[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-41109: Catalytic and non-catalytic mechanisms of histone H4 lysine 20 me... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
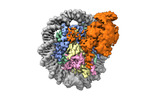
| Title | Catalytic and non-catalytic mechanisms of histone H4 lysine 20 methyltransferase SUV420H1 | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Chromatin / Histone H4 modification / Methyltransferase / GENE REGULATION | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H4K20me methyltransferase activity / [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase / histone H4K20 monomethyltransferase activity / [histone H4]-lysine20 N-methyltransferase / histone H4K20 methyltransferase activity / histone H4 methyltransferase activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding / nucleosomal DNA binding ...histone H4K20me methyltransferase activity / [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase / histone H4K20 monomethyltransferase activity / [histone H4]-lysine20 N-methyltransferase / histone H4K20 methyltransferase activity / histone H4 methyltransferase activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding / nucleosomal DNA binding / muscle organ development / histone methyltransferase activity / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / heterochromatin / intercellular bridge / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / euchromatin / chromatin DNA binding / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / fibrillar center / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / mitotic spindle / structural constituent of chromatin / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / microtubule cytoskeleton / chromatin organization / methylation / cilium / ciliary basal body / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / DNA repair / chromatin binding / centrosome / nucleolus / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Abini-Agbomson S / Armache K-J | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: Catalytic and non-catalytic mechanisms of histone H4 lysine 20 methyltransferase SUV420H1. Authors: Stephen Abini-Agbomson / Kristjan Gretarsson / Rochelle M Shih / Laura Hsieh / Tracy Lou / Pablo De Ioannes / Nikita Vasilyev / Rachel Lee / Miao Wang / Matthew D Simon / Jean-Paul Armache / ...Authors: Stephen Abini-Agbomson / Kristjan Gretarsson / Rochelle M Shih / Laura Hsieh / Tracy Lou / Pablo De Ioannes / Nikita Vasilyev / Rachel Lee / Miao Wang / Matthew D Simon / Jean-Paul Armache / Evgeny Nudler / Geeta Narlikar / Shixin Liu / Chao Lu / Karim-Jean Armache /  Abstract: SUV420H1 di- and tri-methylates histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me2/H4K20me3) and plays crucial roles in DNA replication, repair, and heterochromatin formation. It is dysregulated in several cancers. Many ...SUV420H1 di- and tri-methylates histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me2/H4K20me3) and plays crucial roles in DNA replication, repair, and heterochromatin formation. It is dysregulated in several cancers. Many of these processes were linked to its catalytic activity. However, deletion and inhibition of SUV420H1 have shown distinct phenotypes, suggesting that the enzyme likely has uncharacterized non-catalytic activities. Our cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), biochemical, biophysical, and cellular analyses reveal how SUV420H1 recognizes its nucleosome substrates, and how histone variant H2A.Z stimulates its catalytic activity. SUV420H1 binding to nucleosomes causes a dramatic detachment of nucleosomal DNA from the histone octamer, which is a non-catalytic activity. We hypothesize that this regulates the accessibility of large macromolecular complexes to chromatin. We show that SUV420H1 can promote chromatin condensation, another non-catalytic activity that we speculate is needed for its heterochromatin functions. Together, our studies uncover and characterize the catalytic and non-catalytic mechanisms of SUV420H1, a key histone methyltransferase that plays an essential role in genomic stability. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41109.map.gz emd_41109.map.gz | 32.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41109-v30.xml emd-41109-v30.xml emd-41109.xml emd-41109.xml | 26.6 KB 26.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_41109.png emd_41109.png | 67 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41109.cif.gz emd-41109.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41109_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41109_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41109_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41109_half_map_2.map.gz | 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41109 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41109 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41109 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41109 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8t9fMC  8t9hC  8thuC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41109.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41109.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
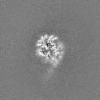
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.079 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
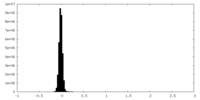
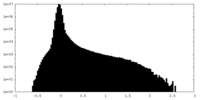
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map from the 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex
| File | emd_41109_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map from the 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map from the 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex
| File | emd_41109_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map from the 3D reconstruction SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex
| Entire | Name: SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex
| Supramolecule | Name: SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5, #7, #6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5B
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.69016 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKWLGESKNM VVNGRRNGGK LSNDHQQNQS KLQHTGKDTL KAGKNAVERR SNRCNGNSGF EGQSRYVPSS GMSAKELCEN DDLATSLVL DPYLGFQTHK MNTSAFPSRS SRHFSKSDSF SHNNPVRFRP IKGRQEELKE VIERFKKDEH LEKAFKCLTS G EWARHYFL ...String: MKWLGESKNM VVNGRRNGGK LSNDHQQNQS KLQHTGKDTL KAGKNAVERR SNRCNGNSGF EGQSRYVPSS GMSAKELCEN DDLATSLVL DPYLGFQTHK MNTSAFPSRS SRHFSKSDSF SHNNPVRFRP IKGRQEELKE VIERFKKDEH LEKAFKCLTS G EWARHYFL NKNKMQEKLF KEHVFIYLRM FATDSGFEIL PCNRYSSEQN GAKIVATKEW KRNDKIELLV GCIAELSEIE EN MLLRHGE NDFSVMYSTR KNCAQLWLGP AAFINHDCRP NCKFVSTGRD TACVKALRDI EPGEEISCYY GDGFFGENNE FCE CYTCER RGTGAFKSRV GLPAPAPVIN SKYGLRETDK RLNRLKKLGD SSKNSDSQSV SSNTDADTTQ EKNNASK UniProtKB: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5B |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.396442 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR MVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #5: Histone H3.2
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.30393 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ARTKQTARKS TGGKAPRKQL ATKAARKSAP ATGGVKKPHR YRPGTVALRE IRRYQKSTEL LIRKLPFQRL VREIAQDFKT DLRFQSSAV MALQEASEAY LVALFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.2 |
-Macromolecule #6: Histone H2A.Z
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A.Z / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.581796 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAGGKAGKDS GKAKTKAVSR SQRAGLQFPV GRIHRHLKSR TTSHGRVGAT AAVYSAAILE YLTAEVLELA GNASKDLKVK RITPRHLQL AIRGDEELDS LIKATIAGGG VIPHIHKSLI GKKGQQKTV UniProtKB: Histone H2A.Z |
-Macromolecule #7: Histone H2B 1.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B 1.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.655948 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAKSAPAPKK GSKKAVTKTQ KKDGKKRRKT RKESYAIYVY KVLKQVHPDT GISSKAMSIM NSFVNDVFER IAGEASRLAH YNKRSTITS REIQTAVRLL LPGELAKHAV SEGTKAVTKY TSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B 1.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (122-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (122-MER) / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.82457 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (122-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (122-MER) / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.304863 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #8: S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
| Macromolecule | Name: S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: SAM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 398.437 Da |
| Chemical component information | 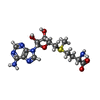 ChemComp-SAM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 Component:
Details: 50 mM HEPES pH 7.9, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM DTT | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)