+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tof | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rpd3S bound to an H3K36Cme3 modified nucleosome | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA / nucleosome / methylation / acetylation / Rpd3S / TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTINTIN complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Snt2C complex / negative regulation of silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of reciprocal meiotic recombination / Rpd3L complex / protein localization to nucleolar rDNA repeats / negative regulation of rDNA heterochromatin formation / Rpd3L-Expanded complex / Rpd3S complex ...TINTIN complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Snt2C complex / negative regulation of silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of reciprocal meiotic recombination / Rpd3L complex / protein localization to nucleolar rDNA repeats / negative regulation of rDNA heterochromatin formation / Rpd3L-Expanded complex / Rpd3S complex / rDNA chromatin condensation / nucleophagy / regulation of RNA stability / HDACs deacetylate histones / histone deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / histone deacetylase / nucleosome disassembly / cellular response to nitrogen starvation / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / histone deacetylase activity / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / histone deacetylase complex / : / Sin3-type complex / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / histone reader activity / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / histone acetyltransferase complex / positive regulation of macroautophagy / nuclear periphery / meiotic cell cycle / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / cellular response to heat / response to oxidative stress / transcription coactivator activity / protein heterodimerization activity / cell division / DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Markert, J.W. / Vos, S.M. / Farnung, L. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structure of the complete Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpd3S-nucleosome complex. Authors: Jonathan W Markert / Seychelle M Vos / Lucas Farnung /  Abstract: Acetylation of histones is a key post-translational modification that guides gene expression regulation. In yeast, the class I histone deacetylase containing Rpd3S complex plays a critical role in ...Acetylation of histones is a key post-translational modification that guides gene expression regulation. In yeast, the class I histone deacetylase containing Rpd3S complex plays a critical role in the suppression of spurious transcription by removing histone acetylation from actively transcribed genes. The S. cerevisiae Rpd3S complex has five subunits (Rpd3, Sin3, Rco1, Eaf3, and Ume1) but its subunit stoichiometry and how the complex engages nucleosomes to achieve substrate specificity remains elusive. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the complete Rpd3S complex bound to a nucleosome. Sin3 and two copies of subunits Rco1 and Eaf3 encircle the deacetylase subunit Rpd3 and coordinate the positioning of Ume1. The Rpd3S complex binds both trimethylated H3 tails at position lysine 36 and makes multiple additional contacts with the nucleosomal DNA and the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Direct regulation via the Sin3 subunit coordinates binding of the acetylated histone substrate to achieve substrate specificity. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tof.cif.gz 8tof.cif.gz | 775.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tof.ent.gz pdb8tof.ent.gz | 586 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tof.json.gz 8tof.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/8tof https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/8tof ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/8tof ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/8tof | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41449MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 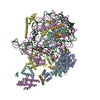
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Transcriptional regulatory protein ... , 2 types, 3 molecules AFG
| #1: Protein | Mass: 175047.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: SIN3, CPE1, GAM2, RPD1, SDI1, SDS16, UME4, YOL004W / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P22579 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P22579 |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 78951.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RCO1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q04779 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q04779 |
-Protein , 6 types, 11 molecules BDEaebfcgdh
| #2: Protein | Mass: 48961.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RPD3, MOF6, REC3, SDI2, SDS6, YNL330C, N0305 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P32561, histone deacetylase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P32561, histone deacetylase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 45266.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: EAF3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12432 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12432#8: Protein | Mass: 15495.247 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #9: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #10: Protein | Mass: 14109.436 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #11: Protein | Mass: 13655.948 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S29T Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  |
-Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules Hx
| #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 515.628 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
|---|---|
| #12: Protein/peptide | Mass: 657.824 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 63931.590 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 66097.227 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 5 molecules 
| #13: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rpd3S bound to H3K36Cme3 nucleosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#12 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 484141 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj







































