+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10315 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
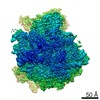
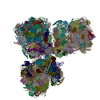
| Title | The cryo-EM structure of SDD1-stalled collided trisome. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | trisome / ribosome / collision / stalling / TRANSLATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmaturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, LSU-rRNA,5S) / regulation of amino acid metabolic process / negative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / translational readthrough / positive regulation of translational fidelity / : / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Protein methylation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / Protein hydroxylation ...maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, LSU-rRNA,5S) / regulation of amino acid metabolic process / negative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / translational readthrough / positive regulation of translational fidelity / : / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Protein methylation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / Protein hydroxylation / ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / pre-mRNA 5'-splice site binding / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit assembly / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay / nonfunctional rRNA decay / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Translation initiation complex formation / response to cycloheximide / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / preribosome, small subunit precursor / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / mRNA destabilization / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / preribosome, large subunit precursor / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / translational elongation / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / Ub-specific processing proteases / 90S preribosome / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / translational termination / regulation of translational fidelity / protein-RNA complex assembly / maturation of LSU-rRNA / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / rescue of stalled cytosolic ribosome / cellular response to amino acid starvation / protein kinase C binding / ribosome assembly / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / macroautophagy / maturation of SSU-rRNA / translational initiation / small-subunit processome / maintenance of translational fidelity / modification-dependent protein catabolic process / protein tag activity / cytoplasmic stress granule / rRNA processing / ribosome biogenesis / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / protein ubiquitination / ribosome / translation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of gene expression / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / nucleolus / mitochondrion / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
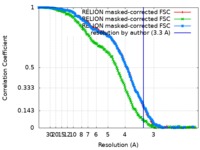
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tesina P / Buschauer R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: RQT complex dissociates ribosomes collided on endogenous RQC substrate SDD1. Authors: Yoshitaka Matsuo / Petr Tesina / Shizuka Nakajima / Masato Mizuno / Akinori Endo / Robert Buschauer / Jingdong Cheng / Okuto Shounai / Ken Ikeuchi / Yasushi Saeki / Thomas Becker / Roland ...Authors: Yoshitaka Matsuo / Petr Tesina / Shizuka Nakajima / Masato Mizuno / Akinori Endo / Robert Buschauer / Jingdong Cheng / Okuto Shounai / Ken Ikeuchi / Yasushi Saeki / Thomas Becker / Roland Beckmann / Toshifumi Inada /   Abstract: Ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) represents a rescue pathway in eukaryotic cells that is triggered upon translational stalling. Collided ribosomes are recognized for subsequent dissociation ...Ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) represents a rescue pathway in eukaryotic cells that is triggered upon translational stalling. Collided ribosomes are recognized for subsequent dissociation followed by degradation of nascent peptides. However, endogenous RQC-inducing sequences and the mechanism underlying the ubiquitin-dependent ribosome dissociation remain poorly understood. Here, we identified SDD1 messenger RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an endogenous RQC substrate and reveal the mechanism of its mRNA-dependent and nascent peptide-dependent translational stalling. In vitro translation of SDD1 mRNA enabled the reconstitution of Hel2-dependent polyubiquitination of collided disomes and, preferentially, trisomes. The distinct trisome architecture, visualized using cryo-EM, provides the structural basis for the more-efficient recognition by Hel2 compared with that of disomes. Subsequently, the Slh1 helicase subunit of the RQC trigger (RQT) complex preferentially dissociates the first stalled polyubiquitinated ribosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Together, these findings provide fundamental mechanistic insights into RQC and its physiological role in maintaining cellular protein homeostasis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10315.map.gz emd_10315.map.gz | 110.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10315-v30.xml emd-10315-v30.xml emd-10315.xml emd-10315.xml | 100.6 KB 100.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10315_fsc_1.xml emd_10315_fsc_1.xml emd_10315_fsc_2.xml emd_10315_fsc_2.xml emd_10315_fsc_3.xml emd_10315_fsc_3.xml | 16 KB 16 KB 16 KB | Display Display Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10315.png emd_10315.png | 81.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10315.cif.gz emd-10315.cif.gz | 18.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_10315_additional_1.map.gz emd_10315_additional_1.map.gz emd_10315_additional_2.map.gz emd_10315_additional_2.map.gz emd_10315_additional_3.map.gz emd_10315_additional_3.map.gz | 149.8 MB 160.4 MB 155.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10315 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10315 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10315 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10315 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6sv4MC 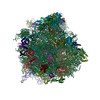 6sntC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10315.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10315.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.084 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
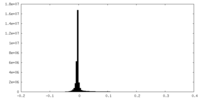
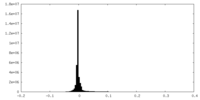
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: First stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined)
| File | emd_10315_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | First stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Third stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined)
| File | emd_10315_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Third stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Second stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined)
| File | emd_10315_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Second stalled ribosome of the trisome (focus-refined) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Trisome assembly of yeast collided ribosomes
+Supramolecule #1: Trisome assembly of yeast collided ribosomes
+Macromolecule #1: 25S rRNA
+Macromolecule #2: 5S rRNA
+Macromolecule #3: 5.8S rRNA
+Macromolecule #18: 18S rRNA
+Macromolecule #80: tRNA (P/P)
+Macromolecule #81: tRNA (A/P)
+Macromolecule #82: tRNA (P/E)
+Macromolecule #4: 60S ribosomal protein L2-A
+Macromolecule #5: 60S ribosomal protein L3
+Macromolecule #6: 60S ribosomal protein L4-A
+Macromolecule #7: 60S ribosomal protein L5
+Macromolecule #8: 60S ribosomal protein L6-A
+Macromolecule #9: 60S ribosomal protein L7-A
+Macromolecule #10: 60S ribosomal protein L8-A
+Macromolecule #11: 60S ribosomal protein L9-A
+Macromolecule #12: 60S ribosomal protein L10
+Macromolecule #13: 60S ribosomal protein L11-A
+Macromolecule #14: 60S ribosomal protein L13-A
+Macromolecule #15: 60S ribosomal protein L14-A
+Macromolecule #16: 60S ribosomal protein L15-A
+Macromolecule #17: 60S ribosomal protein L16-A
+Macromolecule #19: 40S ribosomal protein S0-A
+Macromolecule #20: 40S ribosomal protein S1-A
+Macromolecule #21: 40S ribosomal protein S2
+Macromolecule #22: 40S ribosomal protein S3
+Macromolecule #23: 40S ribosomal protein S4-A
+Macromolecule #24: Rps5p
+Macromolecule #25: 40S ribosomal protein S6-A
+Macromolecule #26: 40S ribosomal protein S7-A
+Macromolecule #27: 40S ribosomal protein S8-A
+Macromolecule #28: 40S ribosomal protein S9-A
+Macromolecule #29: 40S ribosomal protein S10-A
+Macromolecule #30: 40S ribosomal protein S11-A
+Macromolecule #31: 40S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #32: 40S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #33: 40S ribosomal protein S14-A
+Macromolecule #34: 40S ribosomal protein S15
+Macromolecule #35: 40S ribosomal protein S16-A
+Macromolecule #36: 40S ribosomal protein S17-B
+Macromolecule #37: 40S ribosomal protein S18-A
+Macromolecule #38: 40S ribosomal protein S19-A
+Macromolecule #39: 40S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #40: 40S ribosomal protein S21-A
+Macromolecule #41: 40S ribosomal protein S22-A
+Macromolecule #42: 40S ribosomal protein S23-A
+Macromolecule #43: 40S ribosomal protein S24-A
+Macromolecule #44: 40S ribosomal protein S25-A
+Macromolecule #45: 40S ribosomal protein S26-A
+Macromolecule #46: 40S ribosomal protein S27-A
+Macromolecule #47: 40S ribosomal protein S28-B
+Macromolecule #48: 40S ribosomal protein S29-A
+Macromolecule #49: 40S ribosomal protein S30-A
+Macromolecule #50: Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S31
+Macromolecule #51: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein
+Macromolecule #52: 60S ribosomal protein L17-A
+Macromolecule #53: 60S ribosomal protein L18-A
+Macromolecule #54: 60S ribosomal protein L19-A
+Macromolecule #55: 60S ribosomal protein L20-A
+Macromolecule #56: 60S ribosomal protein L21-A
+Macromolecule #57: 60S ribosomal protein L22-A
+Macromolecule #58: 60S ribosomal protein L23-A
+Macromolecule #59: 60S ribosomal protein L24-A
+Macromolecule #60: 60S ribosomal protein L25
+Macromolecule #61: 60S ribosomal protein L26-A
+Macromolecule #62: 60S ribosomal protein L27-A
+Macromolecule #63: 60S ribosomal protein L28
+Macromolecule #64: 60S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #65: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #66: 60S ribosomal protein L31-A
+Macromolecule #67: 60S ribosomal protein L32
+Macromolecule #68: 60S ribosomal protein L33-A
+Macromolecule #69: 60S ribosomal protein L34-A
+Macromolecule #70: 60S ribosomal protein L35-A
+Macromolecule #71: 60S ribosomal protein L36-A
+Macromolecule #72: 60S ribosomal protein L37-A
+Macromolecule #73: 60S ribosomal protein L38
+Macromolecule #74: 60S ribosomal protein L39
+Macromolecule #75: Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40
+Macromolecule #76: 60S ribosomal protein L41-B
+Macromolecule #77: 60S ribosomal protein L42-A
+Macromolecule #78: 60S ribosomal protein L43-A
+Macromolecule #79: 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)