[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1667: Cryo-EM structure of the active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to the p... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1667 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
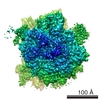
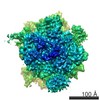
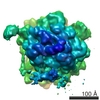
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to the programmed yeast 80S ribosome bearing a P-site tRNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | This map represents a yeast 80S ribosome bearing a nascent chain of the first 120 amino acid of the type I signal anchor membrane protein DPAP-B, a tRNA in the P-site and the yeast Ssh complex bound at the exit tunnel. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome / protein exit tunnel / cotranslational protein translocation / protein conducting channel / signal sequence | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranslocon complex / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / signal sequence binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / nuclear inner membrane ...translocon complex / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / signal sequence binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / nuclear inner membrane / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / preribosome, large subunit precursor / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / protein transmembrane transporter activity / regulation of translational fidelity / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosome binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / mRNA binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / structural molecule activity / endoplasmic reticulum / RNA binding / membrane / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 8.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Becker T / Mandon E / Bhushan S / Jarasch A / Armache JP / Funes S / Jossinet F / Gumbart J / Mielke T / Berninghausen O ...Becker T / Mandon E / Bhushan S / Jarasch A / Armache JP / Funes S / Jossinet F / Gumbart J / Mielke T / Berninghausen O / Schulten K / Westhof E / Gilmore R / Beckmann R | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2009 Journal: Science / Year: 2009Title: Structure of monomeric yeast and mammalian Sec61 complexes interacting with the translating ribosome. Authors: Thomas Becker / Shashi Bhushan / Alexander Jarasch / Jean-Paul Armache / Soledad Funes / Fabrice Jossinet / James Gumbart / Thorsten Mielke / Otto Berninghausen / Klaus Schulten / Eric ...Authors: Thomas Becker / Shashi Bhushan / Alexander Jarasch / Jean-Paul Armache / Soledad Funes / Fabrice Jossinet / James Gumbart / Thorsten Mielke / Otto Berninghausen / Klaus Schulten / Eric Westhof / Reid Gilmore / Elisabet C Mandon / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: The trimeric Sec61/SecY complex is a protein-conducting channel (PCC) for secretory and membrane proteins. Although Sec complexes can form oligomers, it has been suggested that a single copy may ...The trimeric Sec61/SecY complex is a protein-conducting channel (PCC) for secretory and membrane proteins. Although Sec complexes can form oligomers, it has been suggested that a single copy may serve as an active PCC. We determined subnanometer-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of eukaryotic ribosome-Sec61 complexes. In combination with biochemical data, we found that in both idle and active states, the Sec complex is not oligomeric and interacts mainly via two cytoplasmic loops with the universal ribosomal adaptor site. In the active state, the ribosomal tunnel and a central pore of the monomeric PCC were occupied by the nascent chain, contacting loop 6 of the Sec complex. This provides a structural basis for the activity of a solitary Sec complex in cotranslational protein translocation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1667.map.gz emd_1667.map.gz | 18.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1667-v30.xml emd-1667-v30.xml emd-1667.xml emd-1667.xml | 12.4 KB 12.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1667.gif 1667.gif 1667_EMD_1667_active_yeast.jpg 1667_EMD_1667_active_yeast.jpg | 97.1 KB 232.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1667 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1667 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1667 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1667 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2ww9MC  3izdM  1651C  1652C  1668C  1669C  2wwaC  2wwbC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1667.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 185.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1667.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 185.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | This map represents a yeast 80S ribosome bearing a nascent chain of the first 120 amino acid of the type I signal anchor membrane protein DPAP-B, a tRNA in the P-site and the yeast Ssh complex bound at the exit tunnel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2375 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
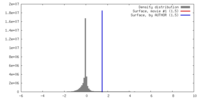
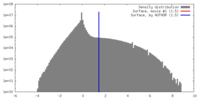
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : An active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to a translating yeast ribosome
| Entire | Name: An active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to a translating yeast ribosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: An active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to a translating yeast ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: An active yeast Ssh1 complex bound to a translating yeast ribosome type: sample / ID: 1000 Details: 80S ribosomes and the detergent solubilized Ssh1 complex were reconstituted in vitro by adding 1 pmol of ribosome and Ssh1 complex in 5 fold molar excess Oligomeric state: 80S Ribosome bound to one copy of the heterotrimeric Ssh1 complex Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 4.2 MDa / Theoretical: 4.2 MDa / Method: Known for 80S ribosomes |
-Supramolecule #1: Yeast 80S ribosome bound to the yeast Ssh1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Yeast 80S ribosome bound to the yeast Ssh1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 Name.synonym: Yeast 80S ribosome bound to the yeast Ssh1 complex Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 4.2 MDa / Theoretical: 4.2 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Ssh1 complex
| Macromolecule | Name: Ssh1 complex / type: ligand / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Ssh1 complex / Details: His FLAG-tagged / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Heterotrimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.5 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM HEPES/KOH, pH 7.5 100 mM KOAc, 10 mM Mg(OAc)2, 1.5 mM DTT, 0.1 % (w/v) digitonin |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: cryo-EM |
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil grids (3/3) with 2 nm carbon on top |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Instrument: OTHER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Vitrobot Method: Blot for 10 seconds before plunging, use 2 layer of filter paper |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 84 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 100000 times magnification |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: PRIMESCAN / Digitization - Sampling interval: 4.76 µm / Number real images: 185 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Details: Scanned at 5334 dpi / Od range: 1.2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Tilt angle max | 0 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 38000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.26 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: FEI Polara cartridge system / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | Particles were selected using the program SIGNATURE and visually inspected. This map resulted from sorting against the ES27 exit position and subsequent sorting for tRNA and the Ssh1 complex. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: defocus group volumes |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 8.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER Details: Map was filtered between 8.3 and 10.3 Angstrom to better visualize the Ssh1 complex Number images used: 35800 |
| Final angle assignment | Details: SPIDER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


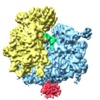
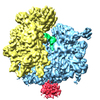








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)