+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8hif | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
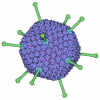
| Title | One asymmetric unit of Singapore grouper iridovirus capsid | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Singapore grouper iridovirus / capsid proteins | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Singapore grouper iridovirus Singapore grouper iridovirus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, Z.N. / Liu, C.C. / Zhu, D.J. / Qi, J.X. / Zhang, X.Z. / Gao, G.F. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Near-atomic architecture of Singapore grouper iridovirus and implications for giant virus assembly. Authors: Zhennan Zhao / Youhua Huang / Congcong Liu / Dongjie Zhu / Shuaixin Gao / Sheng Liu / Ruchao Peng / Ya Zhang / Xiaohong Huang / Jianxun Qi / Catherine C L Wong / Xinzheng Zhang / Peiyi Wang ...Authors: Zhennan Zhao / Youhua Huang / Congcong Liu / Dongjie Zhu / Shuaixin Gao / Sheng Liu / Ruchao Peng / Ya Zhang / Xiaohong Huang / Jianxun Qi / Catherine C L Wong / Xinzheng Zhang / Peiyi Wang / Qiwei Qin / George F Gao /   Abstract: Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV), one of the nucleocytoviricota viruses (NCVs), is a highly pathogenic iridovirid. SGIV infection results in massive economic losses to the aquaculture industry and ...Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV), one of the nucleocytoviricota viruses (NCVs), is a highly pathogenic iridovirid. SGIV infection results in massive economic losses to the aquaculture industry and significantly threatens global biodiversity. In recent years, high morbidity and mortality in aquatic animals have been caused by iridovirid infections worldwide. Effective control and prevention strategies are urgently needed. Here, we present a near-atomic architecture of the SGIV capsid and identify eight types of capsid proteins. The viral inner membrane-integrated anchor protein colocalizes with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), supporting the hypothesis that the biogenesis of the inner membrane is associated with the ER. Additionally, immunofluorescence assays indicate minor capsid proteins (mCPs) could form various building blocks with major capsid proteins (MCPs) before the formation of a viral factory (VF). These results expand our understanding of the capsid assembly of NCVs and provide more targets for vaccine and drug design to fight iridovirid infections. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8hif.cif.gz 8hif.cif.gz | 9.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8hif.ent.gz pdb8hif.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8hif.json.gz 8hif.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hi/8hif https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hi/8hif ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hi/8hif ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hi/8hif | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  34815MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 144 molecules A1A2A3B1B2B3C1C2C3D1D2D3E1E2E3F1F2F3G1G2G3H1H2H3I1I2I3J1J3K1...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50573.141 Da / Num. of mol.: 123 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFJ3 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFJ3#2: Protein | Mass: 19070.715 Da / Num. of mol.: 15 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFM7 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFM7#3: Protein | Mass: 49777.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFC8 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFC8#4: Protein | | Mass: 54052.152 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFH7 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFH7#5: Protein | | Mass: 16343.806 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFK6 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFK6#6: Protein | | Mass: 11354.337 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFC6 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFC6#7: Protein | | Mass: 15872.862 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFQ1 Singapore grouper iridovirus / References: UniProt: Q5YFQ1 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Singapore grouper iridovirus / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Singapore grouper iridovirus Singapore grouper iridovirus |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: STRAIN / Type: VIRION |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 37161 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 82.32 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj