+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10099 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of ovine transhydrogenase in the apo state | |||||||||
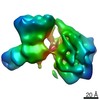
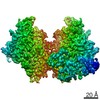
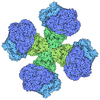
 Map data Map data | Density for apo-NNT. dI density from consensus full NNT refinement and dIIdIII density from focused refinement. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | mitochondrial / proton-translocating / nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-translocating NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase activity / proton-translocating NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase / NADPH regeneration / NADP binding / oxidoreductase activity / mitochondrial inner membrane / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
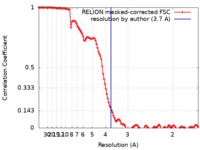
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kampjut D / Sazanov LA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, 1 items Austria, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Structure and mechanism of mitochondrial proton-translocating transhydrogenase. Authors: Domen Kampjut / Leonid A Sazanov /  Abstract: Proton-translocating transhydrogenase (also known as nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT)) is found in the plasma membranes of bacteria and the inner mitochondrial membranes of eukaryotes. ...Proton-translocating transhydrogenase (also known as nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT)) is found in the plasma membranes of bacteria and the inner mitochondrial membranes of eukaryotes. NNT catalyses the transfer of a hydride between NADH and NADP, coupled to the translocation of one proton across the membrane. Its main physiological function is the generation of NADPH, which is a substrate in anabolic reactions and a regulator of oxidative status; however, NNT may also fine-tune the Krebs cycle. NNT deficiency causes familial glucocorticoid deficiency in humans and metabolic abnormalities in mice, similar to those observed in type II diabetes. The catalytic mechanism of NNT has been proposed to involve a rotation of around 180° of the entire NADP(H)-binding domain that alternately participates in hydride transfer and proton-channel gating. However, owing to the lack of high-resolution structures of intact NNT, the details of this process remain unclear. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of intact mammalian NNT in different conformational states. We show how the NADP(H)-binding domain opens the proton channel to the opposite sides of the membrane, and we provide structures of these two states. We also describe the catalytically important interfaces and linkers between the membrane and the soluble domains and their roles in nucleotide exchange. These structures enable us to propose a revised mechanism for a coupling process in NNT that is consistent with a large body of previous biochemical work. Our results are relevant to the development of currently unavailable NNT inhibitors, which may have therapeutic potential in ischaemia reperfusion injury, metabolic syndrome and some cancers. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10099.map.gz emd_10099.map.gz | 3.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10099-v30.xml emd-10099-v30.xml emd-10099.xml emd-10099.xml | 13.7 KB 13.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10099_fsc.xml emd_10099_fsc.xml | 12 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10099.png emd_10099.png | 60.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10099.cif.gz emd-10099.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10099 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10099 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10099 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10099 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6s59MC 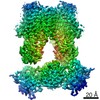 4635C  4637C  6qtiC  6queC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10099.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 14 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10099.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 14 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density for apo-NNT. dI density from consensus full NNT refinement and dIIdIII density from focused refinement. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.84 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase in the apo state
| Entire | Name: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase in the apo state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase in the apo state
| Supramolecule | Name: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase in the apo state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase
| Macromolecule | Name: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 114.010305 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MANLLKTVVT GCSCPFLSNL GSCKVLPGKK NFLRTFHTHR ILWCKAPVKP GIPYKQLTVG VPKEIFQNEK RVALSPAGVQ ALVKQGFNV VVESGAGEAS KFSDDHYRAA GAQIQGAKEV LASDLVVKVR APMLNPTLGI HEADLLKTSG TLISFIYPAQ N PDLLNKLS ...String: MANLLKTVVT GCSCPFLSNL GSCKVLPGKK NFLRTFHTHR ILWCKAPVKP GIPYKQLTVG VPKEIFQNEK RVALSPAGVQ ALVKQGFNV VVESGAGEAS KFSDDHYRAA GAQIQGAKEV LASDLVVKVR APMLNPTLGI HEADLLKTSG TLISFIYPAQ N PDLLNKLS KRNTTVLAMD QVPRVTIAQG YDALSSMANI AGYKAVVLAA NHFGRFFTGQ ITAAGKVPPA KILIVGGGVA GL ASAGAAK SMGAIVRGFD TRAAALEQFK SLGAEPLEVD LKESGEGQGG YAKEMSKEFI EAEMKLFAQQ CKEVDILIST ALI PGKKAP ILFNKEMIES MKEGSVVVDL AAEAGGNFET TKPGELYVHK GITHIGYTDL PSRMATQAST LYSNNITKLL KAIS PDKDN FYFEVKDDFD FGTMGHVIRG TVVMKDGQVI FPAPTPKNIP QGAPVKQKTV AELEAEKAAT ITPFRKTMTS ASVYT AGLT GILGLGIAAP NLAFSQMVTT FGLAGIVGYH TVWGVTPALH SPLMSVTNAI SGLTAVGGLV LMGGHLYPST TSQGLA ALA TFISSVNIAG GFLVTQRMLD MFKRPTDPPE YNYLYLLPAG TFVGGYLASL YSGYNIEQIM YLGSGLCCVG ALAGLST QG TARLGNALGM IGVAGGLAAT LGGLKPCPEL LAQMSGAMAL GGTIGLTIAK RIQISDLPQL VAAFHSLVGL AAVLTCIA E YIIEYPHFAT DAAANLTKIV AYLGTYIGGV TFSGSLVAYG KLQGILKSAP LLLPGRHLLN AGLLAASVGG IIPFMMDPS FTTGITCLGS VSALSAVMGV TLTAAIGGAD MPVVITVLNS YSGWALCAEG FLLNNNLLTI VGALIGSSGA ILSYIMCVAM NRSLANVIL GGYGTTSTAG GKPMEISGTH TEINLDNAID MIREANSIII TPGYGLCAAK AQYPIADLVK MLSEQGKKVR F GIHPVAGR MPGQLNVLLA EAGVPYDIVL EMDEINHDFP DTDLVLVIGA NDTVNSAAQE DPNSIIAGMP VLEVWKSKQV IV MKRSLGV GYAAVDNPIF YKPNTAMLLG DAKKTCDALQ AKVRESYQK UniProtKB: NAD(P) transhydrogenase, mitochondrial |
-Macromolecule #2: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PC1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 790.145 Da |
| Chemical component information | 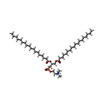 ChemComp-PC1: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 4-6 s blotting time. | ||||||||||||
| Details | Sample was purified in LMNG (final conc. 0.06%) and contained 0.05% CHAPS as a secondary detergent. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 760 / Average exposure time: 3.25 sec. / Average electron dose: 90.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 137 / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient, EMRinger score |
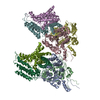
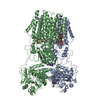
| Output model |  PDB-6s59: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)