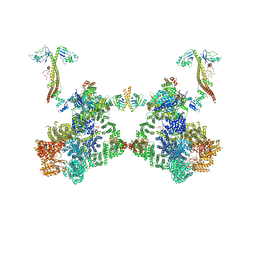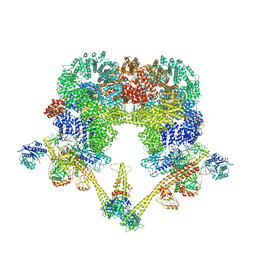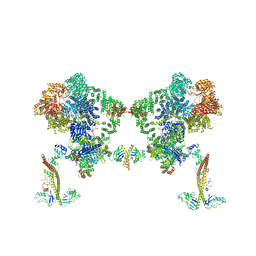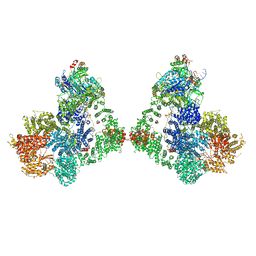+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | DNA-PK Ku80 mediated dimer bound to PAXX | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | DNA-PK / DNA-PKcs / Ku70 / Ku80 / PAXX / NHEJ / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報FHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / positive regulation of platelet formation / DNA ligase activity / Ku70:Ku80 complex / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / negative regulation of t-circle formation / DNA ligase (ATP) ...FHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / positive regulation of platelet formation / DNA ligase activity / Ku70:Ku80 complex / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / negative regulation of t-circle formation / DNA ligase (ATP) / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / DNA end binding / pro-B cell differentiation / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / nonhomologous end joining complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / immature B cell differentiation / single strand break repair / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / cellular response to X-ray / V(D)J recombination / nuclear telomere cap complex / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / protein localization to site of double-strand break / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / telomere capping / isotype switching / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / positive regulation of neurogenesis / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / regulation of telomere maintenance / recombinational repair / U3 snoRNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / DNA biosynthetic process / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / T cell lineage commitment / cellular response to lithium ion / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / 2-LTR circle formation / telomeric DNA binding / B cell lineage commitment / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / ligase activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / site of DNA damage / 付加脱離酵素(リアーゼ); 炭素-酸素リアーゼ類; その他の炭素-酸素リアーゼ / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / response to X-ray / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / chromosome organization / telomere maintenance via telomerase / somitogenesis / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / neurogenesis / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / cellular response to ionizing radiation / telomere maintenance / activation of innate immune response / DNA helicase activity / cyclin binding / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of translation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / central nervous system development / stem cell proliferation / response to gamma radiation / small-subunit processome / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / enzyme activator activity / cellular response to gamma radiation / regulation of circadian rhythm / protein destabilization / protein-DNA complex / base-excision repair / brain development / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / protein modification process / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / 加水分解酵素; 酸無水物に作用; 酸無水物に作用・細胞または細胞小器官の運動に関与 / establishment of integrated proviral latency / cellular response to insulin stimulus 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.55 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Hardwick SW / Chaplin AK | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  英国, 1件 英国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Sci Adv / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: Sci Adv / 年: 2023タイトル: PAXX binding to the NHEJ machinery explains functional redundancy with XLF. 著者: Seif-El-Dahan M / Kefala-Stavridi A / Frit P / Hardwick SW / Chirgadze DY / Maia De Oliviera T / Britton S / Barboule N / Bossaert M / Pandurangan AP / Meek K / Blundell TL / Ropars V / ...著者: Seif-El-Dahan M / Kefala-Stavridi A / Frit P / Hardwick SW / Chirgadze DY / Maia De Oliviera T / Britton S / Barboule N / Bossaert M / Pandurangan AP / Meek K / Blundell TL / Ropars V / Calsou P / Charbonnier JB / Chaplin AK | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_16044.map.gz emd_16044.map.gz | 557.3 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-16044-v30.xml emd-16044-v30.xml emd-16044.xml emd-16044.xml | 33 KB 33 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_16044_fsc.xml emd_16044_fsc.xml | 24.8 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_16044.png emd_16044.png | 67.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16044.cif.gz emd-16044.cif.gz | 11.4 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_16044_additional_1.map.gz emd_16044_additional_1.map.gz emd_16044_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16044_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16044_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16044_half_map_2.map.gz | 558.3 MB 557.4 MB 557.4 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16044 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16044 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16044 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16044 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_16044_validation.pdf.gz emd_16044_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_16044_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16044_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_16044_validation.xml.gz emd_16044_validation.xml.gz | 26.6 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_16044_validation.cif.gz emd_16044_validation.cif.gz | 35.8 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16044 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16044 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16044 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16044 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_16044.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 600.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_16044.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 600.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.304 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
+全体 : NHEJ supercomplex bound to PAXX
+超分子 #1: NHEJ supercomplex bound to PAXX
+分子 #1: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
+分子 #2: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6
+分子 #3: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5
+分子 #4: Protein PAXX
+分子 #5: DNA repair protein XRCC4
+分子 #6: DNA ligase 4
+分子 #7: DNA (25-MER)
+分子 #8: DNA (27-MER)
+分子 #9: DNA (26-MER)
+分子 #10: DNA (28-MER)
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
| グリッド | モデル: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / 前処理 - タイプ: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 52.1 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | C2レンズ絞り径: 50.0 µm / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.5 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.8 µm / 倍率(公称値): 130000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー