[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDA86: NetrinVIV DCC56(M933R) complex (Netrin-1, NetrinVIV + Deleted in ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 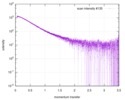 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | NetrinVIV DCC56(M933R) complex
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of glial cell migration / DSCAM interactions / chemorepulsion of axon / Cdc42 protein signal transduction / anterior/posterior axon guidance / Netrin-1 signaling / Role of second messengers in netrin-1 signaling / Regulation of commissural axon pathfinding by SLIT and ROBO / motor neuron migration / negative regulation of axon extension ...regulation of glial cell migration / DSCAM interactions / chemorepulsion of axon / Cdc42 protein signal transduction / anterior/posterior axon guidance / Netrin-1 signaling / Role of second messengers in netrin-1 signaling / Regulation of commissural axon pathfinding by SLIT and ROBO / motor neuron migration / negative regulation of axon extension / substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension / mammary gland duct morphogenesis / Netrin mediated repulsion signals / DCC mediated attractive signaling / positive regulation of cell motility / inner ear morphogenesis / nuclear migration / regulation of synapse assembly / basement membrane / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / positive regulation of axon extension / glial cell proliferation / cell-cell adhesion / actin cytoskeleton / Ras protein signal transduction / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / apoptotic process / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / glutamatergic synapse / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Neuron / Year: 2014 Journal: Neuron / Year: 2014Title: The crystal structure of netrin-1 in complex with DCC reveals the bifunctionality of netrin-1 as a guidance cue. Authors: Lorenzo I Finci / Nina Krüger / Xiaqin Sun / Jie Zhang / Magda Chegkazi / Yu Wu / Gundolf Schenk / Haydyn D T Mertens / Dmitri I Svergun / Yan Zhang / Jia-Huai Wang / Rob Meijers /    Abstract: Netrin-1 is a guidance cue that can trigger either attraction or repulsion effects on migrating axons of neurons, depending on the repertoire of receptors available on the growth cone. How a single ...Netrin-1 is a guidance cue that can trigger either attraction or repulsion effects on migrating axons of neurons, depending on the repertoire of receptors available on the growth cone. How a single chemotropic molecule can act in such contradictory ways has long been a puzzle at the molecular level. Here we present the crystal structure of netrin-1 in complex with the Deleted in Colorectal Cancer (DCC) receptor. We show that one netrin-1 molecule can simultaneously bind to two DCC molecules through a DCC-specific site and through a unique generic receptor binding site, where sulfate ions staple together positively charged patches on both DCC and netrin-1. Furthermore, we demonstrate that UNC5A can replace DCC on the generic receptor binding site to switch the response from attraction to repulsion. We propose that the modularity of binding allows for the association of other netrin receptors at the generic binding site, eliciting alternative turning responses. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDA86 SASDA86 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4urtC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: NetrinVIV DCC56(M933R) complex / Specimen concentration: 0.30-3.90 / Entity id: 113 / 118 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: MES / Concentration: 25.00 mM / pH: 7 / Comment: MES/TRIS Composition: NaCl 200.000 mM, Tris 50.000 mM, (NH4)2(SO4) 0.200 M ammonium sulfate, CaCl2 1.000 mM calcium chloride |
| Entity #113 | Name: NetrinVIV / Type: protein / Description: Netrin-1 / Formula weight: 49.1 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: O95631 Sequence: GPGLSMFAGQ AAQPDPCSDE NGHPRRCIPD FVNAAFGKDV RVSSTCGRPP ARYCVVSERG EERLRSCHLC NASDPKKAHP PAFLTDLNNP HNLTCWQSEN YLQFPHNVTL TLSLGKKFEV TYVSLQFCSP RPESMAIYKS MDYGRTWVPF QFYSTQCRKM YNRPHRAPIT ...Sequence: GPGLSMFAGQ AAQPDPCSDE NGHPRRCIPD FVNAAFGKDV RVSSTCGRPP ARYCVVSERG EERLRSCHLC NASDPKKAHP PAFLTDLNNP HNLTCWQSEN YLQFPHNVTL TLSLGKKFEV TYVSLQFCSP RPESMAIYKS MDYGRTWVPF QFYSTQCRKM YNRPHRAPIT KQNEQEAVCT DSHTDMRPLS GGLIAFSTLD GRPSAHDFDN SPVLQDWVTA TDIRVAFSRL HTFGDENEDD SELARDSYFY AVSDLQVGGR CKCNGHAARC VRDRDDSLVC DCRHNTAGPE CDRCKPFHYD RPWQRATARE ANECVACNCN LHARRCRFNM ELYKLSGRKS GGVCLNCRHN TAGRHCHYCK EGYYRDMGKP ITHRKACKAC DCHPVGAAGK TCNQTTGQCP CKDGVTGITC NRCAKGYQQS RSPIAPCIKE LHHHHHH |
| Entity #118 | Name: DCC56 (M933R) / Type: protein Description: Deleted in Colorectal Cancer (FN5 & FN6) M933R mutant Formula weight: 25.5 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens Sequence: MLPPVGVQAV ALTHDAVRVS WADNSVPKNQ KTSEVRLYTV RWRTSFSASA KYKSEDTTSL SYTATGLKPN TMYEFSVMVT KNRRSSTWSR TAHATTYEAA PTSAPKDLTV ITREGKPRAV IVSWQPPLEA NGKITAYILF YTLDKNIPID DWIMETISGD RLTHQIMDLN ...Sequence: MLPPVGVQAV ALTHDAVRVS WADNSVPKNQ KTSEVRLYTV RWRTSFSASA KYKSEDTTSL SYTATGLKPN TMYEFSVMVT KNRRSSTWSR TAHATTYEAA PTSAPKDLTV ITREGKPRAV IVSWQPPLEA NGKITAYILF YTLDKNIPID DWIMETISGD RLTHQIMDLN LDTMYYFRIQ ARNSKGVGPL SDPILFRTLK LEVLFQGPGG HHHHHHGGWS HPQFEK |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: PETRA III P12 / City: Hamburg / 国: Germany  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.12 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 3.1 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.12 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 3.1 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 2M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








