+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 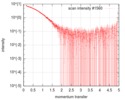 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | Thymine dioxygenase J-containing DNA binding domain (JDBD)
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthymine dioxygenase / thymine dioxygenase activity / base J metabolic process / DNA binding / metal ion binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2019 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2019Title: The domain architecture of the protozoan protein J-DNA-binding protein 1 suggests synergy between base J DNA binding and thymidine hydroxylase activity. Authors: Athanassios Adamopoulos / Tatjana Heidebrecht / Jeroen Roosendaal / Wouter G Touw / Isabelle Q Phan / Jos Beijnen / Anastassis Perrakis /   Abstract: J-DNA-binding protein 1 (JBP1) contributes to the biosynthesis and maintenance of base J (β-d-glucosyl-hydroxymethyluracil), an epigenetic modification of thymidine (T) confined to pathogenic ...J-DNA-binding protein 1 (JBP1) contributes to the biosynthesis and maintenance of base J (β-d-glucosyl-hydroxymethyluracil), an epigenetic modification of thymidine (T) confined to pathogenic protozoa such as and JBP1 has two known functional domains: an N-terminal T hydroxylase (TH) homologous to the 5-methylcytosine hydroxylase domain in TET proteins and a J-DNA-binding domain (JDBD) that resides in the middle of JBP1. Here, we show that removing JDBD from JBP1 results in a soluble protein (Δ-JDBD) with the N- and C-terminal regions tightly associated together in a well-ordered structure. We found that this Δ-JDBD domain retains TH activity but displays a 15-fold lower apparent rate of hydroxylation compared with JBP1. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) experiments on JBP1 and JDBD in the presence or absence of J-DNA and on Δ-JDBD enabled us to generate low-resolution three-dimensional models. We conclude that Δ-JDBD, and not the N-terminal region of JBP1 alone, is a distinct folding unit. Our SAXS-based model supports the notion that binding of JDBD specifically to J-DNA can facilitate T hydroxylation 12-14 bp downstream on the complementary strand of the J-recognition site. We postulate that insertion of the JDBD module into the Δ-JDBD scaffold during evolution provided a mechanism that synergized J recognition and T hydroxylation, ensuring inheritance of base J in specific sequence patterns following DNA replication in kinetoplastid parasites. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Thymine dioxygenase J-containing DNA binding domain (JDBD) Specimen concentration: 3.75 mg/ml |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM HEPES, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP / pH: 7.5 |
| Entity #898 | Name: JDBD / Type: protein / Description: J-DNA binding domain / Formula weight: 21.244 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Leishmania tarentolae / References: UniProt: Q9U6M1 Sequence: GPGPLSRLGG FSETNLMVST AVEKKKYLDS EFLLHCISAQ LLDMWKQARA RWLELVGKEW AHMLALNPER KDFLWKNQSE MNSAFFDLCE VGKQVMLGLL GKEVALPKEE QAFWIMYAVH LSAACAEELH MPEVAMSLRK LNVKLKDFNF GGTRYFKDMP PEEKKRRMER KQRIEEARRH GMP |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: ESRF BM29 / City: Grenoble / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.867 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.867 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M / Type: Dectris / Pixsize x: 172 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
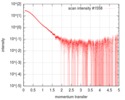
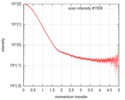
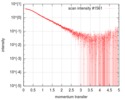
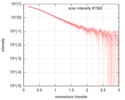
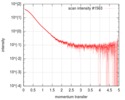
| Scan | Measurement date: Feb 4, 2017 / Cell temperature: 4 °C / Exposure time: 1 sec. / Number of frames: 34 / Unit: 1/nm /
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 SASDGR2
SASDGR2