+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7zu0 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | HOPS tethering complex from yeast | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / HOPS / tethering complex / lysosome / membrane fusion / Rab GTPase / cryo-EM | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone catabolic process / organelle fusion / CORVET complex / HOPS complex / endosomal vesicle fusion / vesicle tethering / regulation of vacuole fusion, non-autophagic / vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / vacuolar protein processing / Golgi to vacuole transport ...histone catabolic process / organelle fusion / CORVET complex / HOPS complex / endosomal vesicle fusion / vesicle tethering / regulation of vacuole fusion, non-autophagic / vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / vacuolar protein processing / Golgi to vacuole transport / regulation of SNARE complex assembly / vesicle fusion with vacuole / vacuole fusion, non-autophagic / cytoplasm to vacuole targeting by the Cvt pathway / Golgi to endosome transport / vesicle docking / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / late endosome to vacuole transport / endosome organization / piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus / fungal-type vacuole / fungal-type vacuole membrane / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / endosomal transport / vesicle-mediated transport / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / cellular response to starvation / intracellular protein transport / macroautophagy / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / autophagy / small GTPase binding / endocytosis / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / late endosome / protein transport / actin binding / early endosome membrane / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / endosome / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shvarev, D. / Schoppe, J. / Koenig, C. / Perz, A. / Fuellbrunn, N. / Kiontke, S. / Langemeyer, L. / Januliene, D. / Schnelle, K. / Kuemmel, D. ...Shvarev, D. / Schoppe, J. / Koenig, C. / Perz, A. / Fuellbrunn, N. / Kiontke, S. / Langemeyer, L. / Januliene, D. / Schnelle, K. / Kuemmel, D. / Froehlich, F. / Moeller, A. / Ungermann, C. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 3items Germany, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the HOPS tethering complex, a lysosomal membrane fusion machinery. Authors: Dmitry Shvarev / Jannis Schoppe / Caroline König / Angela Perz / Nadia Füllbrunn / Stephan Kiontke / Lars Langemeyer / Dovile Januliene / Kilian Schnelle / Daniel Kümmel / Florian ...Authors: Dmitry Shvarev / Jannis Schoppe / Caroline König / Angela Perz / Nadia Füllbrunn / Stephan Kiontke / Lars Langemeyer / Dovile Januliene / Kilian Schnelle / Daniel Kümmel / Florian Fröhlich / Arne Moeller / Christian Ungermann /  Abstract: Lysosomes are essential for cellular recycling, nutrient signaling, autophagy, and pathogenic bacteria and viruses invasion. Lysosomal fusion is fundamental to cell survival and requires HOPS, a ...Lysosomes are essential for cellular recycling, nutrient signaling, autophagy, and pathogenic bacteria and viruses invasion. Lysosomal fusion is fundamental to cell survival and requires HOPS, a conserved heterohexameric tethering complex. On the membranes to be fused, HOPS binds small membrane-associated GTPases and assembles SNAREs for fusion, but how the complex fulfills its function remained speculative. Here, we used cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the structure of HOPS. Unlike previously reported, significant flexibility of HOPS is confined to its extremities, where GTPase binding occurs. The SNARE-binding module is firmly attached to the core, therefore, ideally positioned between the membranes to catalyze fusion. Our data suggest a model for how HOPS fulfills its dual functionality of tethering and fusion and indicate why it is an essential part of the membrane fusion machinery. #1:  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the endosomal CORVET tethering complex. Authors: Dmitry Shvarev / Caroline König / Nicole Susan / Lars Langemeyer / Stefan Walter / Angela Perz / Florian Fröhlich / Christian Ungermann / Arne Moeller /  Abstract: Cells depend on their endolysosomal system for nutrient uptake and downregulation of plasma membrane proteins. These processes rely on endosomal maturation, which requires multiple membrane fusion ...Cells depend on their endolysosomal system for nutrient uptake and downregulation of plasma membrane proteins. These processes rely on endosomal maturation, which requires multiple membrane fusion steps. Early endosome fusion is promoted by the Rab5 GTPase and its effector, the hexameric CORVET tethering complex, which is homologous to the lysosomal HOPS. How these related complexes recognize their specific target membranes remains entirely elusive. Here, we solve the structure of CORVET by cryo-electron microscopy and revealed its minimal requirements for membrane tethering. As expected, the core of CORVET and HOPS resembles each other. However, the function-defining subunits show marked structural differences. Notably, we discover that unlike HOPS, CORVET depends not only on Rab5 but also on phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) and membrane lipid packing defects for tethering, implying that an organelle-specific membrane code enables fusion. Our data suggest that both shape and membrane interactions of CORVET and HOPS are conserved in metazoans, thus providing a paradigm how tethering complexes function. #2:  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the HOPS tethering complex, a lysosomal membrane fusion machinery. Authors: Dmitry Shvarev / Jannis Schoppe / Caroline König / Angela Perz / Nadia Füllbrunn / Stephan Kiontke / Lars Langemeyer / Dovile Januliene / Kilian Schnelle / Daniel Kümmel / Florian ...Authors: Dmitry Shvarev / Jannis Schoppe / Caroline König / Angela Perz / Nadia Füllbrunn / Stephan Kiontke / Lars Langemeyer / Dovile Januliene / Kilian Schnelle / Daniel Kümmel / Florian Fröhlich / Arne Moeller / Christian Ungermann /  Abstract: Lysosomes are essential for cellular recycling, nutrient signaling, autophagy, and pathogenic bacteria and viruses invasion. Lysosomal fusion is fundamental to cell survival and requires HOPS, a ...Lysosomes are essential for cellular recycling, nutrient signaling, autophagy, and pathogenic bacteria and viruses invasion. Lysosomal fusion is fundamental to cell survival and requires HOPS, a conserved heterohexameric tethering complex. On the membranes to be fused, HOPS binds small membrane-associated GTPases and assembles SNAREs for fusion, but how the complex fulfills its function remained speculative. Here, we used cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the structure of HOPS. Unlike previously reported, significant flexibility of HOPS is confined to its extremities, where GTPase binding occurs. The SNARE-binding module is firmly attached to the core, therefore, ideally positioned between the membranes to catalyze fusion. Our data suggest a model for how HOPS fulfills its dual functionality of tethering and fusion and indicate why it is an essential part of the membrane fusion machinery. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7zu0.cif.gz 7zu0.cif.gz | 649.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7zu0.ent.gz pdb7zu0.ent.gz | 484.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7zu0.json.gz 7zu0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zu/7zu0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zu/7zu0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zu/7zu0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zu/7zu0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14964MC 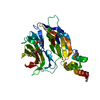 7ztyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ACE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 117617.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c Gene: PEP5, END1, VAM1, VPL9, VPS11, VPT11, YMR231W, YM9959.13 Production host:  References: UniProt: P12868, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 107531.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PEP3, VAM8, VPS18, VPT18, YLR148W, L9634.2 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 123049.414 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: VAM6, CVT4, VPL18, VPL22, VPS39, YDL077C / Production host:  |
-Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein ... , 3 types, 3 molecules BDF
| #2: Protein | Mass: 92857.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: VPS16, VAM9, VPT16, YPL045W / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 79354.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: VPS33, SLP1, VAM5, YLR396C, L8084.15 / Production host:  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 116530.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: VPS41, FET2, VAM2, YDR080W, D446, YD8554.13 / Production host:  |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Tethering complex HOPS / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.4 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Num. of particles: 244661 Details: Resolution of the consensus map of the lower part of the complex is used here Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj



