[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
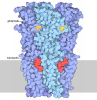
Yorodumi- EMDB-13792: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel, DeCLIC at pH 7 with 10 mM EDTA -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel, DeCLIC at pH 7 with 10 mM EDTA | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / ligand-gated channel / pentameric channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationextracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lycksell M / Rovsnik U | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 3 items Sweden, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Biophysical characterization of calcium-binding and modulatory-domain dynamics in a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Authors: Marie Lycksell / Urška Rovšnik / Anton Hanke / Anne Martel / Rebecca J Howard / Erik Lindahl /    Abstract: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) perform electrochemical signal transduction in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. Among the prokaryotic pLGICs, there is architectural diversity ...Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) perform electrochemical signal transduction in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. Among the prokaryotic pLGICs, there is architectural diversity involving N-terminal domains (NTDs) not found in eukaryotic relatives, exemplified by the calcium-sensitive channel (DeCLIC) from a deltaproteobacterium, which has an NTD in addition to the canonical pLGIC structure. Here, we have characterized the structure and dynamics of DeCLIC through cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. In the presence and absence of calcium, cryo-EM yielded structures with alternative conformations of the calcium-binding site. SANS profiles further revealed conformational diversity at room temperature beyond that observed in static structures, shown through MD to be largely attributable to rigid-body motions of the NTD relative to the protein core, with expanded and asymmetric conformations improving the fit of the SANS data. This work reveals the range of motion available to the DeCLIC NTD and calcium-binding site, expanding the conformational landscape of the pLGIC family. Further, these findings demonstrate the power of combining low-resolution scattering, high-resolution structural, and MD simulation data to elucidate interfacial interactions that are highly conserved in the pLGIC family. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
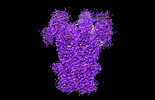
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13792.map.gz emd_13792.map.gz | 9.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13792-v30.xml emd-13792-v30.xml emd-13792.xml emd-13792.xml | 20.3 KB 20.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_13792.png emd_13792.png | 76 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13792_msk_1.map emd_13792_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13792.cif.gz emd-13792.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13792_additional_1.map.gz emd_13792_additional_1.map.gz emd_13792_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13792_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13792_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13792_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.1 MB 49.5 MB 49.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13792 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13792 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13792 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13792 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7q3hMC  7q3gC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13792.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13792.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
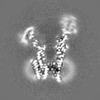
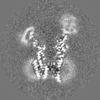
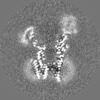
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
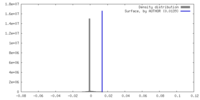
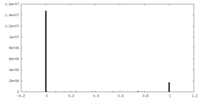
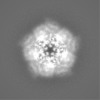
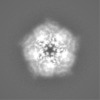
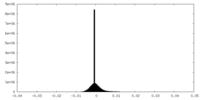
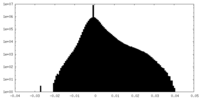
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13792_msk_1.map emd_13792_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
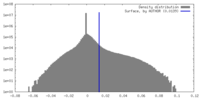
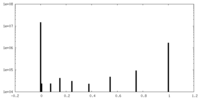
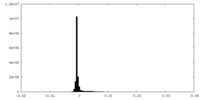
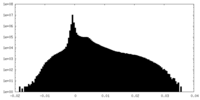
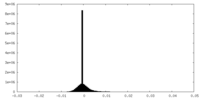
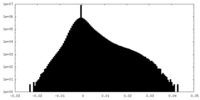
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_13792_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_13792_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_13792_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel DeCLIC
| Entire | Name: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel DeCLIC |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel DeCLIC
| Supramolecule | Name: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channel DeCLIC / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 364.31 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Neur_chan_LBD domain-containing protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Neur_chan_LBD domain-containing protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) Desulfofustis sp. PB-SRB1 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.733992 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHNLQQLLPT RSLIWIFSFL TSISIWCTVA HAETEGRVQH FTGYIEDGRG IFYSLPDMKQ GDIIYASMQN TGGNLDPLVG IMAEEIDPA VSLGQVLEKA LASENDLISE LTAVADRIFL GWDDDGGKGY SASLEFTIPR DGTYHIFAGS TITNQRLDKF Q PTYTTGSF ...String: MHNLQQLLPT RSLIWIFSFL TSISIWCTVA HAETEGRVQH FTGYIEDGRG IFYSLPDMKQ GDIIYASMQN TGGNLDPLVG IMAEEIDPA VSLGQVLEKA LASENDLISE LTAVADRIFL GWDDDGGKGY SASLEFTIPR DGTYHIFAGS TITNQRLDKF Q PTYTTGSF QLILGLNAPQ VISGEGEPEG EVFASLASLE IKPEAHVQEL EIRLDKDTRY LTQHTRNLQP GDTFHALVEP IG EAPLPRL RLTDSGGKPL AFGLIDQPGE SVELNYTCDQ DICELVVHVD GTDGQKDSGE AVYRLLVGIN APNLRESGQT PVG SSVFLE SDLVTVGLAV DQIVGVDQRS ENFSVVGTLK LSWHDPKLGF SPDQCGCTVK SFEDASIRAV AGEINLPLPS FSFY NQQGN RWSQNQVIFV TPDGRASYFE RFTVTLQAPD FDFLAYPFDR QKFSIKVDLA VPTNMFIFNE IERFQQVVGD QLGEE EWVV TSYSQEITEV PFERGSTNSR FTTTLLVKRN LEYYILRIFV PLFLIISVSW VIFFLKDYGR QLEVASGNLL VFVAFN FTI SGDLPRLGYL TVLDRFMIVS FCLTAIVVLI SVCQKRLGAV GKQAVAAQID TWVLVIYPLV YSLYIIWVYL RFFTDHI GW UniProtKB: Uncharacterized protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | 3D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 6.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)