[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7nca: Type 1A alpha-synuclein filament seeded in vitro by filaments pur... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7nca | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
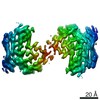
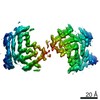
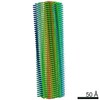
| Title | Type 1A alpha-synuclein filament seeded in vitro by filaments purified from Multiple Systems Atrophy Case 2 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Alpha-synuclein | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / Amyloid / Multiple System Atrophy / Neurodegeneration / alpha-synuclein / filament | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of phospholipase activity / negative regulation of monooxygenase activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / positive regulation of glutathione peroxidase activity / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process ...regulation of phospholipase activity / negative regulation of monooxygenase activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / positive regulation of glutathione peroxidase activity / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process / supramolecular fiber / negative regulation of transporter activity / mitochondrial membrane organization / negative regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein localization to cell periphery / negative regulation of exocytosis / regulation of glutamate secretion / response to iron(II) ion / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / dopamine biosynthetic process / regulation of locomotion / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / synaptic vesicle priming / regulation of macrophage activation / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization / synaptic vesicle transport / dynein complex binding / dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / positive regulation of receptor recycling / regulation of dopamine secretion / protein kinase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / cuprous ion binding / response to magnesium ion / response to type II interferon / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of endocytosis / kinesin binding / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process / mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of presynapse assembly / negative regulation of serotonin uptake / alpha-tubulin binding / phospholipid metabolic process / supramolecular fiber organization / axon terminus / inclusion body / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / Hsp70 protein binding / response to interleukin-1 / : / adult locomotory behavior / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / SNARE binding / excitatory postsynaptic potential / fatty acid metabolic process / long-term synaptic potentiation / phosphoprotein binding / protein tetramerization / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / protein destabilization / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / microglial cell activation / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / synapse organization / ferrous iron binding / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / tau protein binding / PKR-mediated signaling / receptor internalization / : / phospholipid binding / synaptic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of inflammatory response / actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / actin binding / cell cortex / cellular response to oxidative stress / histone binding / growth cone / chemical synaptic transmission / neuron apoptotic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / postsynapse / response to lipopolysaccharide / amyloid fibril formation / molecular adaptor activity / lysosome / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / oxidoreductase activity / positive regulation of apoptotic process Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.47 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lovestam, S.K.A. / Schweighauser, M. / Scheres, S.H.W. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Japan, 4items Japan, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FEBS Open Bio / Year: 2021 Journal: FEBS Open Bio / Year: 2021Title: Seeded assembly in vitro does not replicate the structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Authors: Sofia Lövestam / Manuel Schweighauser / Tomoyasu Matsubara / Shigeo Murayama / Taisuke Tomita / Takashi Ando / Kazuko Hasegawa / Mari Yoshida / Airi Tarutani / Masato Hasegawa / Michel ...Authors: Sofia Lövestam / Manuel Schweighauser / Tomoyasu Matsubara / Shigeo Murayama / Taisuke Tomita / Takashi Ando / Kazuko Hasegawa / Mari Yoshida / Airi Tarutani / Masato Hasegawa / Michel Goedert / Sjors H W Scheres /   Abstract: The propagation of conformational strains by templated seeding is central to the prion concept. Seeded assembly of α-synuclein into filaments is believed to underlie the prion-like spreading of ...The propagation of conformational strains by templated seeding is central to the prion concept. Seeded assembly of α-synuclein into filaments is believed to underlie the prion-like spreading of protein inclusions in a number of human neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and multiple system atrophy (MSA). We previously determined the atomic structures of α-synuclein filaments from the putamen of five individuals with MSA. Here, we used filament preparations from three of these brains for the in vitro seeded assembly of recombinant human α-synuclein. We find that the structures of the seeded assemblies differ from those of the seeds, suggesting that additional, as yet unknown, factors play a role in the propagation of the seeds. Identification of these factors will be essential for understanding the prion-like spreading of α-synuclein proteinopathies. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7nca.cif.gz 7nca.cif.gz | 228.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7nca.ent.gz pdb7nca.ent.gz | 184.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7nca.json.gz 7nca.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7nca_validation.pdf.gz 7nca_validation.pdf.gz | 971.8 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7nca_full_validation.pdf.gz 7nca_full_validation.pdf.gz | 971.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7nca_validation.xml.gz 7nca_validation.xml.gz | 31.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7nca_validation.cif.gz 7nca_validation.cif.gz | 47.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nc/7nca https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nc/7nca ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nc/7nca ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nc/7nca | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 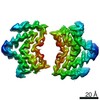 12264MC  7ncgC  7nchC  7nciC  7ncjC  7nckC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10640 (Title: Cryo-EM of Multiple System Atrophy seeded assembly of alpha-synuclein filaments EMPIAR-10640 (Title: Cryo-EM of Multiple System Atrophy seeded assembly of alpha-synuclein filamentsData size: 1.1 TB Data #1: Unaligned movies of alpha-synuclein filament seeded in vitro by filaments purified from Multiple Systems Atrophy Case 1 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Unaligned movies of alpha-synuclein filament seeded in vitro by filaments purified from Multiple Systems Atrophy Case 2 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #3: Unaligned movies of alpha-synuclein filament seeded in vitro by filaments purified from Multiple Systems Atrophy Case 5 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #4: Type 1A particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #5: Type 2A particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #6: Type 1B particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #7: Type 2B particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #8: Type 2AB particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #9: Type 3 particles after Bayesian polishing [picked particles - single frame - processed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 14476.108 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SNCA, NACP, PARK1 / Plasmid: pRK172-WT-Asyn / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SNCA, NACP, PARK1 / Plasmid: pRK172-WT-Asyn / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Alpha synuclein filament / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: LMB vitrobot IV |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 32.6 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -1.04 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 4.76 Å / Axial symmetry: C2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.47 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 67619 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj
