[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8amf: Cryo-EM structure of the RecA postsynaptic filament from S. pneumoniae -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8amf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the RecA postsynaptic filament from S. pneumoniae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RECOMBINATION / Helical reconstruction / Recombinase / Streptococcus pneumoniae / double-stranded DNA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationestablishment of competence for transformation / SOS response / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / damaged DNA binding / DNA repair / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Lambdavirus lambda Lambdavirus lambda | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Perry, T.N. / Fronzes, R. / Polard, P. / Hertzog, M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2023 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2023Title: Assembly mechanism and cryoEM structure of RecA recombination nucleofilaments from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Authors: Maud Hertzog / Thomas Noé Perry / Pauline Dupaigne / Sandra Serres / Violette Morales / Anne-Lise Soulet / Jason C Bell / Emmanuel Margeat / Stephen C Kowalczykowski / Eric Le Cam / Rémi ...Authors: Maud Hertzog / Thomas Noé Perry / Pauline Dupaigne / Sandra Serres / Violette Morales / Anne-Lise Soulet / Jason C Bell / Emmanuel Margeat / Stephen C Kowalczykowski / Eric Le Cam / Rémi Fronzes / Patrice Polard /   Abstract: RecA-mediated homologous recombination (HR) is a key mechanism for genome maintenance and plasticity in bacteria. It proceeds through RecA assembly into a dynamic filament on ssDNA, the presynaptic ...RecA-mediated homologous recombination (HR) is a key mechanism for genome maintenance and plasticity in bacteria. It proceeds through RecA assembly into a dynamic filament on ssDNA, the presynaptic filament, which mediates DNA homology search and ordered DNA strand exchange. Here, we combined structural, single molecule and biochemical approaches to characterize the ATP-dependent assembly mechanism of the presynaptic filament of RecA from Streptococcus pneumoniae (SpRecA), in comparison to the Escherichia coli RecA (EcRecA) paradigm. EcRecA polymerization on ssDNA is assisted by the Single-Stranded DNA Binding (SSB) protein, which unwinds ssDNA secondary structures that block EcRecA nucleofilament growth. We report by direct microscopic analysis of SpRecA filamentation on ssDNA that neither of the two paralogous pneumococcal SSBs could assist the extension of SpRecA nucleopolymers. Instead, we found that the conserved RadA helicase promotes SpRecA nucleofilamentation in an ATP-dependent manner. This allowed us to solve the atomic structure of such a long native SpRecA nucleopolymer by cryoEM stabilized with ATPγS. It was found to be equivalent to the crystal structure of the EcRecA filament with a marked difference in how RecA mediates nucleotide orientation in the stretched ssDNA. Then, our results show that SpRecA and EcRecA HR activities are different, in correlation with their distinct ATP-dependent ssDNA binding modes. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8amf.cif.gz 8amf.cif.gz | 243.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8amf.ent.gz pdb8amf.ent.gz | 193.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8amf.json.gz 8amf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/am/8amf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/am/8amf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/am/8amf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/am/8amf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15525MC  8amdC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 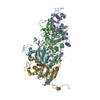
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42007.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: DNA chain | | Mass: 3087.110 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Lambdavirus lambda / Production host: Lambdavirus lambda / Production host:  #3: DNA chain | | Mass: 2996.971 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Lambdavirus lambda / Production host: Lambdavirus lambda / Production host:  #4: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RecA postsynaptic complex from S. pneumoniae / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: EMS Lacey Carbon |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2364 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 58.62 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 14.97 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1109194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 715954 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj



