+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | 3D reconstruction of the membrane domains of the sialic acid TRAP transporter HiSiaQM from Haemophilus influenzae in lipid nanodiscs bound to a high affinity megabody | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | 3D reconstruction of HiSiaQM with a megabody bound to the periplasmic side | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | membrane transporter / TRAP / sialic acid / elevator / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 | TRAP transporter large membrane protein DctM / TRAP C4-dicarboxylate transport system permease DctM subunit / : / Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporters, DctQ component / Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter, DctM component / transmembrane transporter activity / plasma membrane / Sialic acid TRAP transporter permease protein SiaT 機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌) / Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌) /  | |||||||||
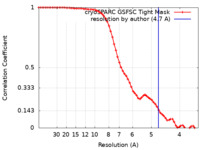
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.7 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Peter MF / Hagelueken G | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  ドイツ, 2件 ドイツ, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2022タイトル: Structural and mechanistic analysis of a tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic TRAP transporter. 著者: Martin F Peter / Jan A Ruland / Peer Depping / Niels Schneberger / Emmanuele Severi / Jonas Moecking / Karl Gatterdam / Sarah Tindall / Alexandre Durand / Veronika Heinz / Jan Peter Siebrasse ...著者: Martin F Peter / Jan A Ruland / Peer Depping / Niels Schneberger / Emmanuele Severi / Jonas Moecking / Karl Gatterdam / Sarah Tindall / Alexandre Durand / Veronika Heinz / Jan Peter Siebrasse / Paul-Albert Koenig / Matthias Geyer / Christine Ziegler / Ulrich Kubitscheck / Gavin H Thomas / Gregor Hagelueken /    要旨: Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters are found widely in bacteria and archaea and consist of three structural domains, a soluble substrate-binding protein (P-domain), and two ...Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters are found widely in bacteria and archaea and consist of three structural domains, a soluble substrate-binding protein (P-domain), and two transmembrane domains (Q- and M-domains). HiSiaPQM and its homologs are TRAP transporters for sialic acid and are essential for host colonization by pathogenic bacteria. Here, we reconstitute HiSiaQM into lipid nanodiscs and use cryo-EM to reveal the structure of a TRAP transporter. It is composed of 16 transmembrane helices that are unexpectedly structurally related to multimeric elevator-type transporters. The idiosyncratic Q-domain of TRAP transporters enables the formation of a monomeric elevator architecture. A model of the tripartite PQM complex is experimentally validated and reveals the coupling of the substrate-binding protein to the transporter domains. We use single-molecule total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy in solid-supported lipid bilayers and surface plasmon resonance to study the formation of the tripartite complex and to investigate the impact of interface mutants. Furthermore, we characterize high-affinity single variable domains on heavy chain (VHH) antibodies that bind to the periplasmic side of HiSiaQM and inhibit sialic acid uptake, providing insight into how TRAP transporter function might be inhibited in vivo. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_13930.map.gz emd_13930.map.gz | 25.5 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-13930-v30.xml emd-13930-v30.xml emd-13930.xml emd-13930.xml | 16.9 KB 16.9 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_13930_fsc.xml emd_13930_fsc.xml | 6.3 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_13930.png emd_13930.png | 33.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13930.cif.gz emd-13930.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_13930_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13930_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13930_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13930_half_map_2.map.gz | 25.1 MB 25.1 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13930 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13930 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_13930_validation.pdf.gz emd_13930_validation.pdf.gz | 712.1 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_13930_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13930_full_validation.pdf.gz | 711.6 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_13930_validation.xml.gz emd_13930_validation.xml.gz | 13.3 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_13930_validation.cif.gz emd_13930_validation.cif.gz | 16.9 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13930 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13930 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  7qe5MC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_13930.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 27 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_13930.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 27 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
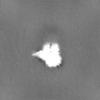
| 注釈 | 3D reconstruction of HiSiaQM with a megabody bound to the periplasmic side | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.72 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: Half map B
| ファイル | emd_13930_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
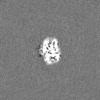
| 注釈 | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
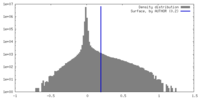
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half map B
| ファイル | emd_13930_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : HiSiaQM/Megabody complex
| 全体 | 名称: HiSiaQM/Megabody complex |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: HiSiaQM/Megabody complex
| 超分子 | 名称: HiSiaQM/Megabody complex / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌) Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌) |
-分子 #1: Sialic acid TRAP transporter permease protein SiaT
| 分子 | 名称: Sialic acid TRAP transporter permease protein SiaT / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌) Haemophilus influenzae (インフルエンザ菌)株: ATCC 51907 / DSM 11121 / KW20 / Rd |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 67.63607 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MKYINKLEEW LGGALFIAIF GILIAQILSR QVFHSPLIWS EELAKLLFVY VGMLGISVAV RKQEHVFIDF LTNLMPEKIR KFTNTFVQL LVFICIFLFI HFGIRTFNGA SFPIDALGGI SEKWIFAALP VVAILMMFRF IQAQTLNFKT GKSYLPATFF I ISAVILFA ...文字列: MKYINKLEEW LGGALFIAIF GILIAQILSR QVFHSPLIWS EELAKLLFVY VGMLGISVAV RKQEHVFIDF LTNLMPEKIR KFTNTFVQL LVFICIFLFI HFGIRTFNGA SFPIDALGGI SEKWIFAALP VVAILMMFRF IQAQTLNFKT GKSYLPATFF I ISAVILFA ILFFAPDWFK VLRISNYIKL GSSSVYVALL VWLIIMFIGV PVGWSLFIAT LLYFSMTRWN VVNAATEKLV YS LDSFPLL AVPFYILTGI LMNTGGITER IFNFAKALLG HYTGGMGHVN IGASLLFSGM SGSALADAGG LGQLEIKAMR DAG YDDDIC GGITAASCII GPLVPPSIAM IIYGVIANES IAKLFIAGFI PGVLITLALM AMNYRIAKKR GYPRTPKATR EQLC SSFKQ SFWAILTPLL IIGGIFSGLF SPTESAIVAA AYSVIIGKFV YKELTLKSLF NSCIEAMAIT GVVALMIMTV TFFGD MIAR EQVAMRVADV FVAVADSPLT VLIMINALLL FLGMFIDALA LQFLVLPMLI PIAMQFNIDL IFFGVMTTLN MMVGIL TPP MGMALFVVAR VGNMSVSTVT KGVLPFLIPV FVTLVLITIF PQIITFVPNL LIP UniProtKB: Sialic acid TRAP transporter permease protein SiaT |
-分子 #2: Megabody3
| 分子 | 名称: Megabody3 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 61.534348 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MQILFQGDSH NEIPIAYGSR WIVITRGPAG HGQVQLVESG GGLVQTKTTT SVIDTTNDAQ NLLTQAQTIV NTLKDYCPIL IAKSSSSNG GTNNANTPSW QTAGGGKNSC ATFGAEFSAA SDMINNAQKI VQETQQLSAN QPKNITQPHN LNLNSPSSLT A LAQKMLKN ...文字列: MQILFQGDSH NEIPIAYGSR WIVITRGPAG HGQVQLVESG GGLVQTKTTT SVIDTTNDAQ NLLTQAQTIV NTLKDYCPIL IAKSSSSNG GTNNANTPSW QTAGGGKNSC ATFGAEFSAA SDMINNAQKI VQETQQLSAN QPKNITQPHN LNLNSPSSLT A LAQKMLKN AQSQAEILKL ANQVESDFNK LSSGHLKDYI GKCDASAISS ANMTMQNQKN NWGNGCAGVE ETQSLLKTSA AD FNNQTPQ INQAQNLANT LIQELGNNPF RASGGGSGGG GSGKLSDTYE QLSRLLTNDN GTNSKTSAQA INQAVNNLNE RAK TLAGGT TNSPAYQATL LALRSVLGLW NSMGYAVICG GYTKSPGENN QKDFHYTDEN GNGTTINCGG STNSNGTHSY NGTN TLKAD KNVSLSIEQY EKIHEAYQIL SKALKQAGLA PLNSKGEKLE AHVTTSYGSL RLSCTASRVT LDYHDIGWFR QAPGK EREG VSYISSSGGS TNYADSVKGR FTISRDNAKN TVYLQMNSLK PEDTAVYYCA RSSAYGSSWL NPSRYDYWGQ GTQVTV SSG GLPETGGHHH HHH |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 50.213 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.5 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.8 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)