[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1341: Three-dimensional structure of a human connexin26 gap junction ch... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1341 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Three-dimensional structure of a human connexin26 gap junction channel reveals a plug in the vestibule. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Three Dimensional Structure of a Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology | Gap junction beta-2 protein (Cx26) / connexin complex Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | electron crystallography / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 10.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oshima A / Tani K / Hiroaki Y / Fujiyoshi Y / Sosinsky GE | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2007 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2007Title: Three-dimensional structure of a human connexin26 gap junction channel reveals a plug in the vestibule. Authors: Atsunori Oshima / Kazutoshi Tani / Yoko Hiroaki / Yoshinori Fujiyoshi / Gina E Sosinsky /  Abstract: Connexin molecules form intercellular membrane channels facilitating electronic coupling and the passage of small molecules between adjoining cells. Connexin26 (Cx26) is the second smallest member of ...Connexin molecules form intercellular membrane channels facilitating electronic coupling and the passage of small molecules between adjoining cells. Connexin26 (Cx26) is the second smallest member of the gap junction protein family, and mutations in Cx26 cause certain hereditary human diseases such as skin disorders and hearing loss. Here, we report the electron crystallographic structure of a human Cx26 mutant (M34A). Although crystallization trials used hemichannel preparations, the density map revealed that two hemichannels redocked at their extracellular surfaces into full intercellular channels. These orthorhombic crystals contained two sets of symmetry-related intercellular channels within three lipid bilayers. The 3D map shows a prominent density in the pore of each hemichannel. This density contacts the innermost helices of the surrounding connexin subunits at the bottom of the vestibule. The density map suggests that physical blocking may play an important role that underlies gap junction channel regulation. Our structure allows us to suggest that the two docked hemichannels can be independent and may regulate their activity autonomously with a plug in the vestibule. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1341.map.gz emd_1341.map.gz | 1.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1341-v30.xml emd-1341-v30.xml emd-1341.xml emd-1341.xml | 11.2 KB 11.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1341.gif 1341.gif | 43.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1341 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1341 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Three Dimensional Structure of a Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X: 1.98571 Å / Y: 2.00714 Å / Z: 2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
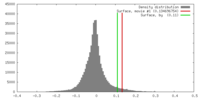
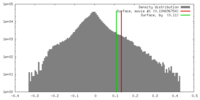
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel
| Entire | Name: Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Connexin26 Gap Junction Channel / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: 12 connexon form a gap junction / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: connexin26
| Macromolecule | Name: connexin26 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: gap junction beta 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Oligomeric state: dodecamer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: cell membrane Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: cell membrane |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Sf9 cells / Recombinant plasmid: pBlueBac4.5 |
| Sequence | GO: connexin complex / InterPro: Gap junction beta-2 protein (Cx26) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron crystallography |
| Aggregation state | 2D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 5.8 Details: 10 mM MES, 100 mM NaCl, 50 mM MgCl2, 5 mM CaCl2, 2 mM DTT, 100 uM carbenoxolone (SIGMA), 0.005% NaN3, 1% glycerol |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: Vitrification |
| Grid | Details: molybdenum grid covered with a thin carbon film |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN / Chamber temperature: 100 K / Instrument: REICHERT-JUNG PLUNGER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Reichert plunger Method: The grid was blotted with filter paper and plunged into liquid nitrogen. |
| Details | crystals grown in dialysis buffer |
| Crystal formation | Details: crystals grown in dialysis buffer |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL KYOTO-3000SFF |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 4.0 K / Max: 4.0 K / Average: 4.0 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: objective astigmatism was corrected using a quadrupole stigmator at 100,000 times magnification |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 7 µm / Number real images: 254 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 12 |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 59100 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 1.6 mm / Nominal defocus max: 19.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 4.7 µm / Nominal magnification: 60000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Top entry liquid helium cooled cryo specimen holder. Specimen holder model: OTHER / Tilt angle max: 45 / Tilt series - Axis1 - Min angle: 0 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Max angle: 45 ° |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 10.0 Å / Software - Name: MRC |
|---|---|
| Crystal parameters | Unit cell - A: 112.4 Å / Unit cell - B: 111.2 Å / Unit cell - C: 300.0 Å / Unit cell - γ: 90.0 ° / Unit cell - α: 90.0 ° / Unit cell - β: 90.0 ° / Plane group: P 2 21 21 |
| CTF correction | Details: Each crystal |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)