+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
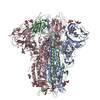
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of bat WIV1 spike glycoprotein | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | spike / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane ...host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1 / Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1 /  Enterobacteria phage T6 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T6 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.96 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang X / Qiao S | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024Title: Structural determinants of spike infectivity in bat SARS-like coronaviruses RsSHC014 and WIV1. Authors: Shuyuan Qiao / Xinquan Wang /  Abstract: The recurrent spillovers of coronaviruses (CoVs) have posed severe threats to public health and the global economy. Bat severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-like CoVs RsSHC014 and WIV1, currently ...The recurrent spillovers of coronaviruses (CoVs) have posed severe threats to public health and the global economy. Bat severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-like CoVs RsSHC014 and WIV1, currently circulating in bat populations, are poised for human emergence. The trimeric spike (S) glycoprotein, responsible for receptor recognition and membrane fusion, plays a critical role in cross-species transmission and infection. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of the RsSHC014 S protein in the closed state at 2.9 Å, the WIV1 S protein in the closed state at 2.8 Å, and the intermediate state at 4.0 Å. In the intermediate state, one receptor-binding domain (RBD) is in the "down" position, while the other two RBDs exhibit poor density. We also resolved the complex structure of the WIV1 S protein bound to human ACE2 (hACE2) at 4.5 Å, which provides structural basis for the future emergence of WIV1 in humans. Through biochemical experiments, we found that despite strong binding affinities between the RBDs and both human and civet ACE2, the pseudoviruses of RsSHC014, but not WIV1, failed to infect 293T cells overexpressing either human or civet ACE2. Mutagenesis analysis revealed that the Y623H substitution, located in the SD2 region, significantly improved the cell entry efficiency of RsSHC014 pseudoviruses, which is likely accomplished by promoting the open conformation of spike glycoproteins. Our findings emphasize the necessity of both efficient RBD lifting and tight RBD-hACE2 binding for viral infection and underscore the significance of the 623 site of the spike glycoprotein for the infectivity of bat SARS-like CoVs. IMPORTANCE: The bat SARS-like CoVs RsSHC014 and WIV1 can use hACE2 for cell entry without further adaptation, indicating their potential risk of emergence in human populations. The S glycoprotein, ...IMPORTANCE: The bat SARS-like CoVs RsSHC014 and WIV1 can use hACE2 for cell entry without further adaptation, indicating their potential risk of emergence in human populations. The S glycoprotein, responsible for receptor recognition and membrane fusion, plays a crucial role in cross-species transmission and infection. In this study, we determined the cryo-EM structures of the S glycoproteins of RsSHC014 and WIV1. Detailed comparisons revealed dynamic structural variations within spike proteins. We also elucidated the complex structure of WIV1 S-hACE2, providing structural evidence for the potential emergence of WIV1 in humans. Although RsSHC014 and WIV1 had similar hACE2-binding affinities, they exhibited distinct pseudovirus cell entry behavior. Through mutagenesis and cryo-EM analysis, we revealed that besides the structural variations, the 623 site in the SD2 region is another important structural determinant of spike infectivity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37635.map.gz emd_37635.map.gz | 8.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37635-v30.xml emd-37635-v30.xml emd-37635.xml emd-37635.xml | 14.4 KB 14.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_37635.png emd_37635.png | 45.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37635.cif.gz emd-37635.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37635_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37635_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37635_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37635_half_map_2.map.gz | 65.4 MB 65.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37635 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37635 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37635 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37635 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8wlyMC  8wluC  8wlzC  8wq0C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37635.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37635.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0742 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
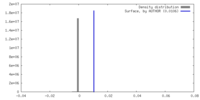
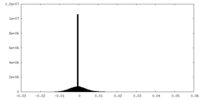
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37635_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
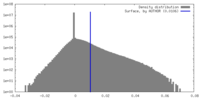
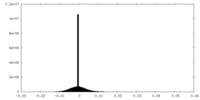
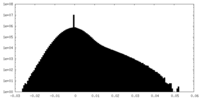
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37635_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : WIV1 glycoprotein
| Entire | Name: WIV1 glycoprotein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: WIV1 glycoprotein
| Supramolecule | Name: WIV1 glycoprotein / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1 Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1 |
-Macromolecule #1: Spike glycoprotein,Fibritin
| Macromolecule | Name: Spike glycoprotein,Fibritin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Enterobacteria phage T6 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T6 (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 140.747688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MKLLVLVFAT LVSSYTIEKC LDFDDRTPPA NTQFLSSHRG VYYPDDIFRS NVLHLVQDHF LPFDSNVTRF ITFGLNFDNP IIPFKDGIY FAATEKSNVI RGWVFGSTMN NKSQSVIIMN NSTNLVIRAC NFELCDNPFF VVLKSNNTQI PSYIFNNAFN C TFEYVSKD ...String: MKLLVLVFAT LVSSYTIEKC LDFDDRTPPA NTQFLSSHRG VYYPDDIFRS NVLHLVQDHF LPFDSNVTRF ITFGLNFDNP IIPFKDGIY FAATEKSNVI RGWVFGSTMN NKSQSVIIMN NSTNLVIRAC NFELCDNPFF VVLKSNNTQI PSYIFNNAFN C TFEYVSKD FNLDLGEKPG NFKDLREFVF RNKDGFLHVY SGYQPISAAS GLPTGFNALK PIFKLPLGIN ITNFRTLLTA FP PRPDYWG TSAAAYFVGY LKPTTFMLKY DENGTITDAV DCSQNPLAEL KCSVKSFEID KGIYQTSNFR VAPSKEVVRF PNI TNLCPF GEVFNATTFP SVYAWERKRI SNCVADYSVL YNSTSFSTFK CYGVSATKLN DLCFSNVYAD SFVVKGDDVR QIAP GQTGV IADYNYKLPD DFTGCVLAWN TRNIDATQTG NYNYKYRSLR HGKLRPFERD ISNVPFSPDG KPCTPPAFNC YWPLN DYGF YITNGIGYQP YRVVVLSFEL LNAPATVCGP KLSTDLIKNQ CVNFNFNGLT GTGVLTPSSK RFQPFQQFGR DVSDFT DSV RDPKTSEILD ISPCSFGGVS VITPGTNTSS EVAVLYQDVN CTDVPVAIHA DQLTPSWRVH STGNNVFQTQ AGCLIGA EH VDTSYECDIP IGAGICASYH TVSSLRSTSQ KSIVAYTMSL GADSSIAYSN NTIAIPTNFS ISITTEVMPV SMAKTSVD C NMYICGDSTE CANLLLQYGS FCTQLNRALS GIAVEQDRNT REVFAQVKQM YKTPTLKDFG GFNFSQILPD PLKPTKRSF IEDLLFNKVT LADAGFMKQY GECLGDINAR DLICAQKFNG LTVLPPLLTD DMIAAYTAAL VSGTATAGWT FGAGAALQIP FAMQMAYRF NGIGVTQNVL YENQKQIANQ FNKAISQIQE SLTTTSTALG KLQDVVNQNA QALNTLVKQL SSNFGAISSV L NDILSRLD PPEAEVQIDR LITGRLQSLQ TYVTQQLIRA AEIRASANLA ATKMSECVLG QSKRVDFCGK GYHLMSFPQA AP HGVVFLH VTYVPSQERN FTTAPAICHE GKAYFPREGV FVFNGTSWFI TQRNFFSPQI ITTDNTFVSG SCDVVIGIIN NTV YDPLQP ELDSFKEELD KYFKNHTSPD VDLGDISGIN ASVVNIQKEI DRLNEVAKNL NESLIDLQEL GKYEQGSGYI PEAP RDGQA YVRKDGEWVL LSTFLGRSLE VLFQGPGHHH HHHHHSAWSH PQFEKGGGSG GGGSGGSAWS HPQFEK UniProtKB: Spike glycoprotein, Fibritin |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 19 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 59319 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)