+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uee | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Atomic structure of Salmonella SipA/F-actin complex by cryo-EM | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL INVASION / actin / Salmonella / type III secretion system / SipA | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity / tropomyosin binding / mesenchyme migration / troponin I binding / myosin heavy chain binding / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / actin filament bundle assembly ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / tropomyosin binding / mesenchyme migration / troponin I binding / myosin heavy chain binding / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / filopodium / actin filament / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / lamellipodium / actin binding / cell body / hydrolase activity / protein domain specific binding / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Niedzialkowska, E. / Runyan, L. / Kudryashova, E. / Kudryashov, D.S. / Egelman, E.H. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2024 Journal: Structure / Year: 2024Title: Stabilization of F-actin by Salmonella effector SipA resembles the structural effects of inorganic phosphate and phalloidin. Authors: Ewa Niedzialkowska / Lucas A Runyan / Elena Kudryashova / Edward H Egelman / Dmitri S Kudryashov /  Abstract: Entry of Salmonella into host enterocytes relies on its pathogenicity island 1 effector SipA. We found that SipA binds to F-actin in a 1:2 stoichiometry with sub-nanomolar affinity. A cryo-EM ...Entry of Salmonella into host enterocytes relies on its pathogenicity island 1 effector SipA. We found that SipA binds to F-actin in a 1:2 stoichiometry with sub-nanomolar affinity. A cryo-EM reconstruction revealed that SipA's globular core binds at the groove between actin strands, whereas the extended C-terminal arm penetrates deeply into the inter-strand space, stabilizing F-actin from within. The unusually strong binding of SipA is achieved by a combination of fast association via the core and very slow dissociation dictated by the arm. Similar to P, BeF, and phalloidin, SipA potently inhibited actin depolymerization by actin depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilin, which correlated with increased filament stiffness, supporting the hypothesis that F-actin's mechanical properties contribute to the recognition of its nucleotide state by protein partners. The remarkably strong binding to F-actin maximizes the toxin's effects at the injection site while minimizing global influence on the cytoskeleton and preventing pathogen detection by the host cell. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uee.cif.gz 8uee.cif.gz | 634.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uee.ent.gz pdb8uee.ent.gz | 522.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uee.json.gz 8uee.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8uee_validation.pdf.gz 8uee_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8uee_full_validation.pdf.gz 8uee_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8uee_validation.xml.gz 8uee_validation.xml.gz | 97.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8uee_validation.cif.gz 8uee_validation.cif.gz | 141.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ue/8uee https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ue/8uee ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ue/8uee ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ue/8uee | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42161MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 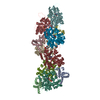
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 11 molecules FHIJKLMBCDA
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41875.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 28413.857 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria)Gene: sipA, sspA, STM2882 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 22 molecules 






| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: Buffer composition: 25 mM TRIS-H-Cl pH 8.0 2 mM DTT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component | Conc.: 25 mM / Name: TRIS / Formula: TRIS-HCl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K Details: 3 uL of sample was applied on Lacey grid, then sample was blotted for 3 seconds and plunge-froze in liquid ethane |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5.58 sec. / Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 12452 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 53.656 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 112.075 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1548993 Details: Reconstruction algorithm: helical refinement and non-uniform refinement in cryoSPARC that is similar to IHRSR algorithm Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj





