+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
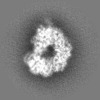
| Title | Type I-FHNH Cascade-dsDNA R-loop complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | protein / RNA / RNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA/RNA / RNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) | |||||||||
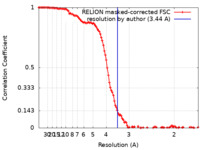
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.44 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li Z | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms for HNH-mediated target DNA cleavage in type I CRISPR-Cas systems. Authors: Chendi Zhang / Fugen Chen / Feng Wang / Haijiang Xu / Jialin Xue / Zhuang Li /  Abstract: The metagenome-derived type I-E and type I-F variant CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (Cascade) complexes, fused with HNH domains, precisely cleave target DNA, representing recently ...The metagenome-derived type I-E and type I-F variant CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (Cascade) complexes, fused with HNH domains, precisely cleave target DNA, representing recently identified genome editing tools. However, the underlying working mechanisms remain unknown. Here, structures of type I-F and I-E Cascade complexes at different states are reported. In type I-F Cascade, Cas8f loosely attaches to Cascade head and is adjacent to the 5' end of the target single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Formation of the full R-loop drives the Cascade head to move outward, allowing Cas8f to detach and rotate ∼150° to accommodate target ssDNA for cleavage. In type I-E Cascade, Cas5e domain is adjacent to the 5' end of the target ssDNA. Full crRNA-target pairing drives the lift of the Cascade head, widening the substrate channel for target ssDNA entrance. Altogether, these analyses into both complexes revealed that crRNA-guided positioning of target DNA and target DNA-induced HNH unlocking are two key factors for their site-specific cleavage of target DNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_39200.map.gz emd_39200.map.gz | 98.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-39200-v30.xml emd-39200-v30.xml emd-39200.xml emd-39200.xml | 19.2 KB 19.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_39200_fsc.xml emd_39200_fsc.xml | 11.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_39200.png emd_39200.png | 119.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-39200.cif.gz emd-39200.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_39200_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39200_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39200_half_map_2.map.gz emd_39200_half_map_2.map.gz | 98.3 MB 98.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39200 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39200 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_39200_validation.pdf.gz emd_39200_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_39200_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_39200_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_39200_validation.xml.gz emd_39200_validation.xml.gz | 18.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_39200_validation.cif.gz emd_39200_validation.cif.gz | 24.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39200 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39200 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8yeoMC  8yb6C  8ydbC  8yh9C  8yhaC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_39200.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_39200.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.85 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
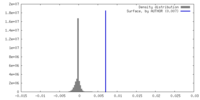
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_39200_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
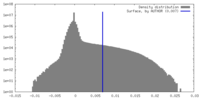
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_39200_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Type I-FHNH Cascade-dsDNA R-loop complex
| Entire | Name: Type I-FHNH Cascade-dsDNA R-loop complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Type I-FHNH Cascade-dsDNA R-loop complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Type I-FHNH Cascade-dsDNA R-loop complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3, #5-#6, #4, #7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cas5f
| Macromolecule | Name: Cas5f / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.703135 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MMKGYILLEK VNIENANAFN NIIVGIPAIT SFLGFARALE RKLNAKEIAI RINGVGLEFH EYELKGYKNK RGQYVTSCPL PGSIPGQNE KKLDAHIMNQ AYIDLNMSFL LEVEGPHVDM STCKSIKSTM ETLRIAGGII RNYKKIRLID TLADIPYGYF L TLRQDNLN ...String: MMKGYILLEK VNIENANAFN NIIVGIPAIT SFLGFARALE RKLNAKEIAI RINGVGLEFH EYELKGYKNK RGQYVTSCPL PGSIPGQNE KKLDAHIMNQ AYIDLNMSFL LEVEGPHVDM STCKSIKSTM ETLRIAGGII RNYKKIRLID TLADIPYGYF L TLRQDNLN DAAGDDMLDK MIHALQQEDT LVPIAVGFKA LSEVGHVEGQ RDPEKDHCFV ESIFSLGGFE CSKILEDINS CL WRYKTEE GLYLCTII |
-Macromolecule #2: Cas8f fusion with HNH
| Macromolecule | Name: Cas8f fusion with HNH / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.339742 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLRNKILAAI SQKIPEEQKI NKYIEGLFQS IDKNHLATHV AKFTETNSPG NIGAYDILSS DMNCGYLDTA NAGWKEPDIV TNDAKYKRP QGFVAMEMSD GRTVMEHLQE DSAELRHEME ELTDKYDEIR DGILNMPSMQ PYRTNQFIKQ VFFPVGGSYH L LSILPSTV ...String: MLRNKILAAI SQKIPEEQKI NKYIEGLFQS IDKNHLATHV AKFTETNSPG NIGAYDILSS DMNCGYLDTA NAGWKEPDIV TNDAKYKRP QGFVAMEMSD GRTVMEHLQE DSAELRHEME ELTDKYDEIR DGILNMPSMQ PYRTNQFIKQ VFFPVGGSYH L LSILPSTV LNYEVSDRLY RSKIPKIRLR LLSSNAASTT GSRLVSKNKW PLVFQALPPK FLEKNLAKAL DKEYLLPDIN ID ELEGVDN GCLIDEALLP LIIDEGKRKG EGNYRPRHLR DERKEETVQA FLDKYGYCNI PVGYEVHHIV PLSQGGADSI KNM IMLSIE HHERVTEAHA SYFKWRNT |
-Macromolecule #3: Cas6f
| Macromolecule | Name: Cas6f / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.735873 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFSQILIIKP GTGISPNIII SEDIFPVLHS LFVEHDKKFG ITFPAYSFDK KGHLGNIIEV LSEDKEALAS LCLEEHLAEV TDYVKVKKE ITFTDDYVLF KRIREENQYE TTARRMRKRG HTELGRPLEM HIKKKNQQIF CHAYIKVKSA STGQSYNIFL A PTDIKHGS FSAYGLLRGD THA |
-Macromolecule #4: Cas7f
| Macromolecule | Name: Cas7f / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38.700172 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAANKKATNV TLKSRPENLS FARCLNTTEA KFWQTDFLKR HTFKLPLLIT DKAVLASKGH EMPPDKLEKE IMDPNPQKSQ SCTLSTECD TLRIDFGIKV LPVKESMYSC SDYNYRTAIY QKIDEYIAED GFLTLAKRYV NNIANARFLW RNRKGAEIIE T IVTIEDKE ...String: MAANKKATNV TLKSRPENLS FARCLNTTEA KFWQTDFLKR HTFKLPLLIT DKAVLASKGH EMPPDKLEKE IMDPNPQKSQ SCTLSTECD TLRIDFGIKV LPVKESMYSC SDYNYRTAIY QKIDEYIAED GFLTLAKRYV NNIANARFLW RNRKGAEIIE T IVTIEDKE YPSFNSKSFN LDTFVEDNAT INEIAQQIAD TFAGKREYLN IYVTCFVKIG CAMEVYPSQE MTFDDDDKGK KL FKFEGSA GMHSQKINNA LRTIDTWYPD YTTYEFPIPV ENYGAARSIG IPFRPDTKSF YKLIDRMILK NEDLPIEDKH YVM AILIRG GMFSKKQEK |
-Macromolecule #5: 60-nt crRNA
| Macromolecule | Name: 60-nt crRNA / type: rna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.440611 KDa |
| Sequence | String: UUUAGAAGGA GAAGUCAUUU AAUAAGGCCA CUGUUAAAAA GUGUACCGCC GGAUAGGCGG |
-Macromolecule #6: TS
| Macromolecule | Name: TS / type: other / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 Classification: polydeoxyribonucleotide/polyribonucleotide hybrid |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.068426 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)AACAG(DT)GG CC(DT)(DT)A(DT)(DT)AA A(DT)GAC(DT)(DT)C(DT)C CGC(DT)AA(DT)AC |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #7: NTS
| Macromolecule | Name: NTS / type: other / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 Classification: polydeoxyribonucleotide/polyribonucleotide hybrid |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) Selenomonas sp. (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.541243 KDa |
| Sequence | String: G(DT)A(DT)(DT)AGCGG A |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 54.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)