+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-0619 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
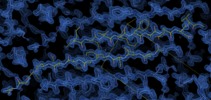
| タイトル | Amyloid Beta KLVFFAENVGS 16-26 D23N Iowa mutation | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | Amyloid Beta KLVFFAENVGS 16-26 D23N Iowa mutation | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | amyloid / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity ...amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity / axon midline choice point recognition / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / growth factor receptor binding / peptidase activator activity / Golgi-associated vesicle / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / astrocyte projection / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / dendrite development / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / signaling receptor activator activity / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / The NLRP3 inflammasome / main axon / transition metal ion binding / regulation of multicellular organism growth / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of T cell migration / neuronal dense core vesicle / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / positive regulation of chemokine production / cellular response to manganese ion / Notch signaling pathway / clathrin-coated pit / extracellular matrix organization / neuron projection maintenance / astrocyte activation / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Mitochondrial protein degradation / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / axonogenesis / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / response to interleukin-1 / platelet alpha granule lumen / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of glycolytic process / central nervous system development / dendritic shaft / trans-Golgi network membrane / endosome lumen / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / adult locomotory behavior / learning / positive regulation of JNK cascade / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / locomotory behavior / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / microglial cell activation / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / recycling endosome / synapse organization / visual learning / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / response to lead ion / Golgi lumen / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / endocytosis / cellular response to amyloid-beta / neuron projection development / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / Platelet degranulation / heparin binding / regulation of translation / regulation of gene expression / early endosome membrane / G alpha (i) signalling events / perikaryon / G alpha (q) signalling events / dendritic spine 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 電子線結晶学 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 1.402 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Griner SL / Sawaya MR | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019 ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019タイトル: Structure-based inhibitors of amyloid beta core suggest a common interface with tau. 著者: Sarah L Griner / Paul Seidler / Jeannette Bowler / Kevin A Murray / Tianxiao Peter Yang / Shruti Sahay / Michael R Sawaya / Duilio Cascio / Jose A Rodriguez / Stephan Philipp / Justyna Sosna ...著者: Sarah L Griner / Paul Seidler / Jeannette Bowler / Kevin A Murray / Tianxiao Peter Yang / Shruti Sahay / Michael R Sawaya / Duilio Cascio / Jose A Rodriguez / Stephan Philipp / Justyna Sosna / Charles G Glabe / Tamir Gonen / David S Eisenberg /   要旨: Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology is characterized by plaques of amyloid beta (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles of tau. Aβ aggregation is thought to occur at early stages of the disease, and ...Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology is characterized by plaques of amyloid beta (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles of tau. Aβ aggregation is thought to occur at early stages of the disease, and ultimately gives way to the formation of tau tangles which track with cognitive decline in humans. Here, we report the crystal structure of an Aβ core segment determined by MicroED and in it, note characteristics of both fibrillar and oligomeric structure. Using this structure, we designed peptide-based inhibitors that reduce Aβ aggregation and toxicity of already-aggregated species. Unexpectedly, we also found that these inhibitors reduce the efficiency of Aβ-mediated tau aggregation, and moreover reduce aggregation and self-seeding of tau fibrils. The ability of these inhibitors to interfere with both Aβ and tau seeds suggests these fibrils share a common epitope, and supports the hypothesis that cross-seeding is one mechanism by which amyloid is linked to tau aggregation and could promote cognitive decline. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_0619.map.gz emd_0619.map.gz | 280.9 KB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-0619-v30.xml emd-0619-v30.xml emd-0619.xml emd-0619.xml | 12.9 KB 12.9 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_0619.png emd_0619.png | 598.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0619.cif.gz emd-0619.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc structureFactors |  emd_0619_sf.cif.gz emd_0619_sf.cif.gz | 49.4 KB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0619 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0619 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0619 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0619 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_0619_validation.pdf.gz emd_0619_validation.pdf.gz | 379.3 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_0619_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_0619_full_validation.pdf.gz | 378.8 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_0619_validation.xml.gz emd_0619_validation.xml.gz | 4.2 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_0619_validation.cif.gz emd_0619_validation.cif.gz | 4.7 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0619 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0619 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0619 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0619 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  6o4jMC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_0619.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 304.7 KB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_0619.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 304.7 KB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Amyloid Beta KLVFFAENVGS 16-26 D23N Iowa mutation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 これらの図は立方格子座標系で作成されたものです | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X: 0.389 Å / Y: 0.36049 Å / Z: 0.35444 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Fibrils of Amyloid Beta segment 16-26
| 全体 | 名称: Fibrils of Amyloid Beta segment 16-26 |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Fibrils of Amyloid Beta segment 16-26
| 超分子 | 名称: Fibrils of Amyloid Beta segment 16-26 / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-分子 #1: Amyloid-beta precursor protein
| 分子 | 名称: Amyloid-beta precursor protein / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 2 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 1.235432 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: (ACE)KLVFFAENV GS(NH2) UniProtKB: Amyloid-beta precursor protein |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 電子線結晶学 |
| 試料の集合状態 | 3D array |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 7.5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 構成要素:
| |||||||||||||||
| グリッド | 支持フィルム - 材質: CARBON / 支持フィルム - トポロジー: HOLEY / 詳細: unspecified | |||||||||||||||
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | nanocrystals | |||||||||||||||
| 結晶化 | 装置: microcentrifuge tube / 雰囲気: air / 温度: 310.0 K / 時間: 4.0 DAY |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: TVIPS TEMCAM-F416 (4k x 4k) デジタル化 - サイズ - 横: 2048 pixel / デジタル化 - サイズ - 縦: 2048 pixel / 回折像の数: 1331 / 平均電子線量: 0.03 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 200 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: DIFFRACTION / カメラ長: 1840 mm |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Tecnai F20 / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 最終 再構成 | 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 1.402 Å / 解像度の算出法: DIFFRACTION PATTERN/LAYERLINES |
|---|---|
| Crystallography statistics | Number intensities measured: 47598 / Number structure factors: 2355 / Fourier space coverage: 85.4 / R sym: 0.24 / R merge: 0.24 / Overall phase error: 0 / Overall phase residual: 0.01 / Phase error rejection criteria: 0 / High resolution: 1.4 Å / 殻 - Shell ID: 1 / 殻 - High resolution: 1.4 Å / 殻 - Low resolution: 1.44 Å / 殻 - Number structure factors: 163 / 殻 - Phase residual: 0.01 / 殻 - Fourier space coverage: 78 / 殻 - Multiplicity: 12.1 |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)






















