[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
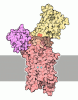
Yorodumi- PDB-9gtb: Cryo-EM structure of Mouse PMCA-NPTN complex captured in E1-Ca state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9gtb | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Mouse PMCA-NPTN complex captured in E1-Ca state | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / P-type Atpase / antiporter / calcium pump | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationotolith mineralization / regulation of receptor localization to synapse / cerebellar Purkinje cell layer morphogenesis / type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor binding / inner ear receptor cell differentiation / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / cGMP metabolic process / cerebellar granule cell differentiation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / calcium-dependent ATPase activity ...otolith mineralization / regulation of receptor localization to synapse / cerebellar Purkinje cell layer morphogenesis / type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor binding / inner ear receptor cell differentiation / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / cGMP metabolic process / cerebellar granule cell differentiation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / calcium-dependent ATPase activity / excitatory synapse assembly / cerebellar Purkinje cell differentiation / positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / photoreceptor ribbon synapse / positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / P-type Ca2+ transporter / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / P-type calcium transporter activity / serotonin metabolic process / Ion homeostasis / positive regulation of calcium ion transport / locomotion / auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization / dendritic spine membrane / negative regulation of cytokine production / inner ear morphogenesis / neuromuscular process controlling balance / regulation of cell size / homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules / inner ear development / cochlea development / immunological synapse / regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / cell adhesion molecule binding / lactation / cerebellum development / PDZ domain binding / locomotory behavior / establishment of localization in cell / sensory perception of sound / synapse organization / positive regulation of neuron projection development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / neuron cellular homeostasis / regulation of synaptic plasticity / long-term synaptic potentiation / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / cell morphogenesis / neuron differentiation / calcium ion transport / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / presynaptic membrane / basolateral plasma membrane / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / cilium / apical plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / dendrite / calcium ion binding / glutamatergic synapse / endoplasmic reticulum / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Vinayagam, D. / Raunser, S. / Sistel, O. / Shulte, U. / Constantin, C.E. / Prubaum, D. / Zolles, G. / Fakler, B. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Title: Molecular mechanism of ultrafast transport by plasma membrane Ca-ATPases. Authors: Deivanayagabarathy Vinayagam / Oleg Sitsel / Uwe Schulte / Cristina E Constantin / Wout Oosterheert / Daniel Prumbaum / Gerd Zolles / Bernd Fakler / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Tight control of intracellular Ca levels is fundamental as they are used to control numerous signal transduction pathways. Plasma membrane Ca-ATPases (PMCAs) have a crucial role in this process by ...Tight control of intracellular Ca levels is fundamental as they are used to control numerous signal transduction pathways. Plasma membrane Ca-ATPases (PMCAs) have a crucial role in this process by extruding Ca against a steep concentration gradient from the cytosol to the extracellular space. Although new details of PMCA biology are constantly being uncovered, the structural basis of the most distinguishing features of these pumps, namely, transport rates in the kilohertz range and regulation of activity by the plasma membrane phospholipid PtdIns(4,5)P, has so far remained elusive. Here we present the structures of mouse PMCA2 in the presence and absence of its accessory subunit neuroplastin in eight different stages of its transport cycle. Combined with whole-cell recordings that accurately track PMCA-mediated Ca extrusion in intact cells, these structures enable us to establish the first comprehensive transport model for a PMCA, reveal the role of disease-causing mutations and uncover the structural underpinnings of regulatory PMCA-phospholipid interaction. The transport cycle-dependent dynamics of PtdIns(4,5)P are fundamental for its role as a 'latch' promoting the fast release of Ca and opening a passageway for counter-ions. These actions are required for maintaining the ultra-fast transport cycle. Moreover, we identify the PtdIns(4,5)P-binding site as an unanticipated target for drug-mediated manipulation of intracellular Ca levels. Our work provides detailed structural insights into the uniquely fast operation of native PMCA-type Ca pumps and its control by membrane lipids and drugs. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9gtb.cif.gz 9gtb.cif.gz | 244.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9gtb.ent.gz pdb9gtb.ent.gz | 186.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9gtb.json.gz 9gtb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9gtb_validation.pdf.gz 9gtb_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9gtb_full_validation.pdf.gz 9gtb_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9gtb_validation.xml.gz 9gtb_validation.xml.gz | 47.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9gtb_validation.cif.gz 9gtb_validation.cif.gz | 70 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/9gtb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/9gtb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/9gtb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/9gtb | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 134647.141 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9R0K7, P-type Ca2+ transporter Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9R0K7, P-type Ca2+ transporter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 46440.059 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P97300 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P97300 | ||||
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / | ||||
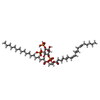
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-KXP / ( | ||||
| #5: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: PMCA-NPTN complex / Type: COMPLEX Details: prepared as separate cDNAs for transient (co)transfection of tsA201 nptn/basi double KO cells Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.18 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: Tris 20mM NaCl 150mM |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: The complex was monodisperse |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 55000 X / Calibrated magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1100 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 113 K / Temperature (min): 93 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3 sec. / Electron dose: 67.63 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 29014 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 201573 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 146.2 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6A69 Accession code: 6A69 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.5 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj