[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-14755: ABCB1 L335C mutant (mABCB1) in the outward facing state bound to AAC -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ABCB1 L335C mutant (mABCB1) in the outward facing state bound to AAC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ABC transporter / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationAtorvastatin ADME / Prednisone ADME / hormone transport / cellular response to nonylphenol / cellular response to borneol / response to codeine / cellular response to mycotoxin / daunorubicin transport / positive regulation of response to drug / terpenoid transport ...Atorvastatin ADME / Prednisone ADME / hormone transport / cellular response to nonylphenol / cellular response to borneol / response to codeine / cellular response to mycotoxin / daunorubicin transport / positive regulation of response to drug / terpenoid transport / ceramide floppase activity / negative regulation of sensory perception of pain / positive regulation of establishment of Sertoli cell barrier / regulation of intestinal absorption / response to cyclosporin A / cellular response to external biotic stimulus / response to quercetin / response to antineoplastic agent / floppase activity / ceramide translocation / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / establishment of blood-retinal barrier / protein localization to bicellular tight junction / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / phosphatidylcholine floppase activity / xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier / response to thyroxine / establishment of blood-brain barrier / intercellular canaliculus / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the plasma membrane / export across plasma membrane / P-type phospholipid transporter / cellular response to L-glutamate / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter / response to vitamin A / response to vitamin D / response to glucagon / response to alcohol / intestinal absorption / response to glycoside / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity / phospholipid translocation / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / cellular response to alkaloid / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / cellular response to antibiotic / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / transmembrane transporter activity / response to cadmium ion / lactation / response to progesterone / placenta development / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / brush border membrane / female pregnancy / circadian rhythm / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / response to hypoxia / apical plasma membrane / response to xenobiotic stimulus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Parey K / Januliene D / Gewering T / Moeller A / Vecchis D / Striednig B / Hilbi H / Schaefer LV / Kuprov I / Bordignon E / Seeger MA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: Tracing the substrate translocation mechanism in P-glycoprotein. Authors: Theresa Gewering / Deepali Waghray / Kristian Parey / Hendrik Jung / Nghi N B Tran / Joel Zapata / Pengyi Zhao / Hao Chen / Dovile Januliene / Gerhard Hummer / Ina Urbatsch / Arne Moeller / Qinghai Zhang /   Abstract: P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is a prototypical ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter of great biological and clinical significance.Pgp confers cancer multidrug resistance and mediates the bioavailability ...P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is a prototypical ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter of great biological and clinical significance.Pgp confers cancer multidrug resistance and mediates the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of many drugs (Juliano and Ling, 1976; Ueda et al., 1986; Sharom, 2011). Decades of structural and biochemical studies have provided insights into how Pgp binds diverse compounds (Loo and Clarke, 2000; Loo et al., 2009; Aller et al., 2009; Alam et al., 2019; Nosol et al., 2020; Chufan et al., 2015), but how they are translocated through the membrane has remained elusive. Here, we covalently attached a cyclic substrate to discrete sites of Pgp and determined multiple complex structures in inward- and outward-facing states by cryoEM. In conjunction with molecular dynamics simulations, our structures trace the substrate passage across the membrane and identify conformational changes in transmembrane helix 1 (TM1) as regulators of substrate transport. In mid-transport conformations, TM1 breaks at glycine 72. Mutation of this residue significantly impairs drug transport of Pgp in vivo, corroborating the importance of its regulatory role. Importantly, our data suggest that the cyclic substrate can exit Pgp without the requirement of a wide-open outward-facing conformation, diverting from the common efflux model for Pgp and other ABC exporters. The substrate transport mechanism of Pgp revealed here pinpoints critical targets for future drug discovery studies of this medically relevant system. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14755.map.gz emd_14755.map.gz | 78.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14755-v30.xml emd-14755-v30.xml emd-14755.xml emd-14755.xml | 22.3 KB 22.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14755_fsc.xml emd_14755_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14755.png emd_14755.png | 59 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_14755_msk_1.map emd_14755_msk_1.map | 83.7 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14755.cif.gz emd-14755.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_14755_additional_1.map.gz emd_14755_additional_1.map.gz emd_14755_additional_2.map.gz emd_14755_additional_2.map.gz emd_14755_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14755_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14755_half_map_2.map.gz emd_14755_half_map_2.map.gz | 41.4 MB 77.8 MB 77.8 MB 77.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14755 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14755 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14755 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14755 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7zk5MC 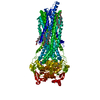 7zk4C 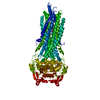 7zk6C  7zk8C  7zk9C  7zkaC  7zkbC  8avyC  8peeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14755.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14755.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.837 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_14755_msk_1.map emd_14755_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: unsharpened map
| File | emd_14755_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: density modified map
| File | emd_14755_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | density modified map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_14755_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_14755_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ABCB1
| Entire | Name: ABCB1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ABCB1
| Supramolecule | Name: ABCB1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 140 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ABC-type xenobiotic transporter |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 146.063859 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) |
| Sequence | String: MELEEDLKGR ADKNFSKMGK KSKKEKKEKK PAVSVLTMFR YAGWLDRLYM LVGTLAAIIH GVALPLMMLI FGDMTDSFAS VGQVSKQST QMSEADKRAM FAKLEEEMTT YAYYYTGIGA GVLIVAYIQV SFWALAAGRQ IHKIRQKFFH AIMNQEIGWF D VHDVGELN ...String: MELEEDLKGR ADKNFSKMGK KSKKEKKEKK PAVSVLTMFR YAGWLDRLYM LVGTLAAIIH GVALPLMMLI FGDMTDSFAS VGQVSKQST QMSEADKRAM FAKLEEEMTT YAYYYTGIGA GVLIVAYIQV SFWALAAGRQ IHKIRQKFFH AIMNQEIGWF D VHDVGELN TRLTDDVSKI NEGIGDKIGM FFQAMATFFG GFIIGFTRGW KLTLVILAIS PVLGLSAGIW AKILSSFTDK EL HAYAKAG AVAEEVLAAI RTVIAFGGQK KELERYNNNL EEAKRLGIKK AITANISMGA AFLLIYASYA LAFWYGTSLV ISK EYSIGQ VLTVFFSVCI GAFSVGQASP NIEAFANARG AAYEVFKIID NKPSIDSFSK SGHKPDNIQG NLEFKNIHFS YPSR KEVQI LKGLNLKVKS GQTVALVGNS GGGKSTTVQL MQRLYDPLDG MVSIDGQDIR TINVRYLREI IGVVSQEPVL FATTI AENI RYGREDVTMD EIEKAVKEAN AYDFIMKLPH QFDTLVGERG AQLSGGQKQR IAIARALVRN PKILLLDEAT SALDTE SEA VVQAALDKAR EGRTTIVIAH RLSTVRNADV IAGFDGGVIV EQGNHDELMR EKGIYFKLVM TQTAGNEIEL GNEAGKS KD EIDNLDMSSK DSGSSLIRRR STRKSITGPH DQDRKLSTKE ALDEDVPPAS FWRILKLNST EWPYFVVGIF AAIINGGL Q PAFSVIFSKV VGVFTNGGPP ETQRQNSNLF SLLFLILGII SFITFFLQGF TFGKAGEILT KRLRYMVFKS MLRQDVSWF DDPKNTTGAL TTRLANDAAQ VKGATGSRLA VIFQNIANLG TGIIISLIYG WQLTLLLLAI VPIIAIAGVV EMKMLSGQAL KDKKELEGS GKIATEAIEN FRTVVSLTRE QKFETMYAQS LQIPYRNAMK KAHVFGITFS FTQAMMYFSY AAAFRFGAYL V TQQLMTFE NVLLVFSAIV FGAMAVGQVS SFAPDYAKAT VSASHIIRII EKTPEIDSYS TQGLKPNMLE GNVQFSGVVF NY PTRPSIP VLQGLSLEVK KGQTLALVGS SGGGKSTVVQ LLERFYDPMA GSVFLDGKEI KQLNVQWLRA QLGIVSQEPI LFD RSIAEN IAYGDNSRVV SYEEIVRAAK EANIHQFIDS LPDKYNTRVG DKGTQLSGGQ KQRIAIARAL VRQPHILLLD EATS ALDTE SEKVVQEALD KAREGRTVIV IAHRLSTIQN ADLIVVIQNG KVKEHGTHQQ LLAQKGIYFS MVSVQAGAKR SLEEN LYFQ GGGASGGSWS HPQFEKAAAG GGSGGGSWSH PQFEKGSGHH HHHH UniProtKB: ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Macromolecule #5: (4~{S},11~{S},18~{S})-4,11-dimethyl-18-(sulfanylmethyl)-6,13,20-t...
| Macromolecule | Name: (4~{S},11~{S},18~{S})-4,11-dimethyl-18-(sulfanylmethyl)-6,13,20-trithia-3,10,17,22,23,24-hexazatetracyclo[17.2.1.1^{5,8}.1^{12,15}]tetracosa-1(21),5(24),7,12(23),14,19(22)-hexaene-2,9,16-trione type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: JIZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 494.634 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-JIZ: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 33 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Material: COPPER |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 75.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)