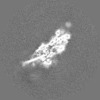
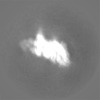
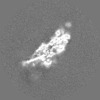
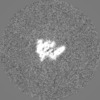
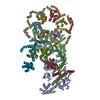
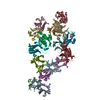
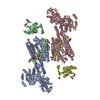
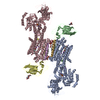
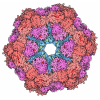
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-12649タイトル cryoEM reconstruction of 1C9-sMAC Locally sharpened 1C9-sMAC map 複合体 : 1C9-sMACタンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C5bタンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C6タンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C7タンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C8 betaタンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C8 alphaタンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C8 gammaタンパク質・ペプチド : Complement protein C9機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.8 Å Menny A / Couves EC / Bubeck D 資金援助 European Union, Organization Grant number 国 European Research Council (ERC) No. 864751 European Union Cancer Research UK C24523/A26234 Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council EP/L015498/1
ジャーナル : Nat Commun / 年 : 2021タイトル : Structural basis of soluble membrane attack complex packaging for clearance.著者 : Anaïs Menny / Marie V Lukassen / Emma C Couves / Vojtech Franc / Albert J R Heck / Doryen Bubeck / 要旨 : Unregulated complement activation causes inflammatory and immunological pathologies with consequences for human disease. To prevent bystander damage during an immune response, extracellular ... Unregulated complement activation causes inflammatory and immunological pathologies with consequences for human disease. To prevent bystander damage during an immune response, extracellular chaperones (clusterin and vitronectin) capture and clear soluble precursors to the membrane attack complex (sMAC). However, how these chaperones block further polymerization of MAC and prevent the complex from binding target membranes remains unclear. Here, we address that question by combining cryo electron microscopy (cryoEM) and cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS) to solve the structure of sMAC. Together our data reveal how clusterin recognizes and inhibits polymerizing complement proteins by binding a negatively charged surface of sMAC. Furthermore, we show that the pore-forming C9 protein is trapped in an intermediate conformation whereby only one of its two transmembrane β-hairpins has unfurled. This structure provides molecular details for immune pore formation and helps explain a complement control mechanism that has potential implications for how cell clearance pathways mediate immune homeostasis. 履歴 登録 2021年3月22日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2021年10月6日 - マップ公開 2021年10月6日 - 更新 2021年11月17日 - 現状 2021年11月17日 処理サイト : PDBe / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 英国, 3件
英国, 3件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2021
ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2021

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_12649.map.gz
emd_12649.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-12649-v30.xml
emd-12649-v30.xml emd-12649.xml
emd-12649.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_12649.png
emd_12649.png emd_12649_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_12649_half_map_1.map.gz emd_12649_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_12649_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12649
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12649 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12649
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12649 emd_12649_validation.pdf.gz
emd_12649_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_12649_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_12649_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_12649_validation.xml.gz
emd_12649_validation.xml.gz emd_12649_validation.cif.gz
emd_12649_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12649
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12649 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12649
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12649 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_12649.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_12649.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)