xml emd_19364_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19364.png emd_19364.png | 35.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19364.cif.gz emd-19364.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19364_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19364_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19364_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19364_half_map_2.map.gz | 77.8 MB 77.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19364 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19364 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19364 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19364 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_19364_validation.pdf.gz emd_19364_validation.pdf.gz | 919 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_19364_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_19364_full_validation.pdf.gz | 918.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_19364_validation.xml.gz emd_19364_validation.xml.gz | 17.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_19364_validation.cif.gz emd_19364_validation.cif.gz | 22.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19364 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19364 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19364 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19364 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8rmmMC  8rmkC  8rmlC  8rmnC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19364.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19364.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
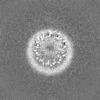
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.302 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
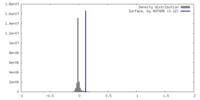
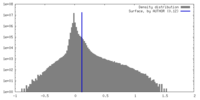
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_19364_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
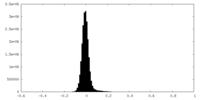
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_19364_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
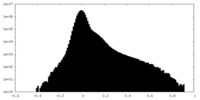
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel with synthetic nanobody SbC4
| Entire | Name: Complex of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel with synthetic nanobody SbC4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel with synthetic nanobody SbC4
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of heteromeric CALHM2/4 channel with synthetic nanobody SbC4 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 0.541 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 4
| Macromolecule | Name: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.981656 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSCPTLNNIV SSLQRNGIFI NSLIAALTIG GQQLFSSSTF SCPCQVGKNF YYGSAFLVIP ALILLVAGFA LRSQMWTITG EYCCSCAPP YRRISPLECK LACLRFFSIT GRAVIAPLTW LAVTLLTGTY YECAASEFAS VDHYPMFDNV SASKREEILA G FPCCRSAP ...String: MSCPTLNNIV SSLQRNGIFI NSLIAALTIG GQQLFSSSTF SCPCQVGKNF YYGSAFLVIP ALILLVAGFA LRSQMWTITG EYCCSCAPP YRRISPLECK LACLRFFSIT GRAVIAPLTW LAVTLLTGTY YECAASEFAS VDHYPMFDNV SASKREEILA G FPCCRSAP SDVILVRDEI ALLHRYQSQM LGWILITLAT IAALVSCCVA KCCSPLTSLQ HCYWTSHLQN ERELFEQAAE QH SRLLMMH RIKKLFGFIP GSEDVKHIRI PSCQDWKDIS VPTLLCMGDD LQGHYSFLGN RVDEDNEEDR SRGIELKPAL EVL FQ UniProtKB: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 4 |
-Macromolecule #2: Synthetic nanobody SbC4
| Macromolecule | Name: Synthetic nanobody SbC4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.87738 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QGPSQVQLVE SGGGLVQAGG SLRLSCAASG FPVYYTHMRW YRQAPGKERE WVAAIYSKGA GTHYADSVKG RFTISRDNAK NTVYLQMNS LKPEDTAVYY CFVGVGNSYI GQGTQVTVSA |
-Macromolecule #3: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.099535 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSAALIAENF RFLSLFFKSK DVMIFNGLVA LGTVGSQELF SVVAFHCPCS PARNYLYGLA AIGVPALVLF IIGIILNNHT WNLVAECQH RRTKNCSAAP TFLLLSSILG RAAVAPVTWS VISLLRGEAY VCALSEFVDP SSLTAREEHF PSAHATEILA R FPCKENPD ...String: MSAALIAENF RFLSLFFKSK DVMIFNGLVA LGTVGSQELF SVVAFHCPCS PARNYLYGLA AIGVPALVLF IIGIILNNHT WNLVAECQH RRTKNCSAAP TFLLLSSILG RAAVAPVTWS VISLLRGEAY VCALSEFVDP SSLTAREEHF PSAHATEILA R FPCKENPD NLSDFREEVS RRLRYESQLF GWLLIGVVAI LVFLTKCLKH YCSPLSYRQE AYWAQYRANE DQLFQRTAEV HS RVLAANN VRRFFGFVAL NKDDEELIAN FPVEGTQPRP QWNAITGVYL YRENQGLPLY SRLHKWAQGL AGNGAAPDNV EMA LLPSAL EVLFQ UniProtKB: Calcium homeostasis modulator protein 2 |
-Macromolecule #4: Synthetic nanobody SbC2
| Macromolecule | Name: Synthetic nanobody SbC2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.067451 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QGPSQVQLVE SGGGSVQAGG SLRLSCAASG NIRNISYLGW FRQAPGKERE GVAALWTTQG QTYYADSVKG RFTVSLDNAK NTVYLQMNS LKPEDTALYY CAAATSGQYN PLRGYHYNEY WGQGTQVTVS A |
-Macromolecule #5: DIUNDECYL PHOSPHATIDYL CHOLINE
| Macromolecule | Name: DIUNDECYL PHOSPHATIDYL CHOLINE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: PLC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 622.834 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PLC: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)