[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7s0q: Head region of a complex of IGF-I with the ectodomain of a hybrid... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7s0q | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Head region of a complex of IGF-I with the ectodomain of a hybrid insulin receptor / type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / insulin receptor / type 1 insulin like growth factor receptor / hybrid receptor / insulin like growth factor I / leucine zipper / cryo electron microscopy | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex / positive regulation of trophectodermal cell proliferation / prostate gland stromal morphogenesis / positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process / type II pneumocyte differentiation ...glycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex / positive regulation of trophectodermal cell proliferation / prostate gland stromal morphogenesis / positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process / type II pneumocyte differentiation / neuronal dense core vesicle lumen / proteoglycan biosynthetic process / regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / protein kinase complex / chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / insulin-like growth factor receptor activity / myotube cell development / positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / negative regulation of neuroinflammatory response / insulin-like growth factor binding / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / skeletal muscle satellite cell maintenance involved in skeletal muscle regeneration / protein transporter activity / bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / lung vasculature development / exocytic vesicle / transcytosis / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of myoblast proliferation / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / lung lobe morphogenesis / positive regulation of myelination / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / cell activation / insulin-like growth factor II binding / glial cell differentiation / positive regulation of developmental growth / positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / prostate gland growth / male sex determination / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / insulin receptor complex / insulin-like growth factor I binding / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / insulin receptor activity / mammary gland development / exocrine pancreas development / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / myoblast differentiation / cell surface receptor signaling pathway via STAT / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / dendritic spine maintenance / regulation of JNK cascade / cargo receptor activity / peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / growth hormone receptor signaling pathway / insulin binding / positive regulation of DNA binding / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / PTB domain binding / lung alveolus development / neuronal cell body membrane / muscle organ development / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / androgen receptor signaling pathway / prostate epithelial cord arborization involved in prostate glandular acinus morphogenesis / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / type I pneumocyte differentiation / positive regulation of respiratory burst / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / inner ear development / amyloid-beta clearance / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / myoblast proliferation / Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and entry / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / insulin receptor substrate binding / regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / epithelial to mesenchymal transition / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / blood vessel remodeling / activation of protein kinase B activity / epidermis development / protein kinase activator activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu, Y. / Lawrence, M.C. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2022 Journal: Structure / Year: 2022Title: How insulin-like growth factor I binds to a hybrid insulin receptor type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Authors: Yibin Xu / Mai B Margetts / Hari Venugopal / John G Menting / Nicholas S Kirk / Tristan I Croll / Carlie Delaine / Briony E Forbes / Michael C Lawrence /   Abstract: Monomers of the insulin receptor and type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) can combine stochastically to form heterodimeric hybrid receptors. These hybrid receptors display ligand ...Monomers of the insulin receptor and type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) can combine stochastically to form heterodimeric hybrid receptors. These hybrid receptors display ligand binding and signaling properties that differ from those of the homodimeric receptors. Here, we describe the cryoelectron microscopy structure of such a hybrid receptor in complex with insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). The structure (ca. 3.7 Å resolution) displays a single IGF-I ligand, bound in a similar fashion to that seen for IGFs in complex with IGF-1R. The IGF-I ligand engages the first leucine-rich-repeat domain and cysteine-rich region of the IGF-1R monomer (rather than those of the insulin receptor monomer), consistent with the determinants for IGF binding residing in the IGF-1R cysteine-rich region. The structure broadens our understanding of this receptor family and assists in delineating the key structural motifs involved in binding their respective ligands. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7s0q.cif.gz 7s0q.cif.gz | 357 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7s0q.ent.gz pdb7s0q.ent.gz | 280.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7s0q.json.gz 7s0q.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/7s0q https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/7s0q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/7s0q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/7s0q | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24791MC  7s8vC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 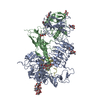
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Insulin-like growth factor ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 108937.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1R / Cell line (production host): CHO Lec8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1R / Cell line (production host): CHO Lec8 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P08069, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 7663.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1, IBP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1, IBP1 / Production host:  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules B
| #2: Protein | Mass: 109809.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): CHO lek8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): CHO lek8 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P06213, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|
-Sugars , 4 types, 11 molecules 


| #4: Polysaccharide | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #5: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #6: Sugar | ChemComp-BMA / | #7: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: a complex of IGF-I with the ectodomain of a hybrid insulin receptor / type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 250 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20mM Tris pH 8.0 160mM NaCl |
| Buffer component | Conc.: 20 mM / Name: TRIS / Formula: C4H11NO3 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 0.2mg/ml |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.44 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17_3644: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 151240 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj
















