[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-18221: Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
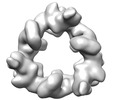
| Title | Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL9 DOC domain | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | postprocess map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cullin-RING RBR E3 Ligase / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of beige fat cell differentiation / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to chemical stress / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / protein K27-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / RNA polymerase II transcription initiation surveillance ...negative regulation of beige fat cell differentiation / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to chemical stress / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / protein K27-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / RNA polymerase II transcription initiation surveillance / protein neddylation / NEDD8 ligase activity / VCB complex / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / Cul5-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of type I interferon production / regulation of mitotic nuclear division / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of mitophagy / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Prolactin receptor signaling / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / cullin family protein binding / protein monoubiquitination / site of DNA damage / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / post-translational protein modification / T cell activation / negative regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / Degradation of DVL / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Hedgehog 'on' state / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Interleukin-1 signaling / protein polyubiquitination / Orc1 removal from chromatin / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / Dual incision in TC-NER / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / cellular response to UV / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / MAPK cascade / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Neddylation / cellular response to oxidative stress / spermatogenesis / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Potential therapeutics for SARS / molecular adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / protein ubiquitination / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / protein-containing complex binding / zinc ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 13.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hopf LVM / Horn-Ghetko D / Schulman BA | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Noncanonical assembly, neddylation and chimeric cullin-RING/RBR ubiquitylation by the 1.8 MDa CUL9 E3 ligase complex. Authors: Daniel Horn-Ghetko / Linus V M Hopf / Ishita Tripathi-Giesgen / Jiale Du / Sebastian Kostrhon / D Tung Vu / Viola Beier / Barbara Steigenberger / J Rajan Prabu / Luca Stier / Elias M Bruss / ...Authors: Daniel Horn-Ghetko / Linus V M Hopf / Ishita Tripathi-Giesgen / Jiale Du / Sebastian Kostrhon / D Tung Vu / Viola Beier / Barbara Steigenberger / J Rajan Prabu / Luca Stier / Elias M Bruss / Matthias Mann / Yue Xiong / Brenda A Schulman /   Abstract: Ubiquitin ligation is typically executed by hallmark E3 catalytic domains. Two such domains, 'cullin-RING' and 'RBR', are individually found in several hundred human E3 ligases, and collaborate with ...Ubiquitin ligation is typically executed by hallmark E3 catalytic domains. Two such domains, 'cullin-RING' and 'RBR', are individually found in several hundred human E3 ligases, and collaborate with E2 enzymes to catalyze ubiquitylation. However, the vertebrate-specific CUL9 complex with RBX1 (also called ROC1), of interest due to its tumor suppressive interaction with TP53, uniquely encompasses both cullin-RING and RBR domains. Here, cryo-EM, biochemistry and cellular assays elucidate a 1.8-MDa hexameric human CUL9-RBX1 assembly. Within one dimeric subcomplex, an E2-bound RBR domain is activated by neddylation of its own cullin domain and positioning from the adjacent CUL9-RBX1 in trans. Our data show CUL9 as unique among RBX1-bound cullins in dependence on the metazoan-specific UBE2F neddylation enzyme, while the RBR domain protects it from deneddylation. Substrates are recruited to various upstream domains, while ubiquitylation relies on both CUL9's neddylated cullin and RBR domains achieving self-assembled and chimeric cullin-RING/RBR E3 ligase activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
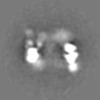
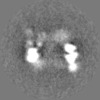
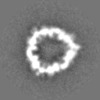
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18221.map.gz emd_18221.map.gz | 9.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18221-v30.xml emd-18221-v30.xml emd-18221.xml emd-18221.xml | 20.9 KB 20.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18221_fsc.xml emd_18221_fsc.xml | 9.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18221.png emd_18221.png | 53.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18221.cif.gz emd-18221.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18221_additional_1.map.gz emd_18221_additional_1.map.gz emd_18221_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18221_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18221_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18221_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.4 MB 49.6 MB 49.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18221 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18221 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18221 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18221 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8q7eC  8q7hC  8rhzC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18221.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18221.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | postprocess map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.997 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: refinement map
| File | emd_18221_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | refinement map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_18221_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_18221_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL...
| Entire | Name: Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL9 DOC domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL...
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of the hexameric CUL9-RBX1 complex with deletion of CUL9 DOC domain type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cullin-9
| Macromolecule | Name: Cullin-9 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MVGERHAGDL MVPLGPRLQA YPEELIRQRP GHDGHPEYLI RWSVLKCGEV GKVGVEEGKA EHILMWLSAP EVYANCPGLL GERALSKGLQ HEPAGVSGSF PRDPGGLDEV AMGEMEADVQ ALVRRAARQL AESGTPSLTA AVLHTIHVLS AYASIGPLTG VFRETGALDL ...String: MVGERHAGDL MVPLGPRLQA YPEELIRQRP GHDGHPEYLI RWSVLKCGEV GKVGVEEGKA EHILMWLSAP EVYANCPGLL GERALSKGLQ HEPAGVSGSF PRDPGGLDEV AMGEMEADVQ ALVRRAARQL AESGTPSLTA AVLHTIHVLS AYASIGPLTG VFRETGALDL LMHMLCNPEP QIRRSAGKML QALAAHDAGS RAHVLLSLSQ QDGIEQHMDF DSRYTLLELF AETTSSEEHC MAFEGIHLPQ IPGKLLFSLV KRYLCVTSLL DQLNSSPELG AGDQSSPCAT REKSRGQREL EFSMAVGNLI SELVRSMGWA RNLSEQGMSP PRPTRSIFQP YISGPSLLLP TIVTTPRRQG WVFRQRSEFS SRSGYGEYVQ QTLQPGMRVR MLDDYEEISA GDEGEFRQSN NGIPPVQVFW QSTGRTYWVH WHMLEILGPE EATEDKASAA VEKGAGATVL GTAFPSWDWN PMDGLYPLPY LQPEPQKNER VGYLTQAEWW ELLFFIKKLD LCEQQPIFQN LWKNLDETLG EKALGEISVS VEMAESLLQV LSSRFEGSTL NDLLNSQIYT KYGLLSNEPS SSSTSRNHSC TPDPEEESKS EASFSEEETE SLKAKAEAPK TEAEPTKTRT ETPMAQSDSQ LFNQLLVTEG MTLPTEMKEA ASEMARALRG PGPRSSLDQH VAAVVATVQI SSLDTNLQLS GLSALSQAVE EVTERDHPLV RPDRSLREKL VKMLVELLTN QVGEKMVVVQ ALRLLYLLMT KHEWRPLFAR EGGIYAVLVC MQEYKTSVLV QQAGLAALKM LAVASSSEIP TFVTGRDSIH SLFDAQMTRE IFASIDSATR PGSESLLLTV PAAVILMLNT EGCSSAARNG LLLLNLLLCN HHTLGDQIIT QELRDTLFRH SGIAPRTEPM PTTRTILMML LNRYSEPPGS PERAALETPI IQGQDGSPEL LIRSLVGGPS AELLLDLERV LCREGSPGGA VRPLLKRLQQ ETQPFLLLLR TLDAPGPNKT LLLSVLRVIT RLLDFPEAMV LPWHEVLEPC LNCLSGPSSD SEIVQELTCF LHRLASMHKD YAVVLCCLGA KEILSKVLDK HSAQLLLGCE LRDLVTECEK YAQLYSNLTS SILAGCIQMV LGQIEDHRRT HQPINIPFFD VFLRHLCQGS SVEVKEGSGS GSGSGPKPTF WPLFREQLCR RTCLFYTIRA QAWSRDIAED HRRLLQLCPR LNRVLRHEQN FADRFLPDDE AAQALGKTCW EALVSPLVQN ITSPDAEGVS ALGWLLDQYL EQRETSRNPL SRAASFASRV RRLCHLLVHV EPPPGPSPEP STRPFSKNSK GRDRSPAPSP VLPSSSLRNI TQCWLSVVQE QVSRFLAAAW RAPDFVPRYC KLYEHLQRAG SELFGPRAAF MLALRSGFSG ALLQQSFLTA AHMSEQFARY IDQQIQGGLI GGAPGVEMLG QLQRHLEPIM VLSGLELATT FEHFYQHYMA DRLLSFGSSW LEGAVLEQIG LCFPNRLPQL MLQSLSTSEE LQRQFHLFQL QRLDKLFLEQ EDEEEKRLEE EEEEEEEEEA EKELFIEDPS PAISILVLSP RCWPVSPLCY LYHPRKCLPT EFCDALDRFS SFYSQSQNHP VLDMGPHRRL QWTWLGRAEL QFGKQILHVS TVQMWLLLKF NQTEEVSVET LLKDSDLSPE LLLQALVPLT SGNGPLTLHE GQDFPHGGVL RLHEPGPQRS GEALWLIPPQ AYLNVEKDEG RTLEQKRNLL SCLLVRILKA HGEKGLHIDQ LVCLVLEAWQ KGPNPPGTLG HTVAGGVACT STDVLSCILH LLGQGYVKRR DDRPQILMYA APEPMGPCRG QADVPFCGSQ SETSKPSPEA VATLASLQLP AGRTMSPQEV EGLMKQTVRQ VQETLNLEPD VAQHLLAHSH WGAEQLLQSY SEDPEPLLLA AGLCVHQAQA VPVRPDHCPV CVSPLGCDDD LPSLCCMHYC CKSCWNEYLT TRIEQNLVLN CTCPIADCPA QPTGAFIRAI VSSPEVISKY EKALLRGYVE SCSNLTWCTN PQGCDRILCR QGLGCGTTCS KCGWASCFNC SFPEAHYPAS CGHMSQWVDD GGYYDGMSVE AQSKHLAKLI SKRCPSCQAP IEKNEGCLHM TCAKCNHGFC WRCLKSWKPN HKDYYNCSAM VSKAARQEKR FQDYNERCTF HHQAREFAVN LRNRVSAIHE VPPPRSFTFL NDACQGLEQA RKVLAYACVY SFYSQDAEYM DVVEQQTENL ELHTNALQIL LEETLLRCRD LASSLRLLRA DCLSTGMELL RRIQERLLAI LQHSAQDFRV GLQSPSVEAW EAKGPNMPGS QPQASSGPEA EEEEEDDEDD VPEWQQDEFD EELDNDSFSY DESENLDQET FFFGDEEEDE DEAYD UniProtKB: Cullin-9 |
-Macromolecule #2: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo (humans) Homo (humans) |
| Sequence | String: MDVDTPSGTN SGAGKKRFEV KKWNAVALWA WDIVVDNCAI CRNHIMDLCI ECQANQ ASA TSEECTVAWG VCNHAFHFHC ISRWLKTRQV CPLDNREWEF QKYGH UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)