+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
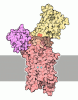
| Title | Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 in E2P state with BeF | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | P-ATPase / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationP-type Cu+ transporter / P-type monovalent copper transporter activity / detoxification of copper ion / vacuolar membrane / transmembrane transport / copper ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
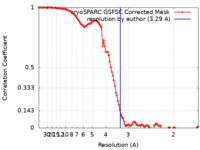
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.29 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guo Z / Gourdon P / Wang K | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 2 items Denmark, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Diverse roles of the metal binding domains and transport mechanism of copper transporting P-type ATPases. Authors: Zongxin Guo / Fredrik Orädd / Viktoria Bågenholm / Christina Grønberg / Jian Feng Ma / Peter Ott / Yong Wang / Magnus Andersson / Per Amstrup Pedersen / Kaituo Wang / Pontus Gourdon /     Abstract: Copper transporting P-type (P-) ATPases are essential for cellular homeostasis. Nonetheless, the E1-E1P-E2P-E2 states mechanism of P-ATPases remains poorly understood. In particular, the role of the ...Copper transporting P-type (P-) ATPases are essential for cellular homeostasis. Nonetheless, the E1-E1P-E2P-E2 states mechanism of P-ATPases remains poorly understood. In particular, the role of the intrinsic metal binding domains (MBDs) is enigmatic. Here, four cryo-EM structures and molecular dynamics simulations of a P-ATPase are combined to reveal that in many eukaryotes the MBD immediately prior to the ATPase core, MBD, serves a structural role, remodeling the ion-uptake region. In contrast, the MBD prior to MBD, MBD, likely assists in copper delivery to the ATPase core. Invariant Tyr, Asn and Ser residues in the transmembrane domain assist in positioning sulfur-providing copper-binding amino acids, allowing for copper uptake, binding and release. As such, our findings unify previously conflicting data on the transport and regulation of P-ATPases. The results are critical for a fundamental understanding of cellular copper homeostasis and for comprehension of the molecular bases of P-disorders and ongoing clinical trials. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18205.map.gz emd_18205.map.gz | 62.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18205-v30.xml emd-18205-v30.xml emd-18205.xml emd-18205.xml | 15.7 KB 15.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18205_fsc.xml emd_18205_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18205.png emd_18205.png | 29.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18205.cif.gz emd-18205.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18205_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18205_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18205_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18205_half_map_2.map.gz | 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18205 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18205 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18205 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18205 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8q76MC  8q73C  8q74C  8q75C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18205.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18205.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_18205_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
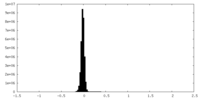
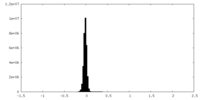
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_18205_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
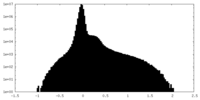
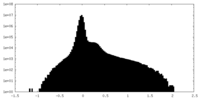
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 from Oryza sativa subsp. japonica
| Entire | Name: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 from Oryza sativa subsp. japonica |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 from Oryza sativa subsp. japonica
| Supramolecule | Name: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 from Oryza sativa subsp. japonica type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4
| Macromolecule | Name: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 105.301398 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEQNGENHLK DPLLQADGGG SGASPAGASP RKERKTRKVM FNVRGISCAS CAVSIETVVA GLKGVESVSV SPLQGQAVVQ YRPEEADAR TIKEAIEGLN FEVDELQEQE IAVCRLQIKG MACTSCSESV ERALQMVPGV KKAAVGLALE EAKVHFDPNI T SRDLIIEA ...String: MEQNGENHLK DPLLQADGGG SGASPAGASP RKERKTRKVM FNVRGISCAS CAVSIETVVA GLKGVESVSV SPLQGQAVVQ YRPEEADAR TIKEAIEGLN FEVDELQEQE IAVCRLQIKG MACTSCSESV ERALQMVPGV KKAAVGLALE EAKVHFDPNI T SRDLIIEA IEDAGFGADL ISSGDDVNKV HLKLEGVSSP EDIKLIQSRL ESVEGVNNVE CDTAGQTIIV AYDPDVTGPR LL IQCIQDA AQPPKYFNAS LYSPPKQREA ERHHEIRNYR NQFLWSCLFS VPVFMFSMVL PMISPFGDWL FYKVCNNMTI GML LRWLLC SPVQFIIGWR FYVGAYHALK RGYSNMDVLV ALGTNAAYFY SVYIVLKALT SESFEGQDFF ETSAMLISFI LLGK YLEVV AKGKTSDALS KLTELAPETA CLLTLDKDGN AISETEISTQ LLQRNDVIKI VPGEKVPVDG VVIKGQSHVN ESMIT GEAR PIAKKPGDKV IGGTVNDNGC IIVKVTHVGS ETALSQIVQL VEAAQLARAP VQKLADRISR FFVPTVVVAA FLTWLG WFV AGQFDIYPRE WIPKAMDSFE LALQFGISVL VVACPCALGL ATPTAVMVAT GKGASQGVLI KGGNALEKAH KVKAIIF (BFD)K TGTLTVGKPS VVQTKVFSKI PLLELCDLAA GAEANSEHPL SKAIVEYTKK LREQYGSHSD HIMESKDFEV HPGA GVSAN VEGKLVLVGN KRLMQEFEVP ISSEVEGHMS ETEELARTCV LVAIDRTICG ALSVSDPLKP EAGRAISYLS SMGIS SIMV TGDNWATAKS IAKEVGIGTV FAEIDPVGKA EKIKDLQMKG LTVAMVGDGI NDSPALAAAD VGLAIGAGTD VAIEAA DIV LMRSSLEDVI TAIDLSRKTL SRIRLNYVWA LGYNVLGMPV AAGVLFPFTG IRLPPWLAGA CMAASSVSVV CSSLLLQ LY KKPLHVEEVA AGPKNDPDLV UniProtKB: Copper-transporting ATPase HMA4 |
-Macromolecule #2: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 2.5 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)