+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | In situ cryo-electron tomogram of a T. kivui cell 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | Cryo-electron tomogram of a T. kivui cell showing HDCR filament bundles. Tomogram was denoised using CRYO-CARE. | ||||||||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |   Thermoanaerobacter kivui (バクテリア) Thermoanaerobacter kivui (バクテリア) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 手法 | 電子線トモグラフィー法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 | ||||||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Dietrich HM / Righetto RD / Kumar A / Wietrzynski W / Schuller SK / Trischler R / Wagner J / Schwarz FM / Engel BD / Mueller V / Schuller JM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  ドイツ, European Union, 5件 ドイツ, European Union, 5件
| ||||||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2022タイトル: Membrane-anchored HDCR nanowires drive hydrogen-powered CO fixation. 著者: Helge M Dietrich / Ricardo D Righetto / Anuj Kumar / Wojciech Wietrzynski / Raphael Trischler / Sandra K Schuller / Jonathan Wagner / Fabian M Schwarz / Benjamin D Engel / Volker Müller / Jan M Schuller /   要旨: Filamentous enzymes have been found in all domains of life, but the advantage of filamentation is often elusive. Some anaerobic, autotrophic bacteria have an unusual filamentous enzyme for CO ...Filamentous enzymes have been found in all domains of life, but the advantage of filamentation is often elusive. Some anaerobic, autotrophic bacteria have an unusual filamentous enzyme for CO fixation-hydrogen-dependent CO reductase (HDCR)-which directly converts H and CO into formic acid. HDCR reduces CO with a higher activity than any other known biological or chemical catalyst, and it has therefore gained considerable interest in two areas of global relevance: hydrogen storage and combating climate change by capturing atmospheric CO. However, the mechanistic basis of the high catalytic turnover rate of HDCR has remained unknown. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the structure of a short HDCR filament from the acetogenic bacterium Thermoanaerobacter kivui. The minimum repeating unit is a hexamer that consists of a formate dehydrogenase (FdhF) and two hydrogenases (HydA2) bound around a central core of hydrogenase Fe-S subunits, one HycB3 and two HycB4. These small bacterial polyferredoxin-like proteins oligomerize through their C-terminal helices to form the backbone of the filament. By combining structure-directed mutagenesis with enzymatic analysis, we show that filamentation and rapid electron transfer through the filament enhance the activity of HDCR. To investigate the structure of HDCR in situ, we imaged T. kivui cells with cryo-electron tomography and found that HDCR filaments bundle into large ring-shaped superstructures attached to the plasma membrane. This supramolecular organization may further enhance the stability and connectivity of HDCR to form a specialized metabolic subcompartment within the cell. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_15055.map.gz emd_15055.map.gz | 1.4 GB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-15055-v30.xml emd-15055-v30.xml emd-15055.xml emd-15055.xml | 14.2 KB 14.2 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_15055.png emd_15055.png | 313.8 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_15055_additional_1.map.gz emd_15055_additional_1.map.gz | 1.4 GB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15055 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15055 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_15055_validation.pdf.gz emd_15055_validation.pdf.gz | 491.4 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_15055_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_15055_full_validation.pdf.gz | 491 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_15055_validation.xml.gz emd_15055_validation.xml.gz | 4.5 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_15055_validation.cif.gz emd_15055_validation.cif.gz | 5 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-15055 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-15055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-15055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-15055 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_15055.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 1.5 GB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_15055.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 1.5 GB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Cryo-electron tomogram of a T. kivui cell showing HDCR filament bundles. Tomogram was denoised using CRYO-CARE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
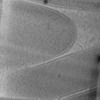
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 これらの図は立方格子座標系で作成されたものです | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 14.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
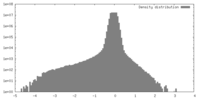
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-追加マップ: Cryo-electron tomogram of a T. kivui cell showing...
| ファイル | emd_15055_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Cryo-electron tomogram of a T. kivui cell showing HDCR filament bundles. Original reconstruction from IMOD. | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
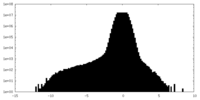
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : T. kivui cell
| 全体 | 名称: T. kivui cell |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: T. kivui cell
| 超分子 | 名称: T. kivui cell / タイプ: cell / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:   Thermoanaerobacter kivui (バクテリア) Thermoanaerobacter kivui (バクテリア) |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 電子線トモグラフィー法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | cell |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| グリッド | モデル: Quantifoil R2/1 / 材質: COPPER / 支持フィルム - 材質: CARBON / 支持フィルム - トポロジー: HOLEY / 前処理 - タイプ: GLOW DISCHARGE / 前処理 - 雰囲気: AIR |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE-PROPANE / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| 切片作成 | 集束イオンビーム - 装置: OTHER / 集束イオンビーム - イオン: OTHER / 集束イオンビーム - 電圧: 30 kV / 集束イオンビーム - 電流: 0.03 nA / 集束イオンビーム - 時間: 1800 sec. / 集束イオンビーム - 温度: 91 K / 集束イオンビーム - Initial thickness: 2000 nm / 集束イオンビーム - 最終 厚さ: 150 nm 集束イオンビーム - 詳細: See https://bio-protocol.org/e1575 for detailed procedure.. The value given for _emd_sectioning_focused_ion_beam.instrument is FEI Aquilos FIB. This is not in a ...集束イオンビーム - 詳細: See https://bio-protocol.org/e1575 for detailed procedure.. The value given for _emd_sectioning_focused_ion_beam.instrument is FEI Aquilos FIB. This is not in a list of allowed values {'DB235', 'OTHER'} so OTHER is written into the XML file. |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 特殊光学系 | エネルギーフィルター - 名称: GIF Quantum LS / エネルギーフィルター - スリット幅: 20 eV |
| 詳細 | Dose-symmetric tilt-series were acquired (Hagen et al., 2017), starting at +10 degrees to match the pre-tilt of the lamella (i.e. from -50 to +70 degrees). |
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 検出モード: COUNTING / 平均電子線量: 1.2 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 5.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 3.5 µm / 倍率(公称値): 42000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 最終 再構成 | アルゴリズム: BACK PROJECTION / ソフトウェア - 名称:  IMOD / 使用した粒子像数: 60 IMOD / 使用した粒子像数: 60 |
|---|---|
| CTF補正 | ソフトウェア: (名称: CTFFIND (ver. 4),  IMOD, NOVACTF) IMOD, NOVACTF) |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)