+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8gb0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | SARS-CoV-2 Spike H655Y variant, One RBD Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Spike glycoprotein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 / Spike Protein / Glycoprotein / Trimeric Complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / Attachment and Entry / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / receptor ligand activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Egri, S.B. / Shen, K. / Luban, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023Title: S:D614G and S:H655Y are gateway mutations that act epistatically to promote SARS-CoV-2 variant fitness. Authors: Leonid Yurkovetskiy / Shawn Egri / Chaitanya Kurhade / Marco A Diaz-Salinas / Javier A Jaimes / Thomas Nyalile / Xuping Xie / Manish C Choudhary / Ann Dauphin / Jonathan Z Li / James B Munro ...Authors: Leonid Yurkovetskiy / Shawn Egri / Chaitanya Kurhade / Marco A Diaz-Salinas / Javier A Jaimes / Thomas Nyalile / Xuping Xie / Manish C Choudhary / Ann Dauphin / Jonathan Z Li / James B Munro / Pei-Yong Shi / Kuang Shen / Jeremy Luban /  Abstract: SARS-CoV-2 variants bearing complex combinations of mutations that confer increased transmissibility, COVID-19 severity, and immune escape, were first detected after S:D614G had gone to fixation, and ...SARS-CoV-2 variants bearing complex combinations of mutations that confer increased transmissibility, COVID-19 severity, and immune escape, were first detected after S:D614G had gone to fixation, and likely originated during persistent infection of immunocompromised hosts. To test the hypothesis that S:D614G facilitated emergence of such variants, S:D614G was reverted to the ancestral sequence in the context of sequential Spike sequences from an immunocompromised individual, and within each of the major SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. In all cases, infectivity of the S:D614G revertants was severely compromised. The infectivity of atypical SARS-CoV-2 lineages that propagated in the absence of S:D614G was found to be dependent upon either S:Q613H or S:H655Y. Notably, Gamma and Omicron variants possess both S:D614G and S:H655Y, each of which contributed to infectivity of these variants. Among sarbecoviruses, S:Q613H, S:D614G, and S:H655Y are only detected in SARS-CoV-2, which is also distinguished by a polybasic S1/S2 cleavage site. Genetic and biochemical experiments here showed that S:Q613H, S:D614G, and S:H655Y each stabilize Spike on virions, and that they are dispensable in the absence of S1/S2 cleavage, consistent with selection of these mutations by the S1/S2 cleavage site. CryoEM revealed that either S:D614G or S:H655Y shift the Spike receptor binding domain (RBD) towards the open conformation required for ACE2-binding and therefore on pathway for infection. Consistent with this, an smFRET reporter for RBD conformation showed that both S:D614G and S:H655Y spontaneously adopt the conformation that ACE2 induces in the parental Spike. Data from these orthogonal experiments demonstrate that S:D614G and S:H655Y are convergent adaptations to the polybasic S1/S2 cleavage site which stabilize S1 on the virion in the open RBD conformation and act epistatically to promote the fitness of variants bearing complex combinations of clinically significant mutations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8gb0.cif.gz 8gb0.cif.gz | 511.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8gb0.ent.gz pdb8gb0.ent.gz | 396.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8gb0.json.gz 8gb0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gb/8gb0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gb/8gb0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gb/8gb0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gb/8gb0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29910MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 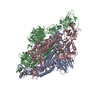
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 142500.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: SARS-CoV-2 Spike H655Y variant, One RBD Open / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 37.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 420953 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj



