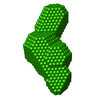
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | Human Filamin A Ig-like domains 20-21 truncation (2151-2329)
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / establishment of Sertoli cell barrier / Myb complex / glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway / formation of radial glial scaffolds / positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / actin crosslink formation / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway ...regulation of membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / establishment of Sertoli cell barrier / Myb complex / glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway / formation of radial glial scaffolds / positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / actin crosslink formation / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / tubulin deacetylation / OAS antiviral response / positive regulation of actin filament bundle assembly / positive regulation of neuron migration / protein localization to bicellular tight junction / Fc-gamma receptor I complex binding / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / apical dendrite / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of platelet activation / positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / protein localization to cell surface / wound healing, spreading of cells / podosome / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / megakaryocyte development / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / SMAD binding / receptor clustering / cortical cytoskeleton / semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / cilium assembly / mitotic spindle assembly / potassium channel regulator activity / : / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / protein sequestering activity / regulation of cell migration / dendritic shaft / protein localization to plasma membrane / actin filament / establishment of protein localization / G protein-coupled receptor binding / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / cerebral cortex development / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / small GTPase binding / platelet aggregation / kinase binding / Z disc / cell-cell junction / actin filament binding / Platelet degranulation / actin cytoskeleton / growth cone / actin cytoskeleton organization / GTPase binding / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / perikaryon / transmembrane transporter binding / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / postsynapse / protein stabilization / cadherin binding / focal adhesion / negative regulation of apoptotic process / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / glutamatergic synapse / protein homodimerization activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2015 Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2015Title: Flexible Structure of Peptide-Bound Filamin A Mechanosensor Domain Pair 20-21. Authors: Jonne Seppälä / Helena Tossavainen / Nebojsa Rodic / Perttu Permi / Ulla Pentikäinen / Jari Ylänne /  Abstract: Filamins (FLNs) are large, multidomain actin cross-linking proteins with diverse functions. Besides regulating the actin cytoskeleton, they serve as important links between the extracellular matrix ...Filamins (FLNs) are large, multidomain actin cross-linking proteins with diverse functions. Besides regulating the actin cytoskeleton, they serve as important links between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton by binding cell surface receptors, functioning as scaffolds for signaling proteins, and binding several other cytoskeletal proteins that regulate cell adhesion dynamics. Structurally, FLNs are formed of an amino terminal actin-binding domain followed by 24 immunoglobulin-like domains (IgFLNs). Recent studies have demonstrated that myosin-mediated contractile forces can reveal hidden protein binding sites in the domain pairs IgFLNa18-19 and 20-21, enabling FLNs to transduce mechanical signals in cells. The atomic structures of these mechanosensor domain pairs in the resting state are known, as well as the structures of individual IgFLN21 with ligand peptides. However, little experimental data is available on how interacting protein binding deforms the domain pair structures. Here, using small-angle x-ray scattering-based modelling, x-ray crystallography, and NMR, we show that the adaptor protein migfilin-derived peptide-bound structure of IgFLNa20-21 is flexible and adopts distinctive conformations depending on the presence or absence of the interacting peptide. The conformational changes reported here may be common for all peptides and may play a role in the mechanosensor function of the site. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDAF8 SASDAF8 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Human Filamin A Ig-like domains 20-21 truncation (2151-2329) Specimen concentration: 1.00-4.00 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: Tris / Concentration: 20.00 mM / pH: 8 / Composition: 50 mM NaCl, 10mM DTT |
| Entity #188 | Name: FilaminA / Type: protein / Description: Human Filamin A Ig-like domains 20-21 / Formula weight: 18.7 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P21333 Sequence: SVANVGSHCD LSLKIPEISI QDMTAQVTSP SGKTHEAEIV EGENHTYCIR FVPAEMGTHT VSVKYKGQHV PGSPFQFTVG PLGEGGAHKV RAGGPGLERA EAGVPAEFSI WTREAGAGGL AIAVEGPSKA EISFEDRKDG SCGVAYVVQE PGDYEVSVKF NEEHIPDSPF VVPVASPS |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: ESRF BM29 / City: Grenoble / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.93 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.43 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.93 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.43 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | Comments: Filamin A fragment residues 2151-2329 (Ig-like domains). NOTE: The displayed SAXS data and data used for P(r) vs r determination are on different I(s) scales.
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller