[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-15043: Infectious mouse-adapted ME7 scrapie prion fibril purified from t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Infectious mouse-adapted ME7 scrapie prion fibril purified from terminally-infected mouse brains | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Prion / PROTEIN FIBRIL | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInsertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / lamin binding / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / ATP-dependent protein binding ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / lamin binding / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / ATP-dependent protein binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / cupric ion binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / response to amyloid-beta / negative regulation of type II interferon production / cuprous ion binding / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane / inclusion body / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / molecular function activator activity / cellular response to copper ion / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / molecular condensate scaffold activity / protein homooligomerization / protein destabilization / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / cellular response to amyloid-beta / terminal bouton / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / signaling receptor activity / protein-folding chaperone binding / regulation of protein localization / amyloid-beta binding / response to oxidative stress / protease binding / nuclear membrane / microtubule binding / molecular adaptor activity / transmembrane transporter binding / learning or memory / intracellular signal transduction / postsynaptic density / membrane raft / copper ion binding / dendrite / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||
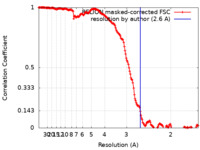
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Manka SW / Wenborn A / Betts J / Joiner S / Saibil HR / Collinge J / Wadsworth JDF | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 5 items United Kingdom, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2023Title: A structural basis for prion strain diversity. Authors: Szymon W Manka / Adam Wenborn / Jemma Betts / Susan Joiner / Helen R Saibil / John Collinge / Jonathan D F Wadsworth /  Abstract: Recent cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) studies of infectious, ex vivo, prion fibrils from hamster 263K and mouse RML prion strains revealed a similar, parallel in-register intermolecular β- ...Recent cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) studies of infectious, ex vivo, prion fibrils from hamster 263K and mouse RML prion strains revealed a similar, parallel in-register intermolecular β-sheet (PIRIBS) amyloid architecture. Rungs of the fibrils are composed of individual prion protein (PrP) monomers that fold to create distinct N-terminal and C-terminal lobes. However, disparity in the hamster/mouse PrP sequence precludes understanding of how divergent prion strains emerge from an identical PrP substrate. In this study, we determined the near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of infectious, ex vivo mouse prion fibrils from the ME7 prion strain and compared this with the RML fibril structure. This structural comparison of two biologically distinct mouse-adapted prion strains suggests defined folding subdomains of PrP rungs and the way in which they are interrelated, providing a structural definition of intra-species prion strain-specific conformations. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2023 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2023Title: A structural basis for prion strain diversity Authors: Manka SW / Wenborn A / Betts J / Joiner S / Saibil HR / Collinge J / Wadsworth JDF | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15043.map.gz emd_15043.map.gz | 19.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15043-v30.xml emd-15043-v30.xml emd-15043.xml emd-15043.xml | 15.7 KB 15.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_15043_fsc.xml emd_15043_fsc.xml | 17 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
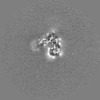
| Images |  emd_15043.png emd_15043.png | 109.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-15043.cif.gz emd-15043.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_15043_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15043_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15043_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15043_half_map_2.map.gz | 337.6 MB 337.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15043 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15043 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15043 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15043 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8a00MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15043.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15043.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
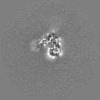
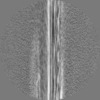
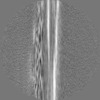
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
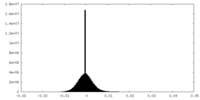
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_15043_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_15043_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : amyloid fibril of prion protein
| Entire | Name: amyloid fibril of prion protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: amyloid fibril of prion protein
| Supramolecule | Name: amyloid fibril of prion protein / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Major prion protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Major prion protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.77663 KDa |
| Sequence | String: THNQWNKPSK PKTNLKHVAG AAAAGAVVGG LGGYMLGSAM SRPMIHFGND WEDRYYRENM YRYPNQVYYR PVDQYSNQNN FVHDCVNIT IKQHTVTTTT KGENFTETDV KMMERVVEQM CVTQYQKESQ AYYDGRR UniProtKB: Major prion protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 49.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8a00: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)