+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13757 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
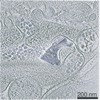
| Title | P. carterae coccolith vesicle with mature base plate | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | P. carterae coccolith vesicle with mature base plate | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Chrysotila carterae (eukaryote) Chrysotila carterae (eukaryote) | |||||||||
| Method | electron tomography / cryo EM | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kadan Y / Mahamid J / Gal A / Tollervey F | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Intracellular nanoscale architecture as a master regulator of calcium carbonate crystallization in marine microalgae. Authors: Yuval Kadan / Fergus Tollervey / Neta Varsano / Julia Mahamid / Assaf Gal /   Abstract: Unicellular marine microalgae are responsible for one of the largest carbon sinks on Earth. This is in part due to intracellular formation of calcium carbonate scales termed coccoliths. ...Unicellular marine microalgae are responsible for one of the largest carbon sinks on Earth. This is in part due to intracellular formation of calcium carbonate scales termed coccoliths. Traditionally, the influence of changing environmental conditions on this process has been estimated using poorly constrained analogies to crystallization mechanisms in bulk solution, yielding ambiguous predictions. Here, we elucidated the intracellular nanoscale environment of coccolith formation in the model species using cryoelectron tomography. By visualizing cells at various stages of the crystallization process, we reconstructed a timeline of coccolith development. The three-dimensional data portray the native-state structural details of coccolith formation, uncovering the crystallization mechanism, and how it is spatially and temporally controlled. Most strikingly, the developing crystals are only tens of nanometers away from delimiting membranes, resulting in a highly confined volume for crystal growth. We calculate that the number of soluble ions that can be found in such a minute volume at any given time point is less than the number needed to allow the growth of a single atomic layer of the crystal and that the uptake of single protons can markedly affect nominal pH values. In such extreme confinement, the crystallization process is expected to depend primarily on the regulation of ion fluxes by the living cell, and nominal ion concentrations, such as pH, become the result, rather than a driver, of the crystallization process. These findings call for a new perspective on coccolith formation that does not rely exclusively on solution chemistry. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13757.map.gz emd_13757.map.gz | 350.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13757-v30.xml emd-13757-v30.xml emd-13757.xml emd-13757.xml | 10.2 KB 10.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_13757.png emd_13757.png | 255.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13757 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13757 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13757 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13757 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13757.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 821.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED INTEGER (2 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13757.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 821.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED INTEGER (2 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | P. carterae coccolith vesicle with mature base plate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 13.48 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
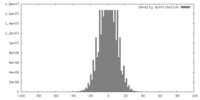
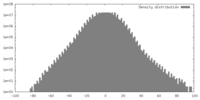
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Pleurochrysis carterae
| Entire | Name: Pleurochrysis carterae |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Pleurochrysis carterae
| Supramolecule | Name: Pleurochrysis carterae / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chrysotila carterae (eukaryote) Chrysotila carterae (eukaryote) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron tomography |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Details: Sterile artificial seawater, supplemented with an f/2 nutrient recipe |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.037 kPa / Details: 15 mA current |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
| Sectioning | Focused ion beam - Instrument: OTHER / Focused ion beam - Ion: OTHER / Focused ion beam - Voltage: 30 kV / Focused ion beam - Current: 0.05 nA / Focused ion beam - Duration: 1800 sec. / Focused ion beam - Temperature: 90 K / Focused ion beam - Initial thickness: 5000 nm / Focused ion beam - Final thickness: 200 nm Focused ion beam - Details: For details, see publication. The value given for _emd_sectioning_focused_ion_beam.instrument is FEI Aquilos. This is not in a list of allowed values {'DB235', 'OTHER'} so ...Focused ion beam - Details: For details, see publication. The value given for _emd_sectioning_focused_ion_beam.instrument is FEI Aquilos. This is not in a list of allowed values {'DB235', 'OTHER'} so OTHER is written into the XML file. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE / Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3710 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3838 pixel / Average exposure time: 1.6 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.24 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 42000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Software - Name:  IMOD / Number images used: 51 IMOD / Number images used: 51 |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)